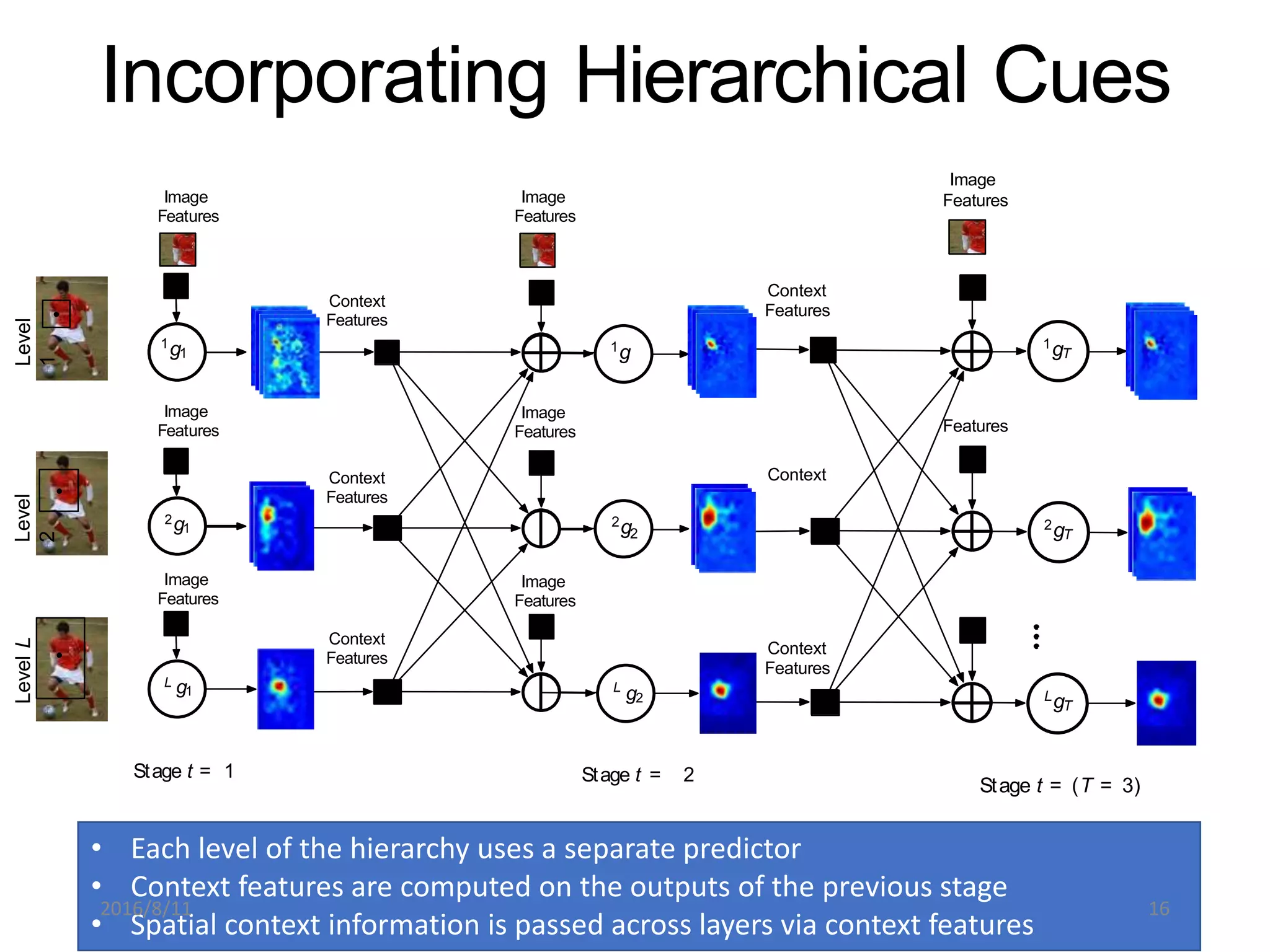
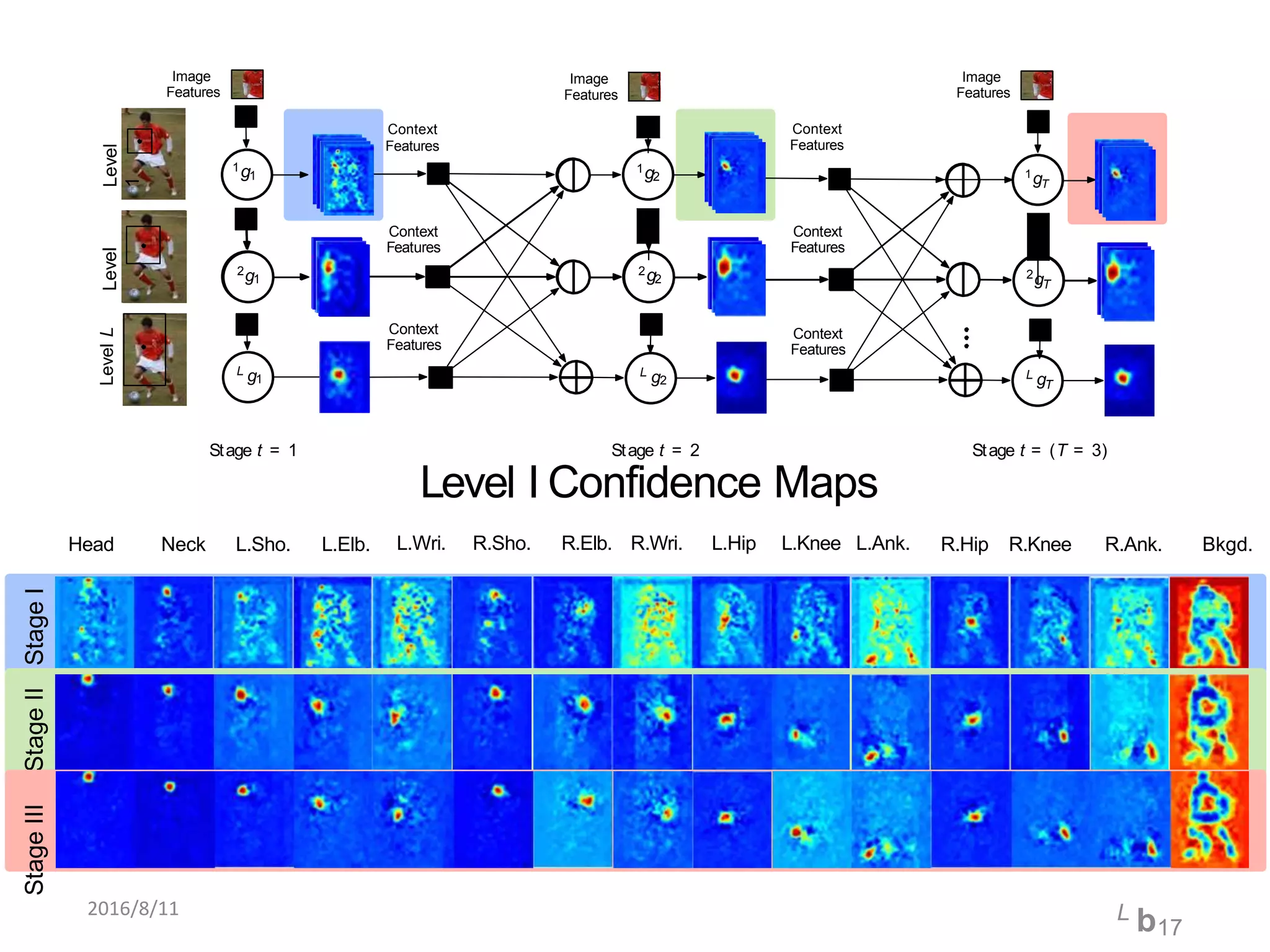
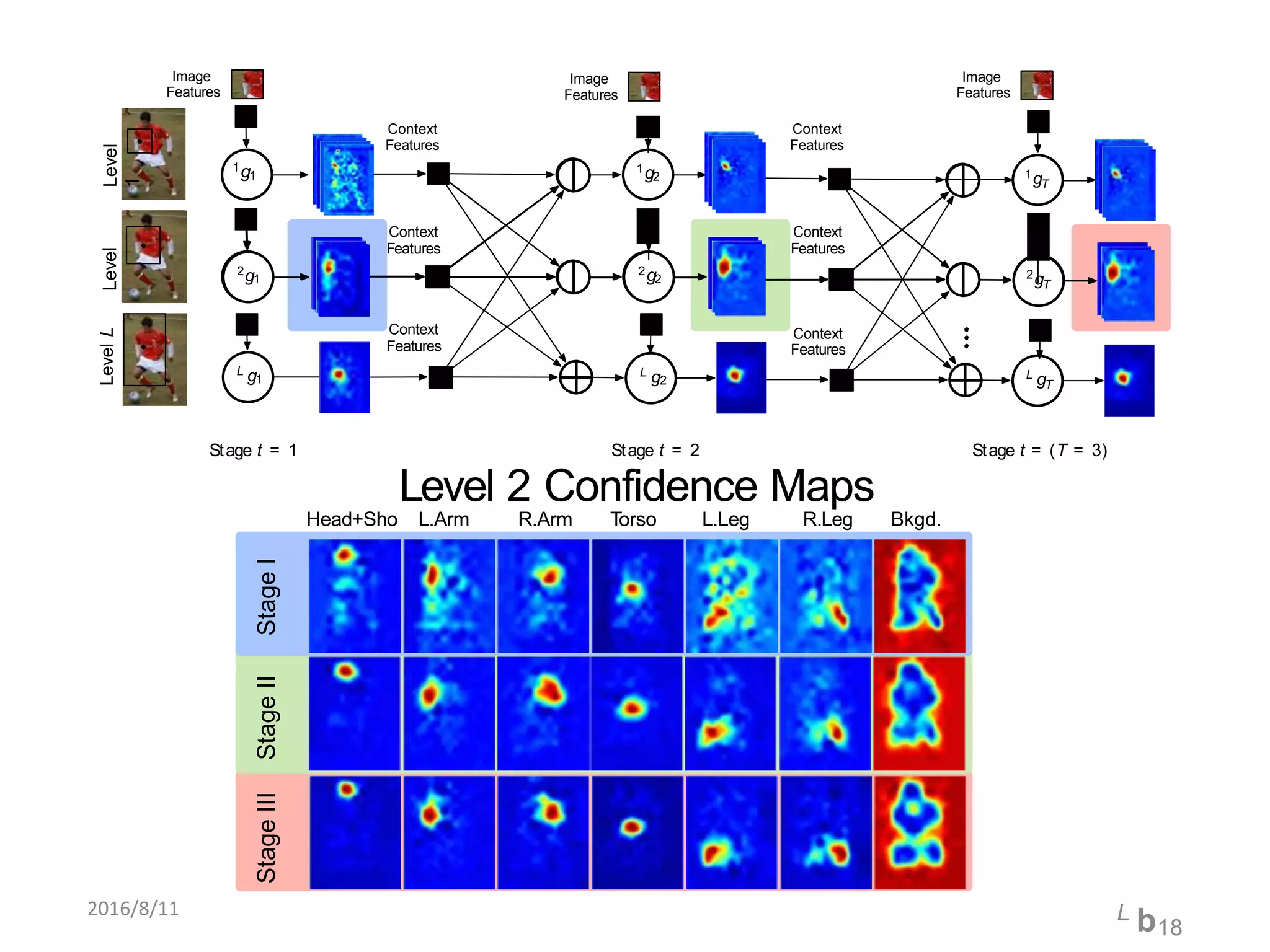
