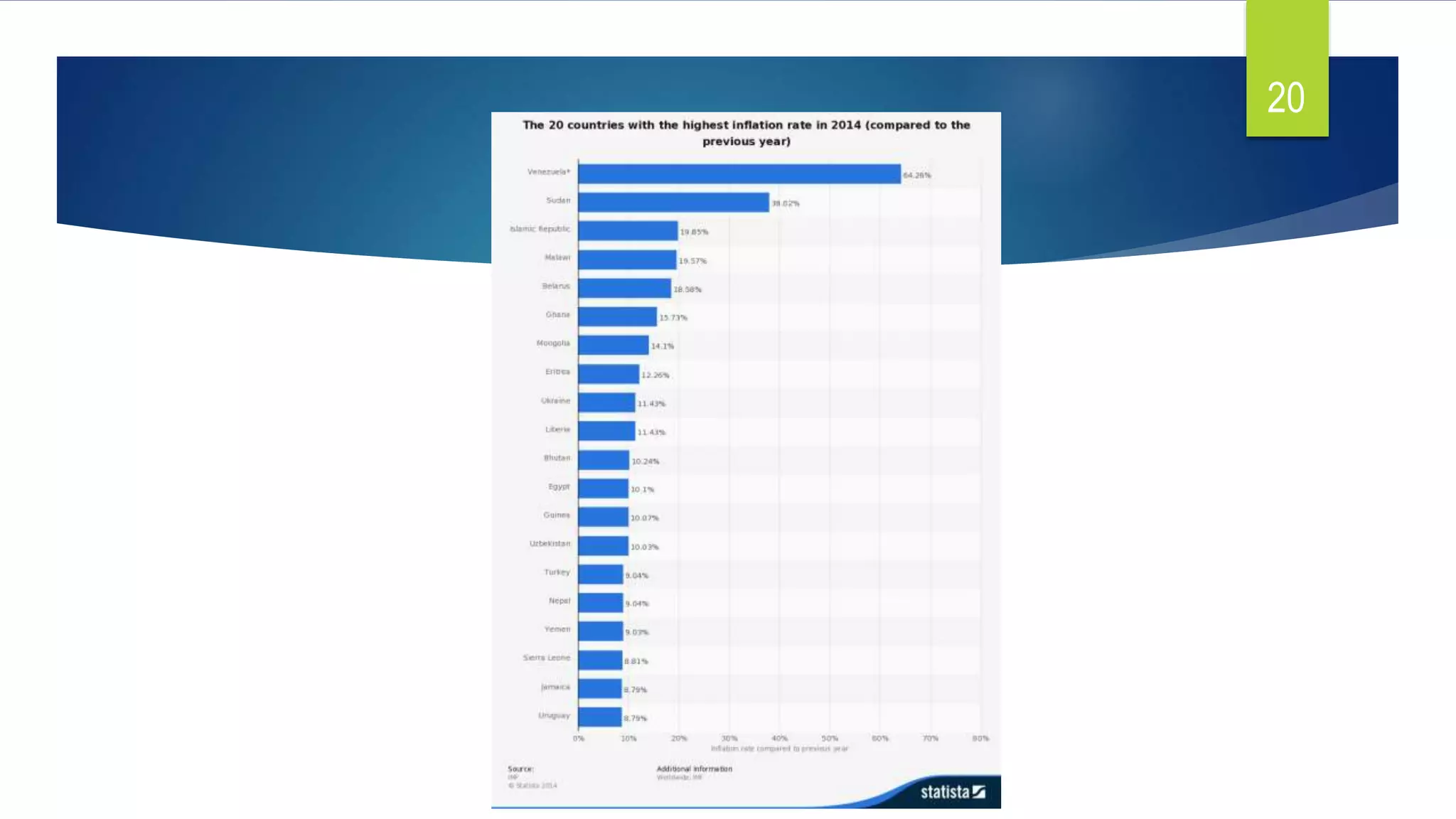
Inflation is a macroeconomic problem that can have detrimental effects on an economy. It causes a rise in general price levels which decreases the value of money. The effects of inflation can be categorized into output effects and redistribution effects. Output effects include reduced confidence, international competitiveness and investment, which can decrease output and employment. Redistribution effects involve a shifting of income and wealth between different groups as the purchasing power of money changes. Borrowers benefit while those on fixed incomes lose out.












