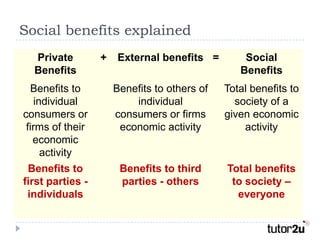
Positive externalities are benefits to third parties from certain economic activities. Activities that generate positive externalities include education and training, public broadcasting, healthcare, vaccination programs, and environmental protection. These external benefits are not fully captured by the private market. As a result, the free market underprovides goods and services with positive externalities, leading to a net loss of social welfare. Government intervention, such as subsidies or regulation, may be needed to encourage the optimal level of supply that accounts for positive external spillovers. However, accurately quantifying externalities and avoiding overconsumption can be challenging issues for policymakers.