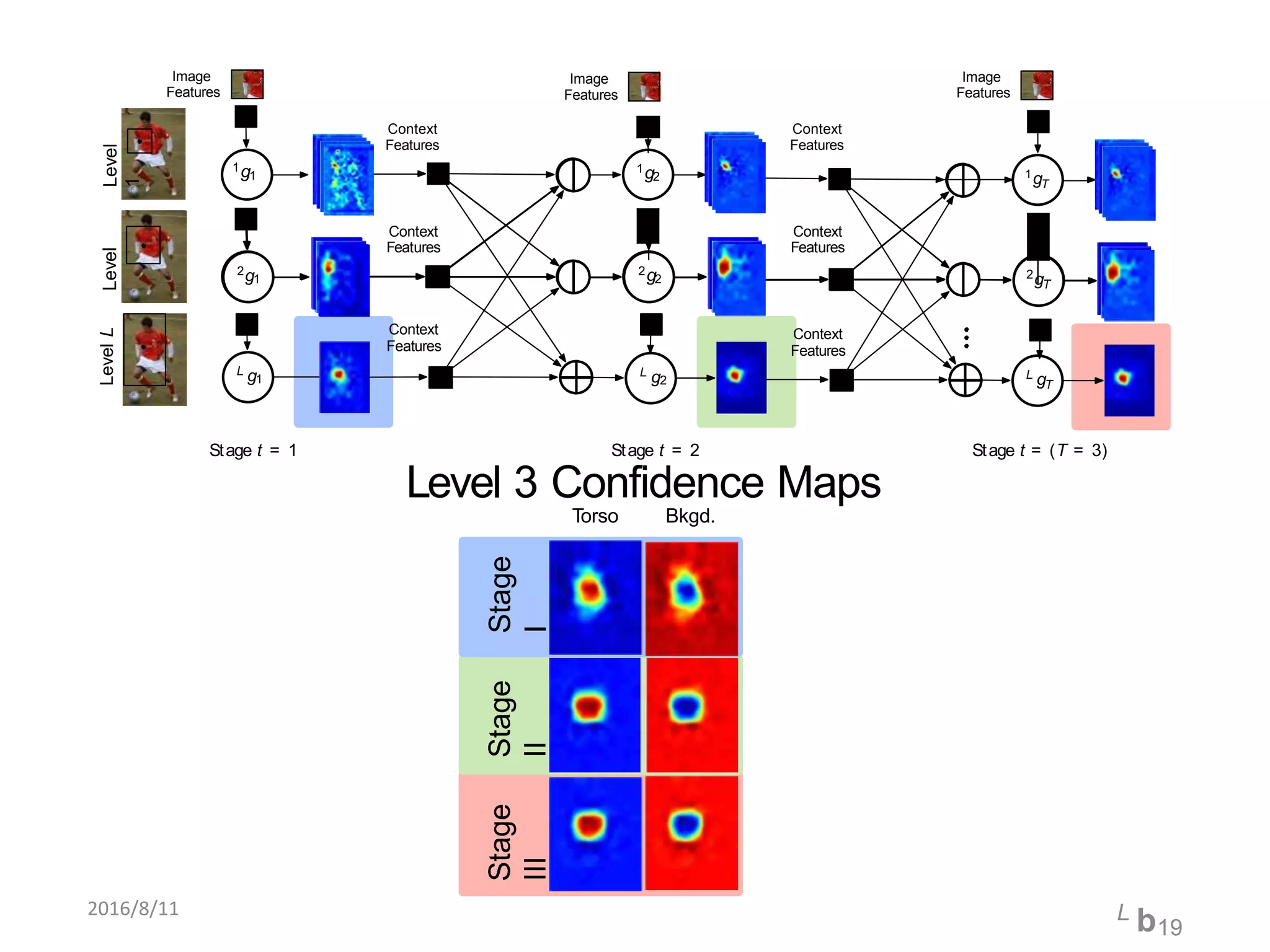
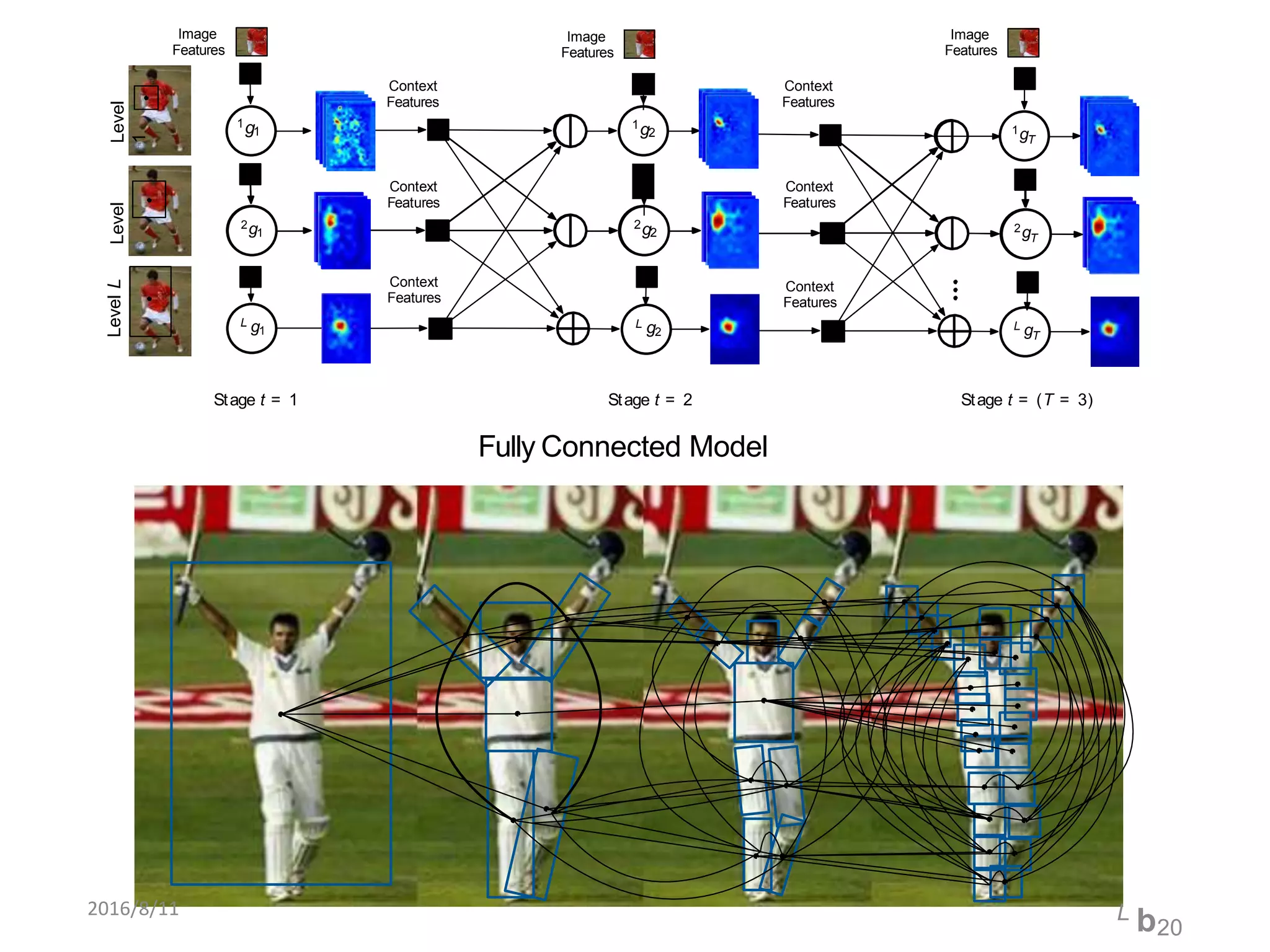
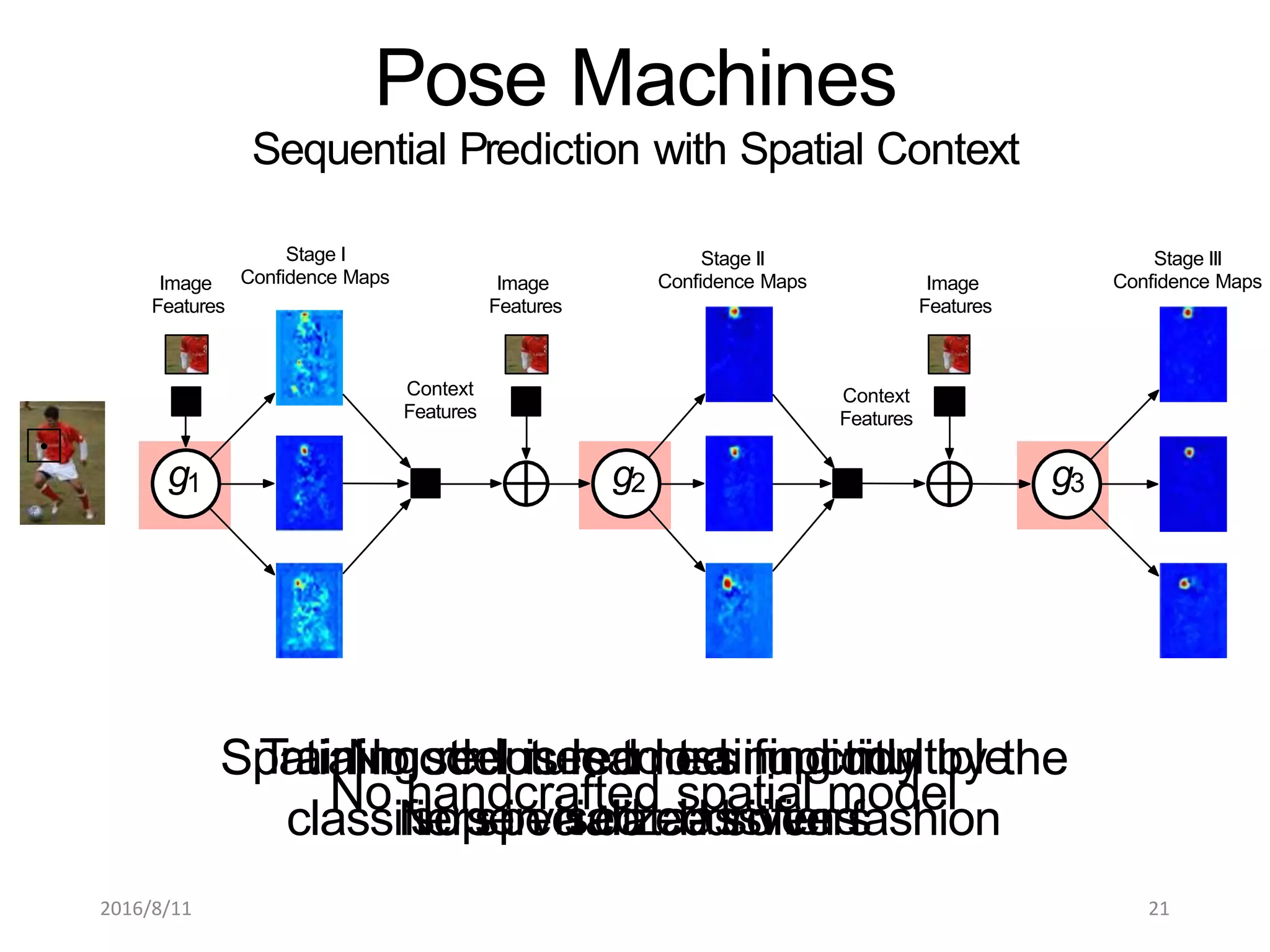