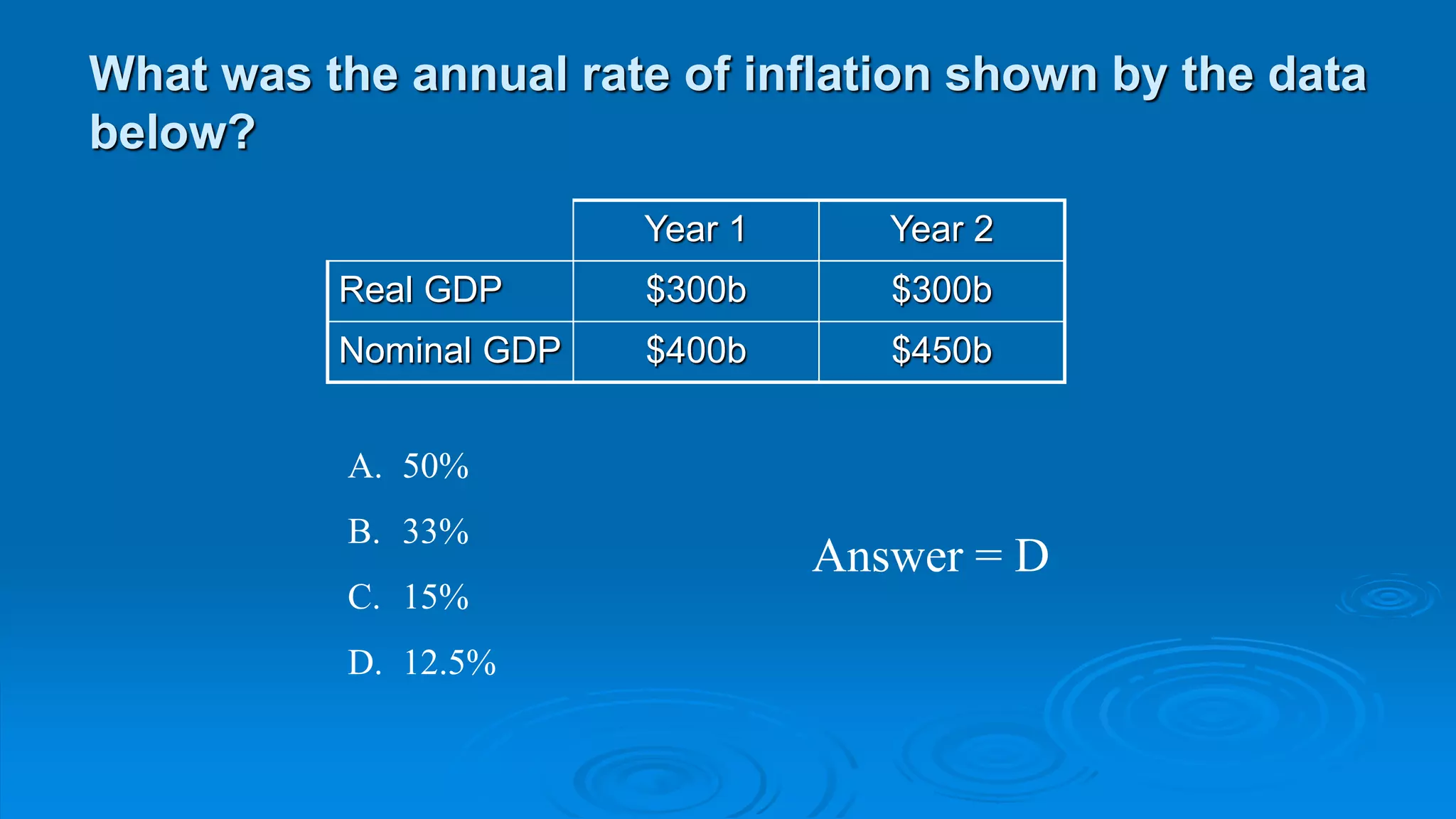





![PLAN!!!!!!!!!!!!
Inf - rise gen level of ps
Dem-pull and cost-push
gen measure by CPI
[(CPI2 - CPI1) ÷ CPI1] x 100
Nos 140, 147 = 5%
a)
b)
RBA target 2%-3% per annum
Strong C (building and credit) = dem-pull
So must be reduced cost-push (use AD/AS graph)
- resource use prod/appreciation of $AUD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/effectsofinflationteacher-230508111639-782390ee/75/Effects-of-Inflation-Teacher-ppt-19-2048.jpg)