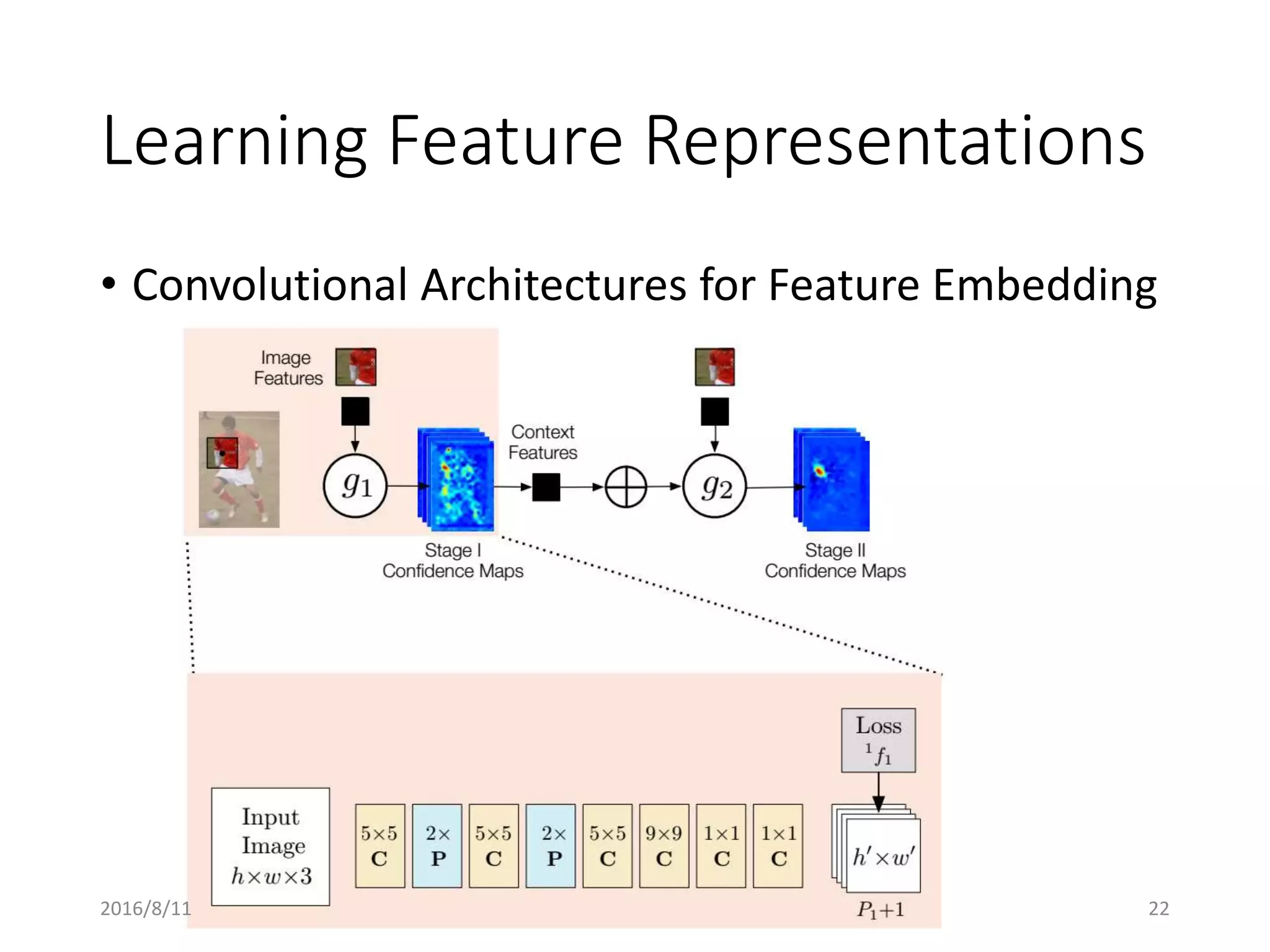
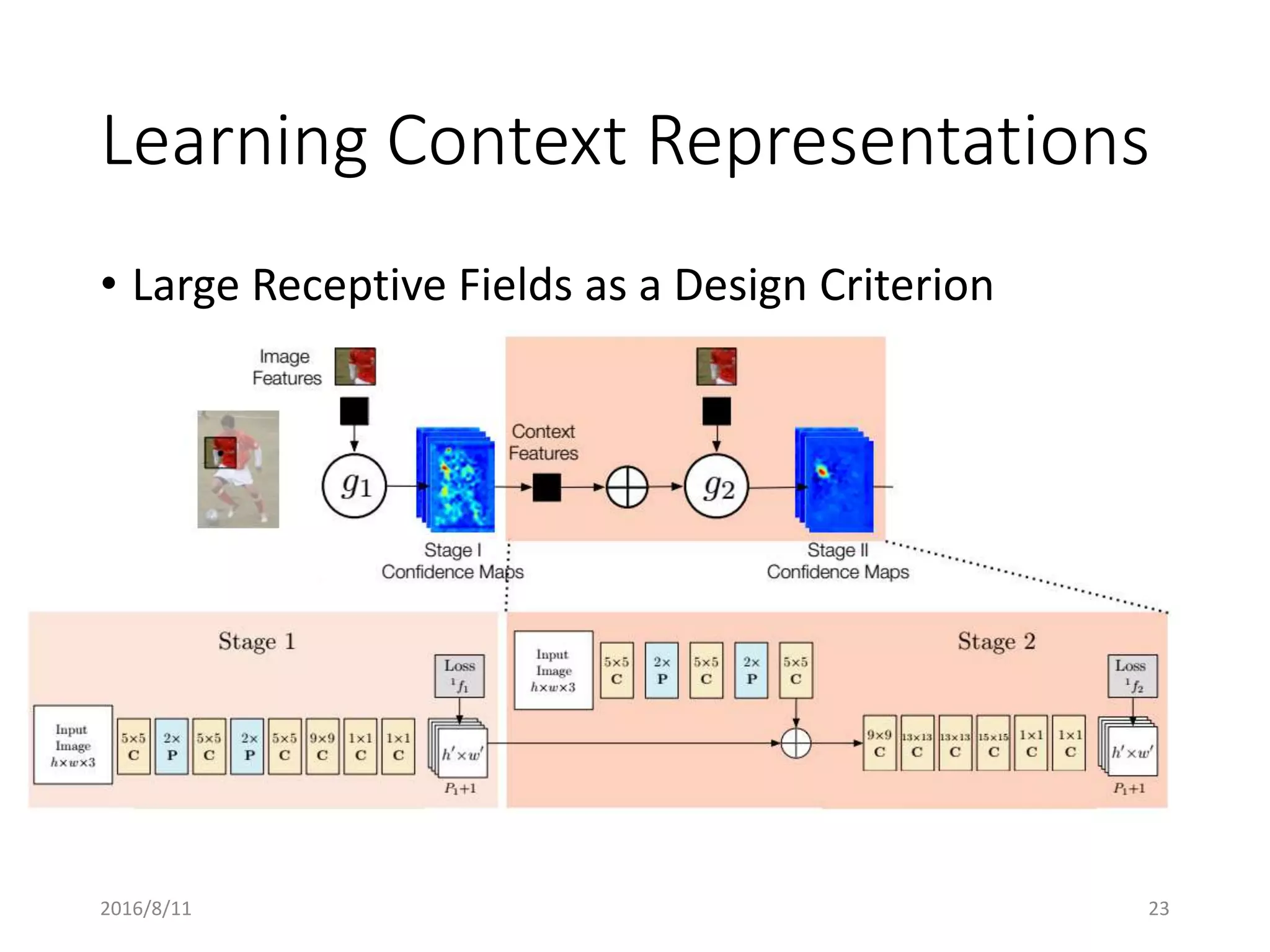
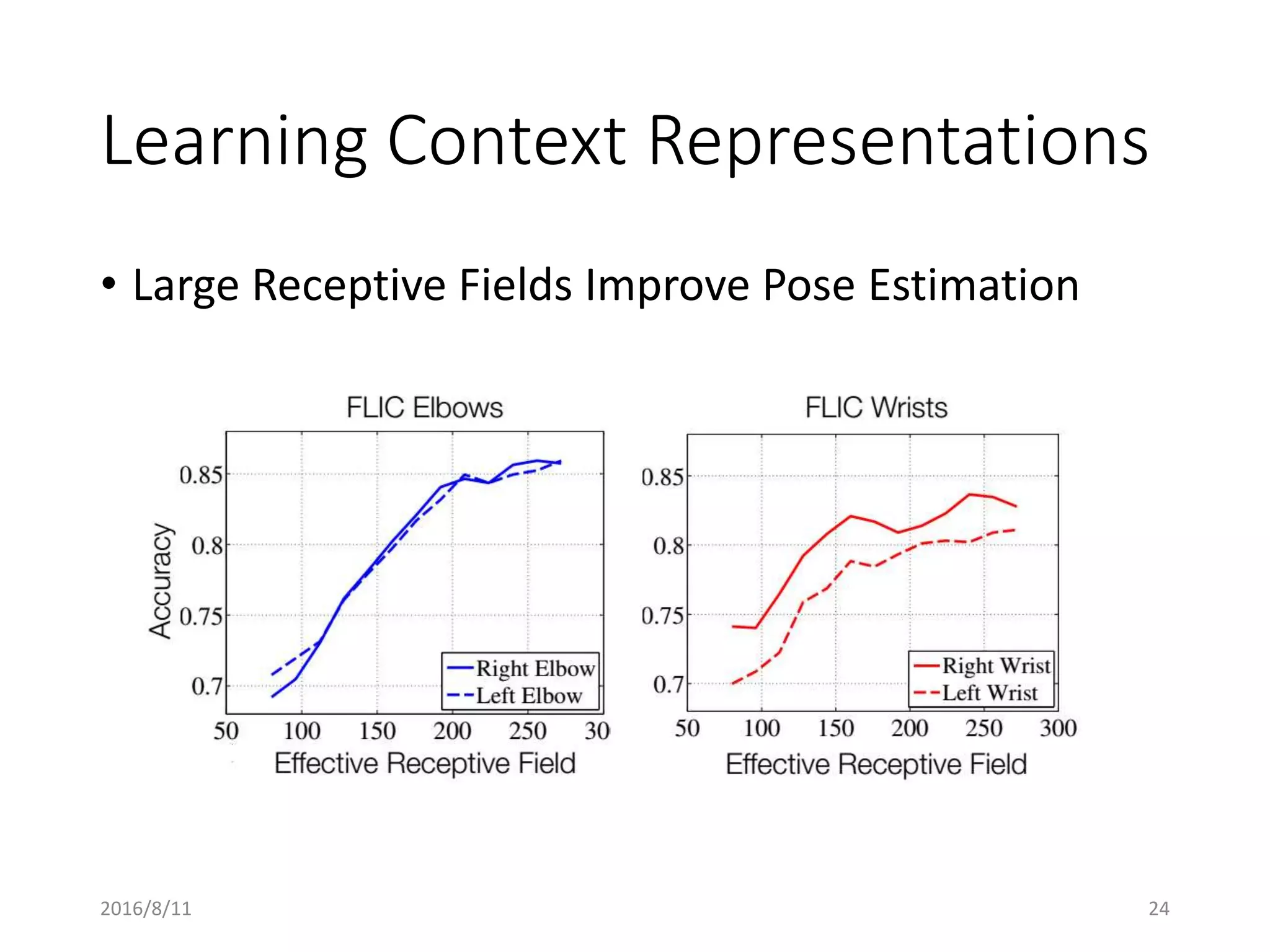
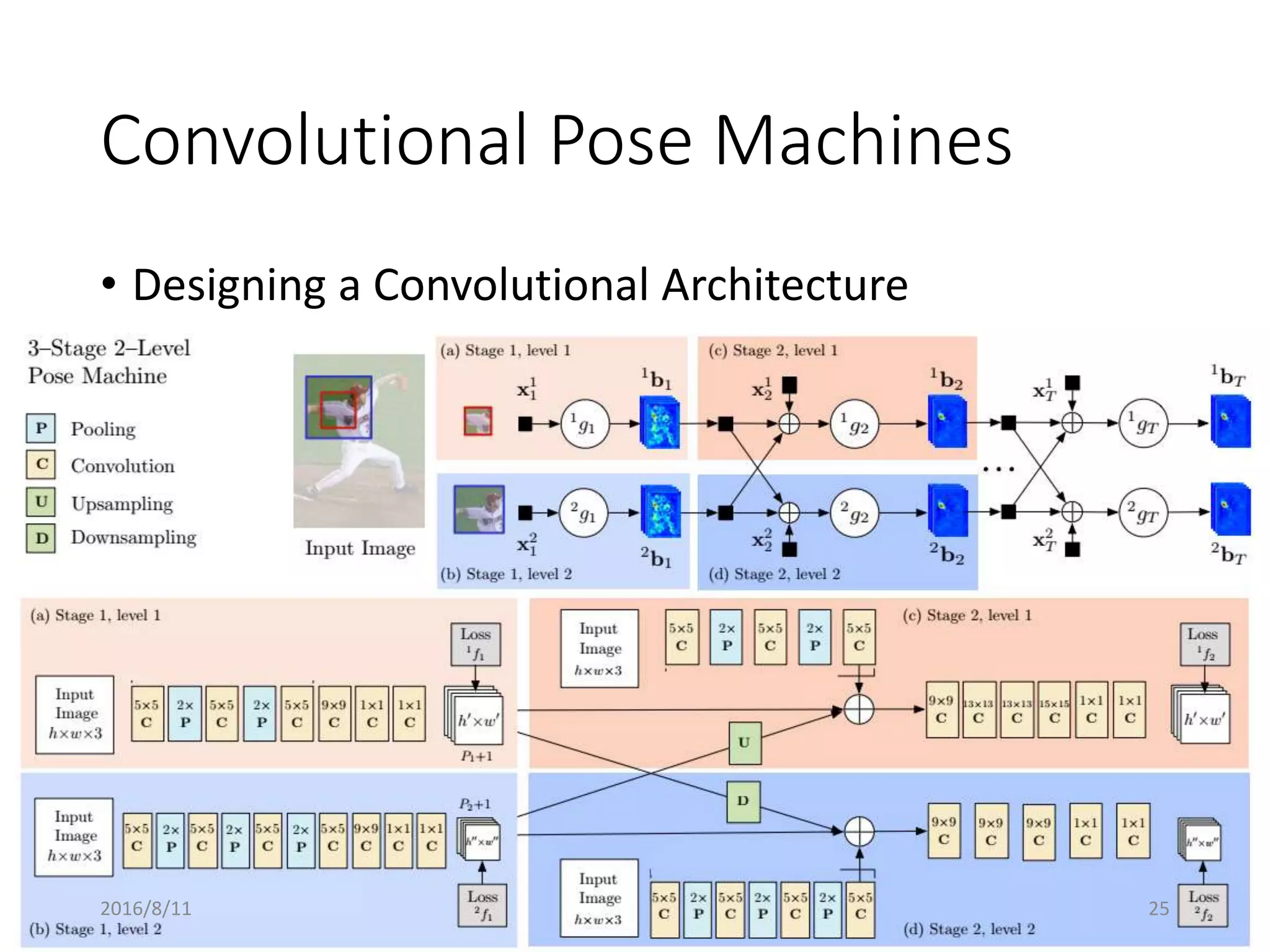
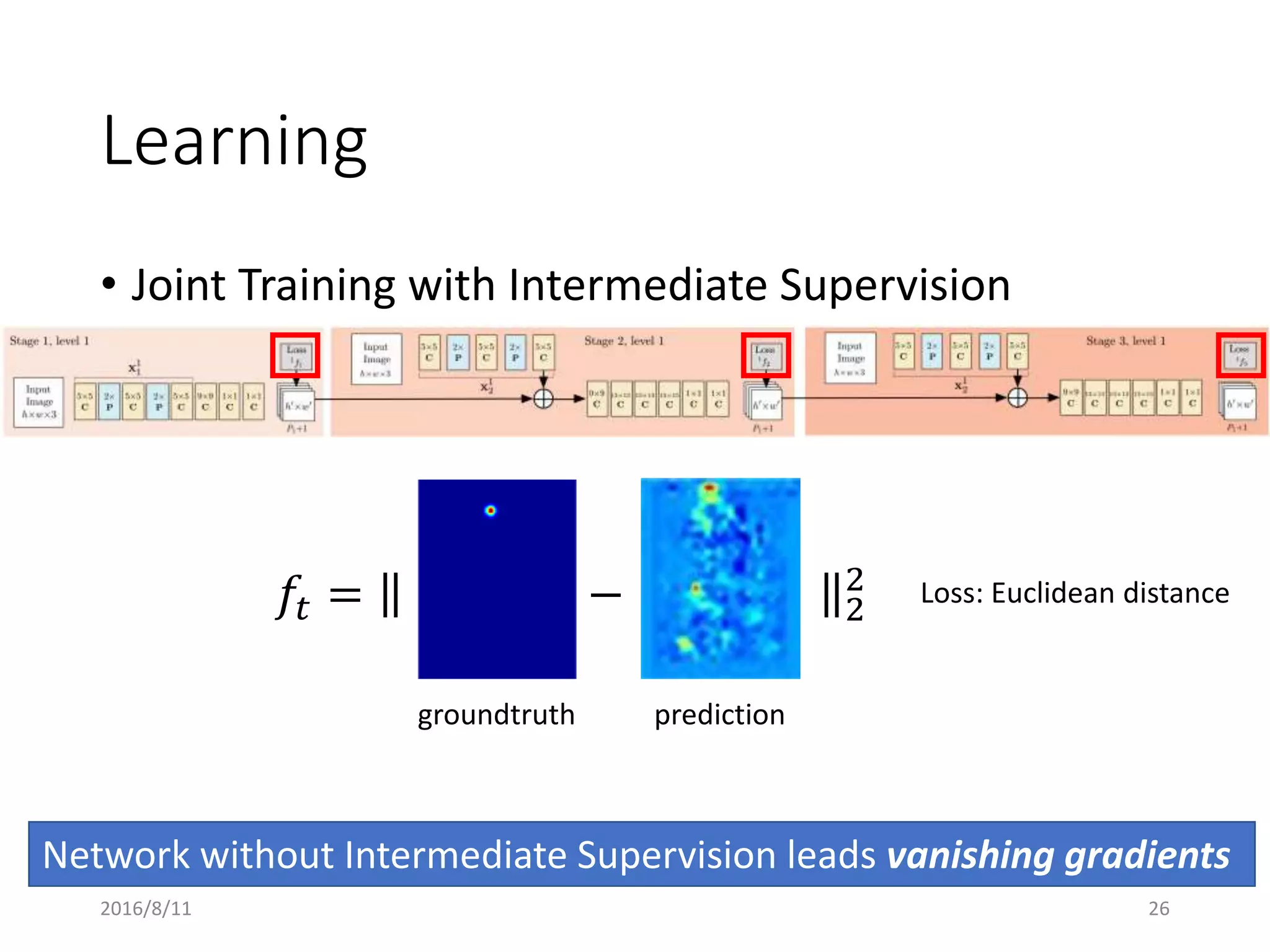
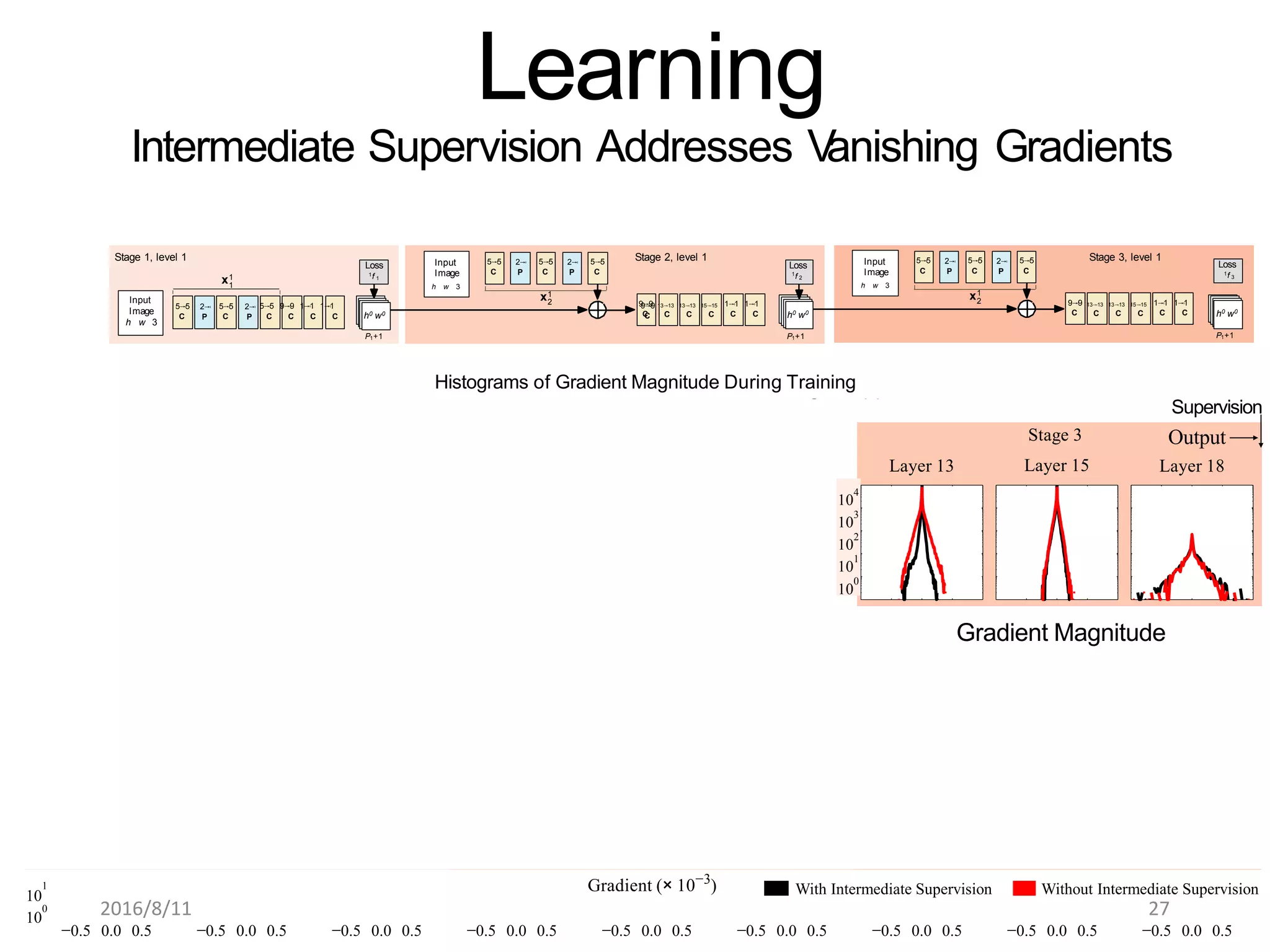
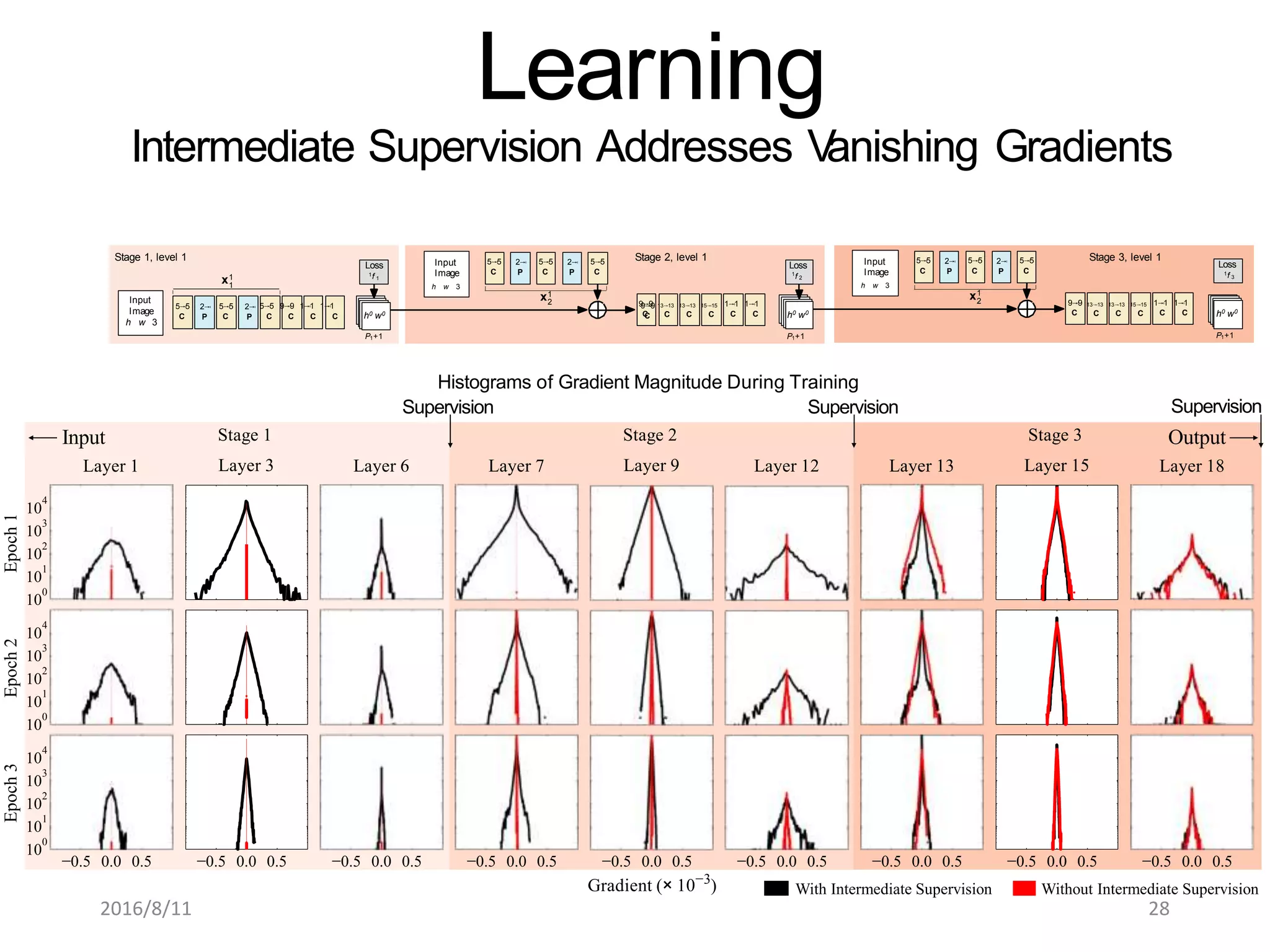
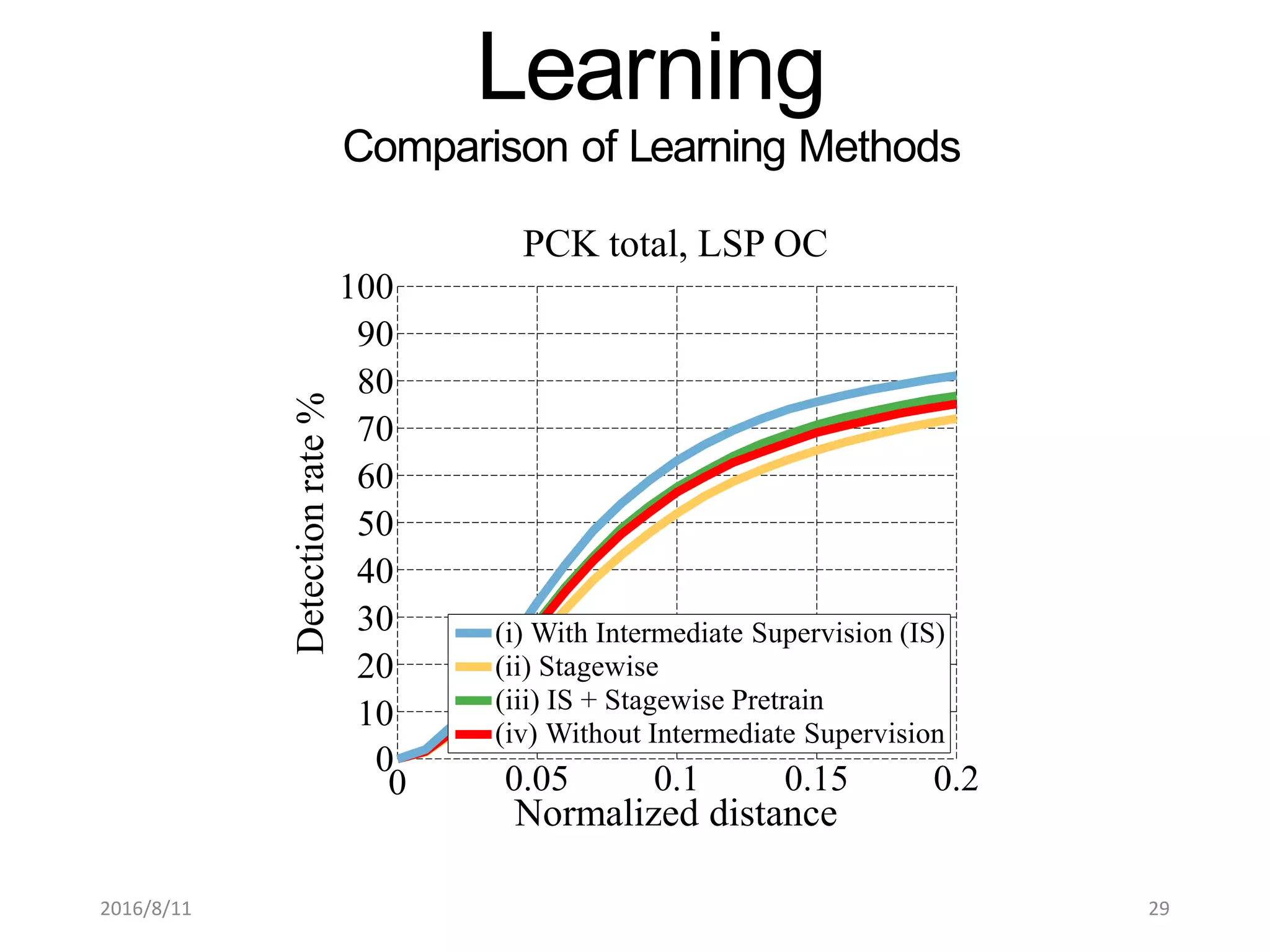
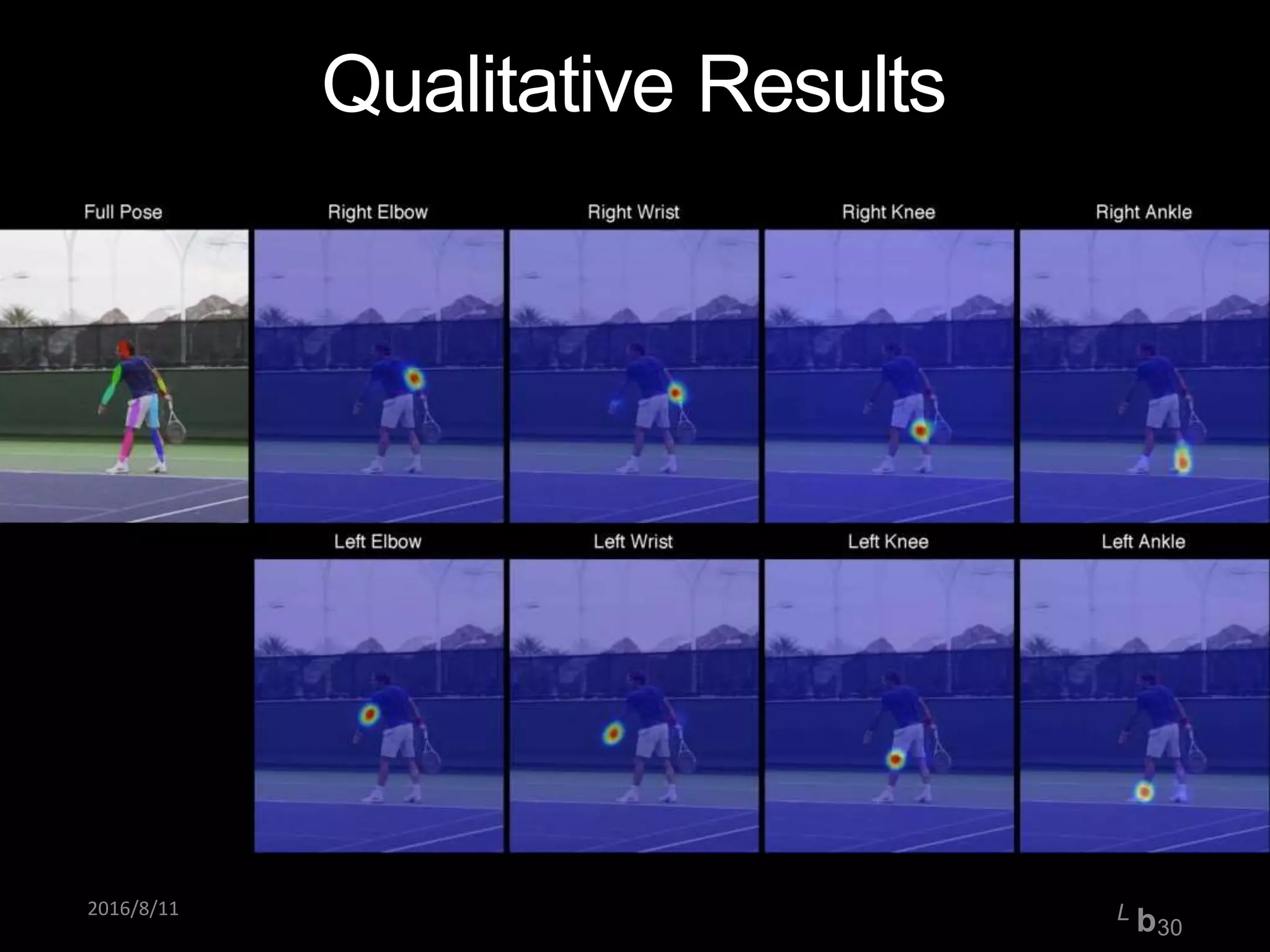
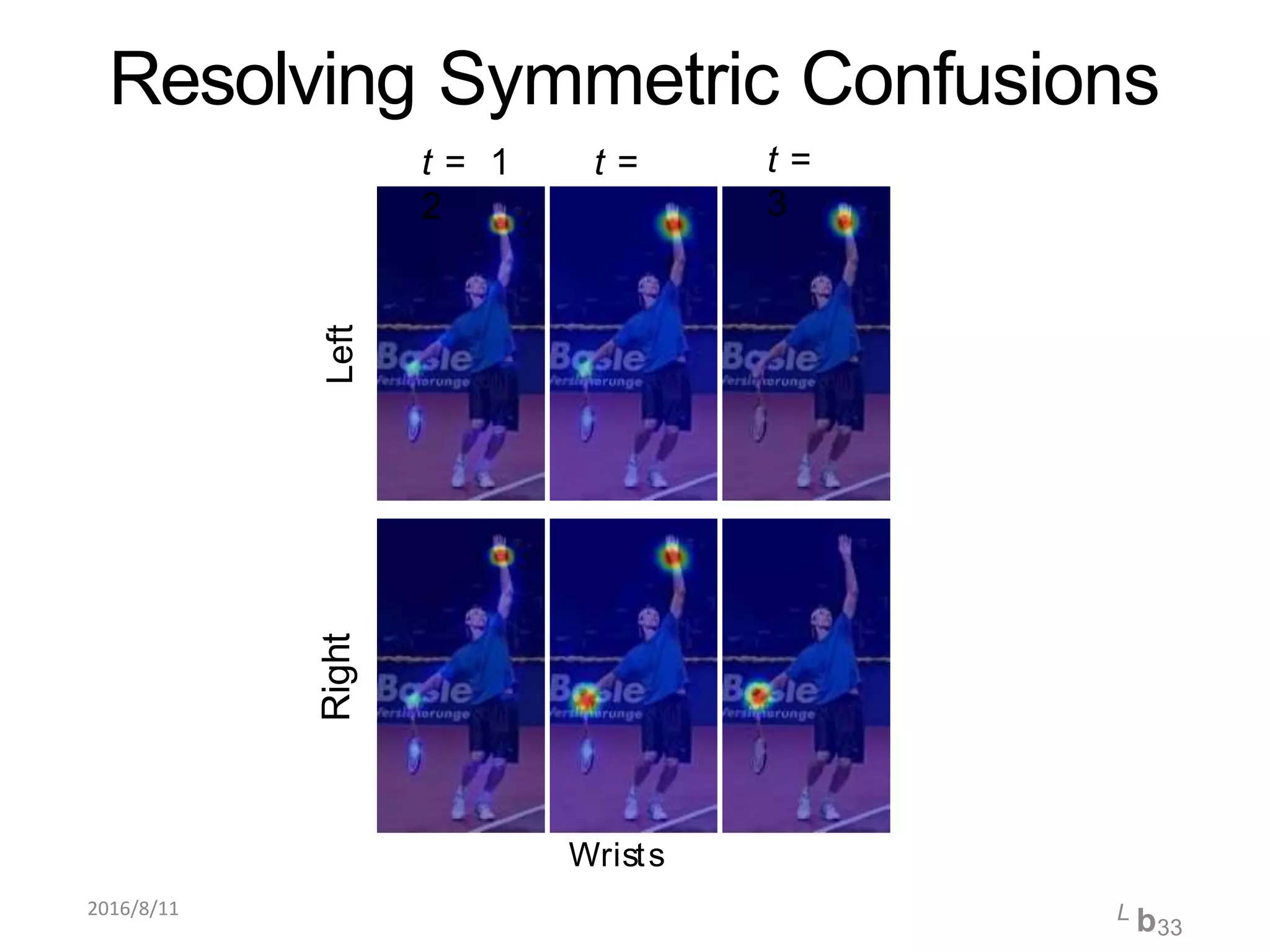
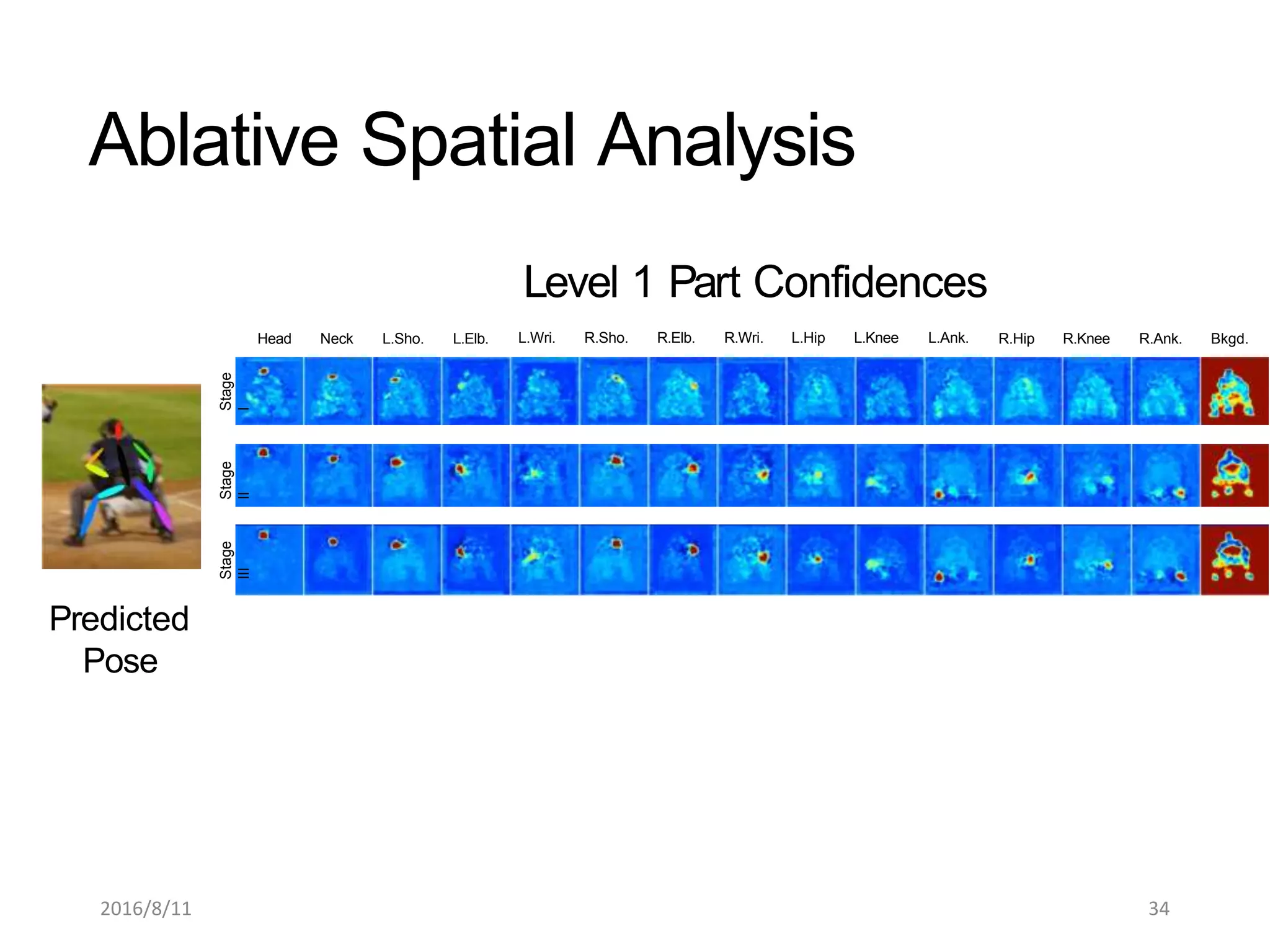
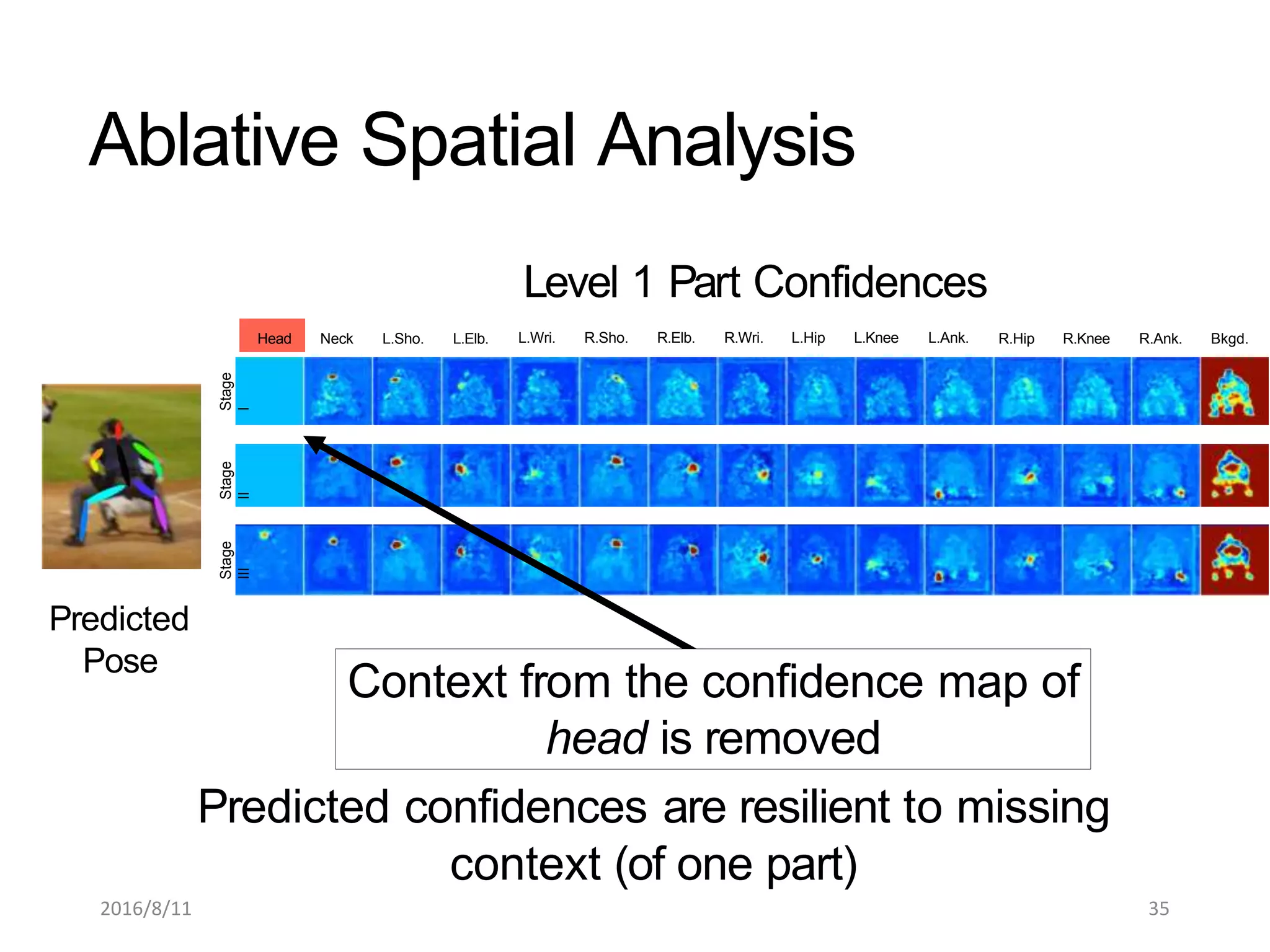
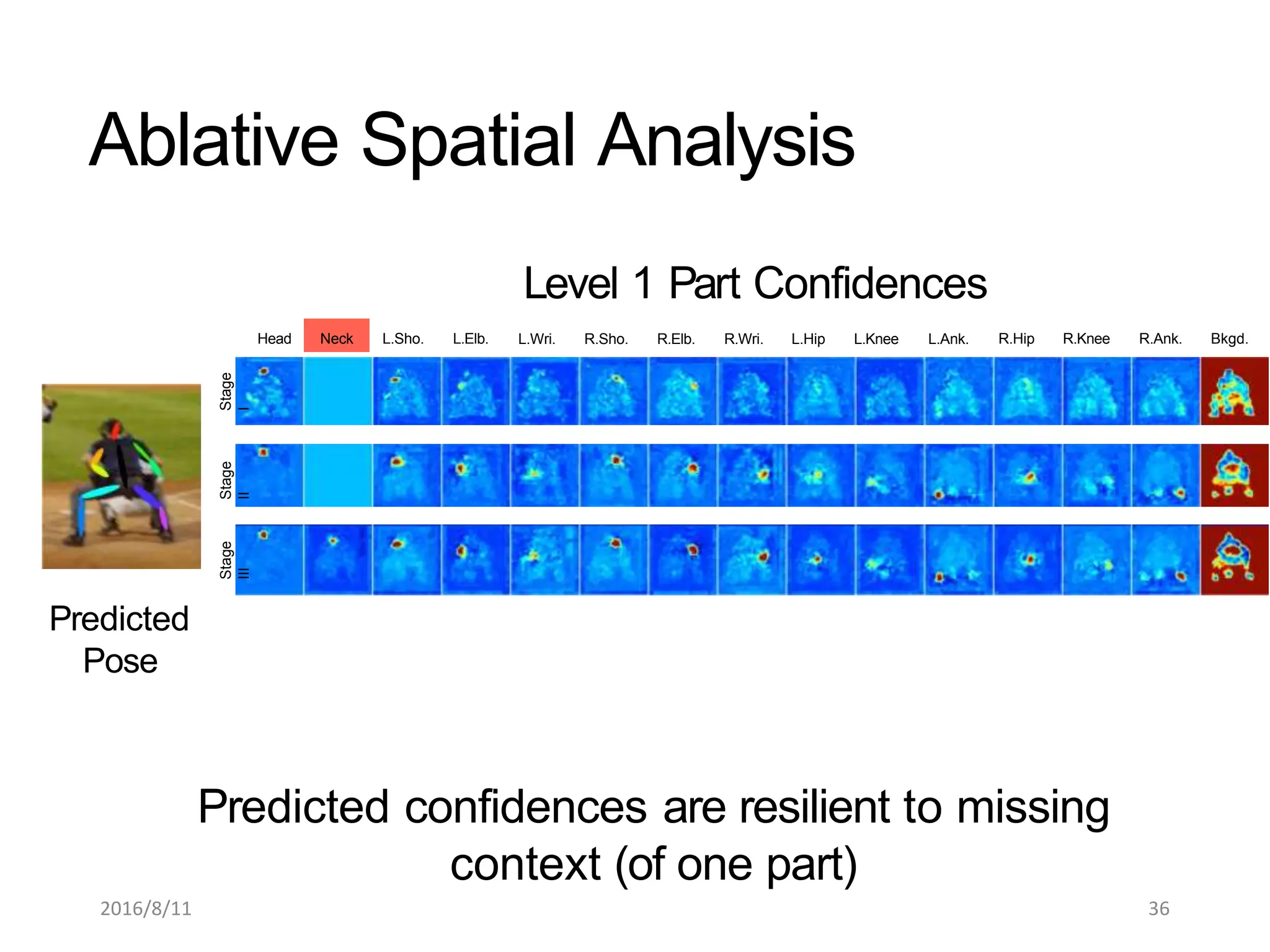
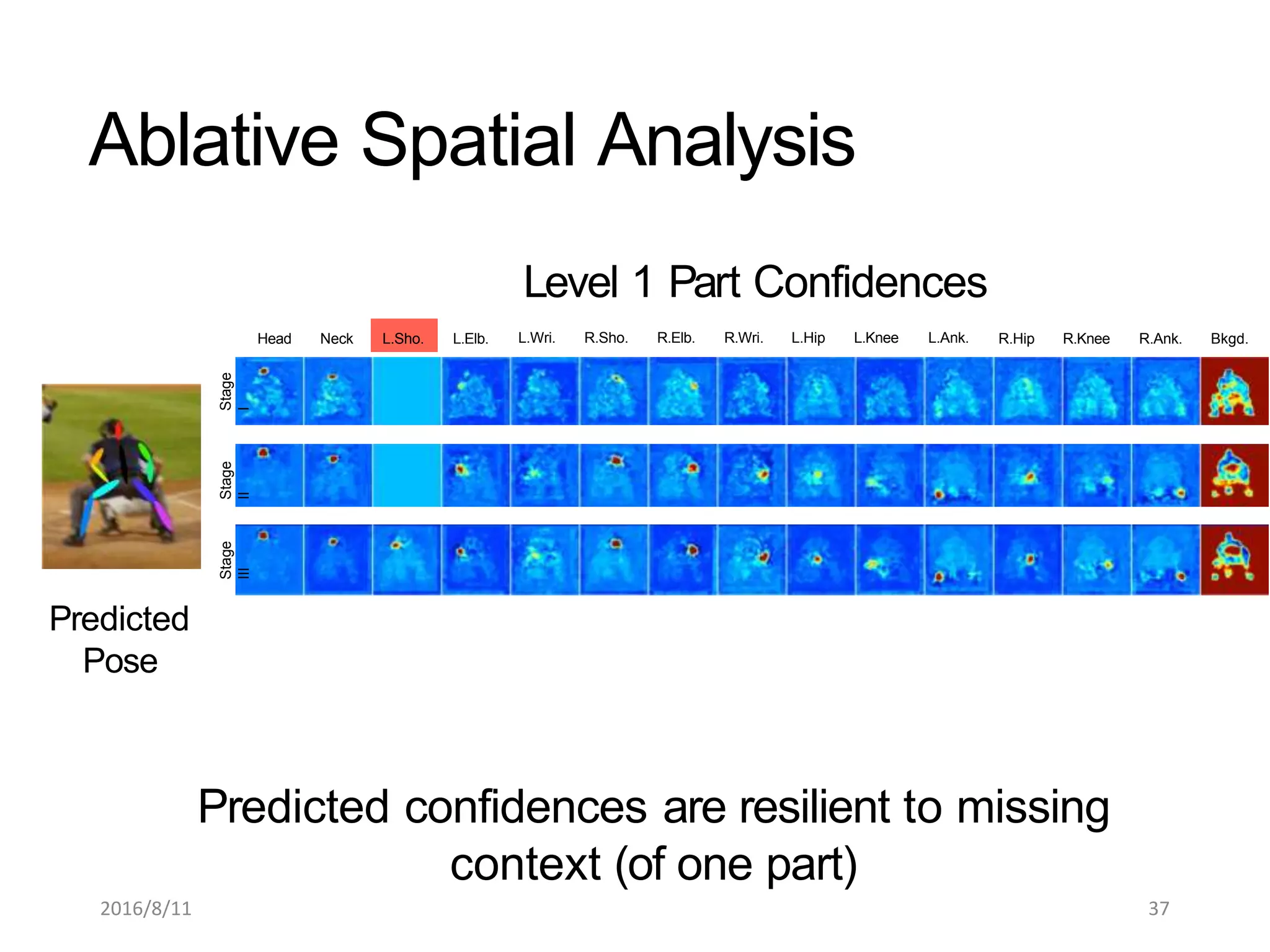
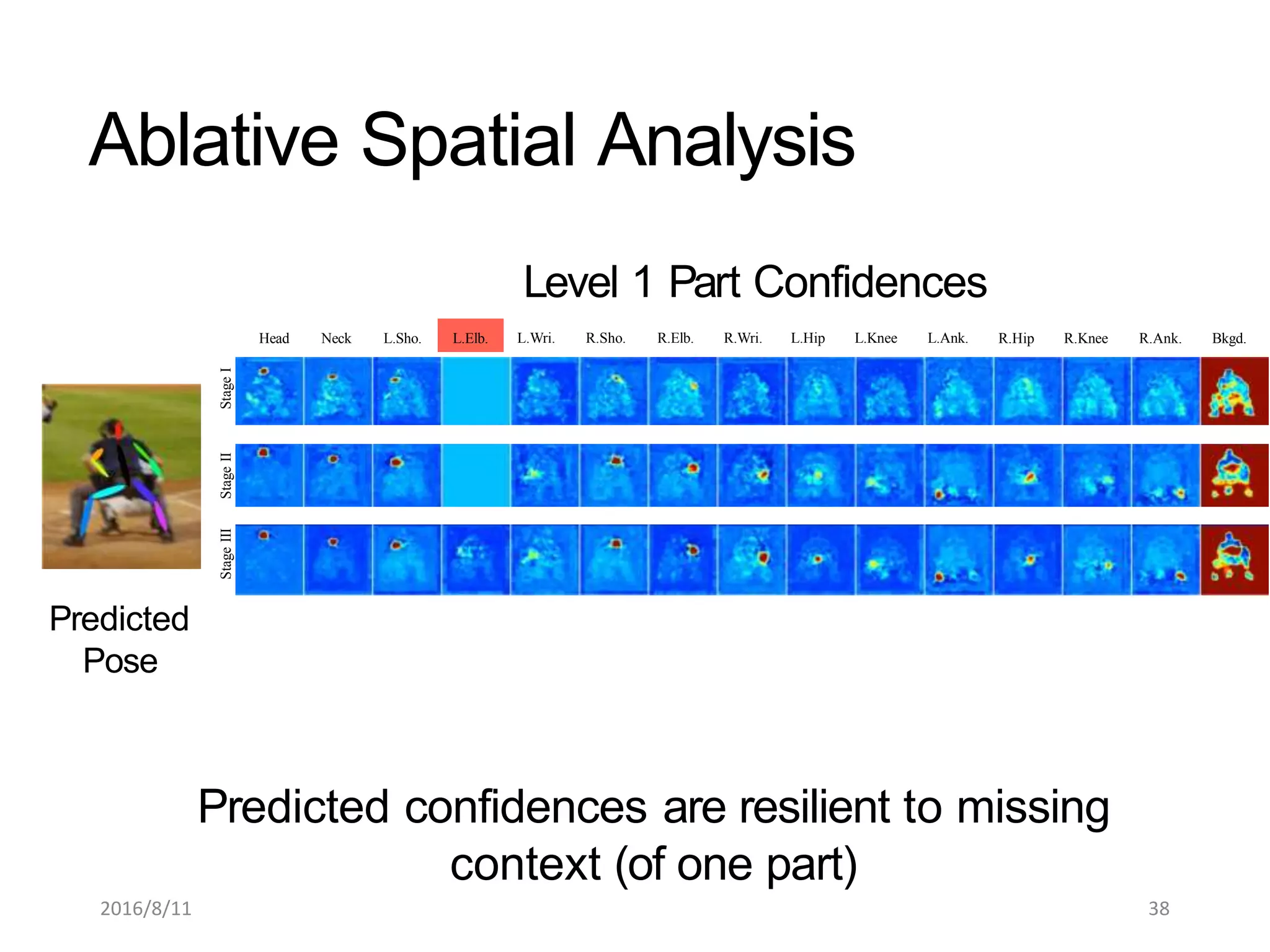
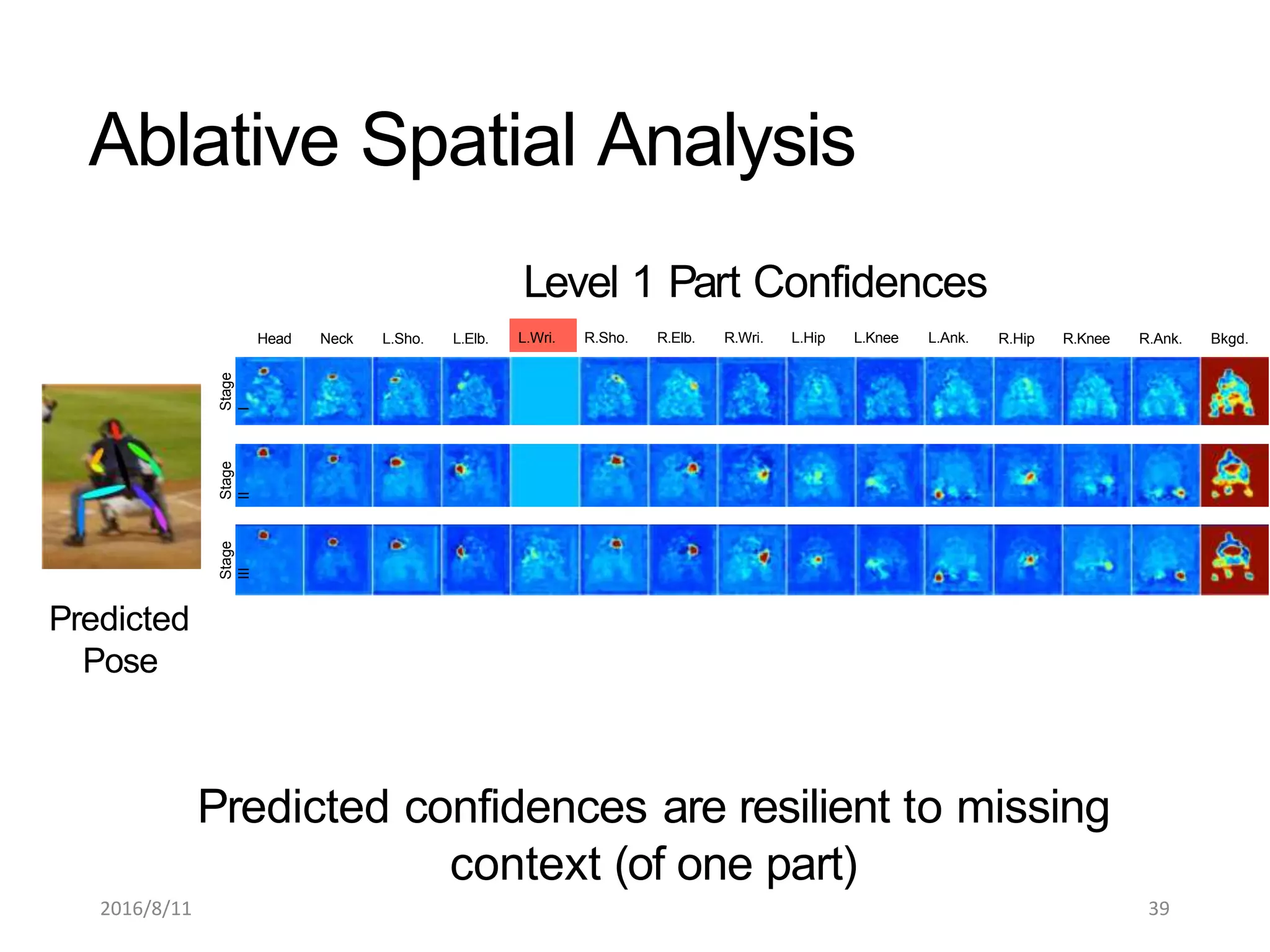
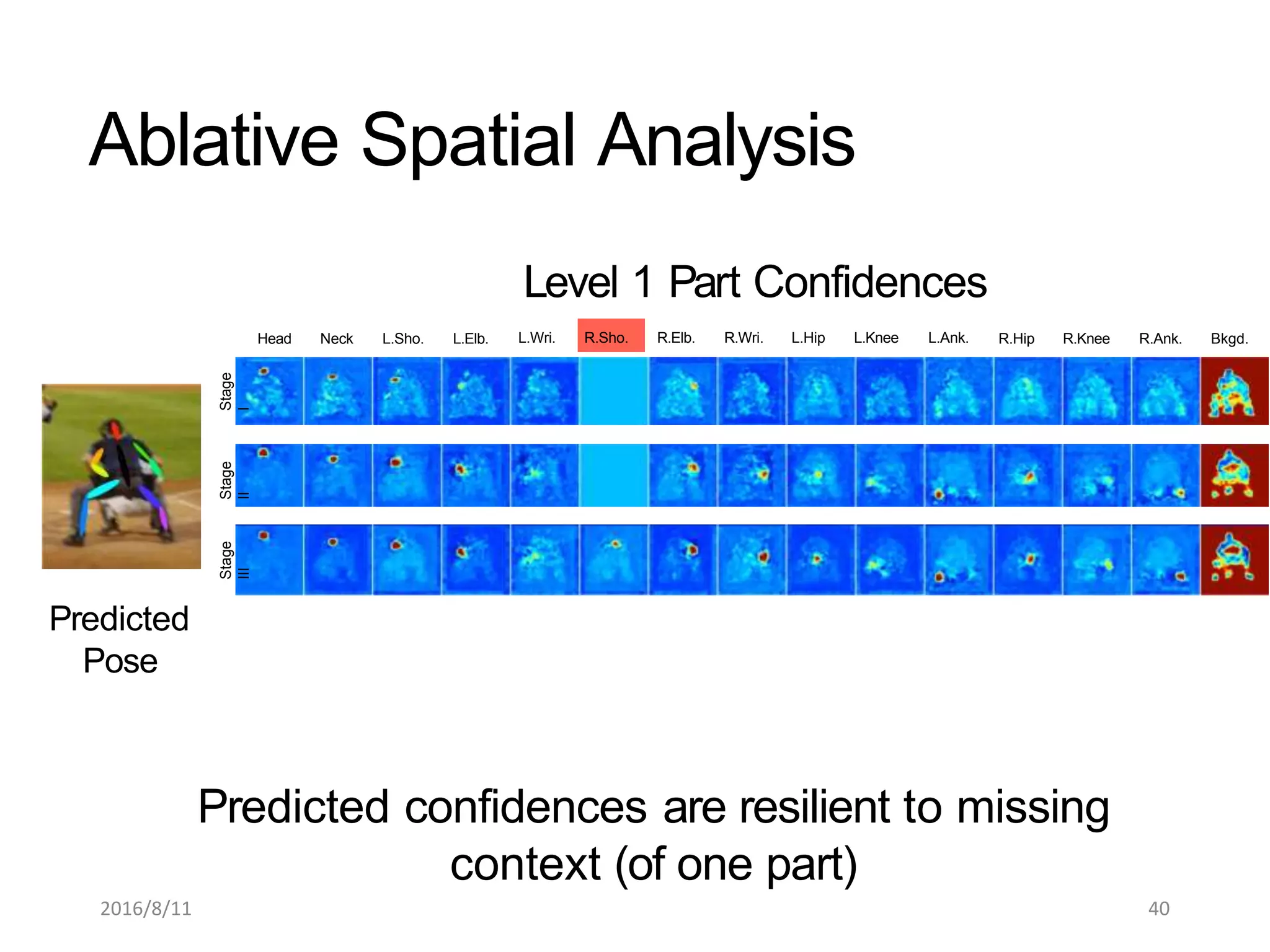
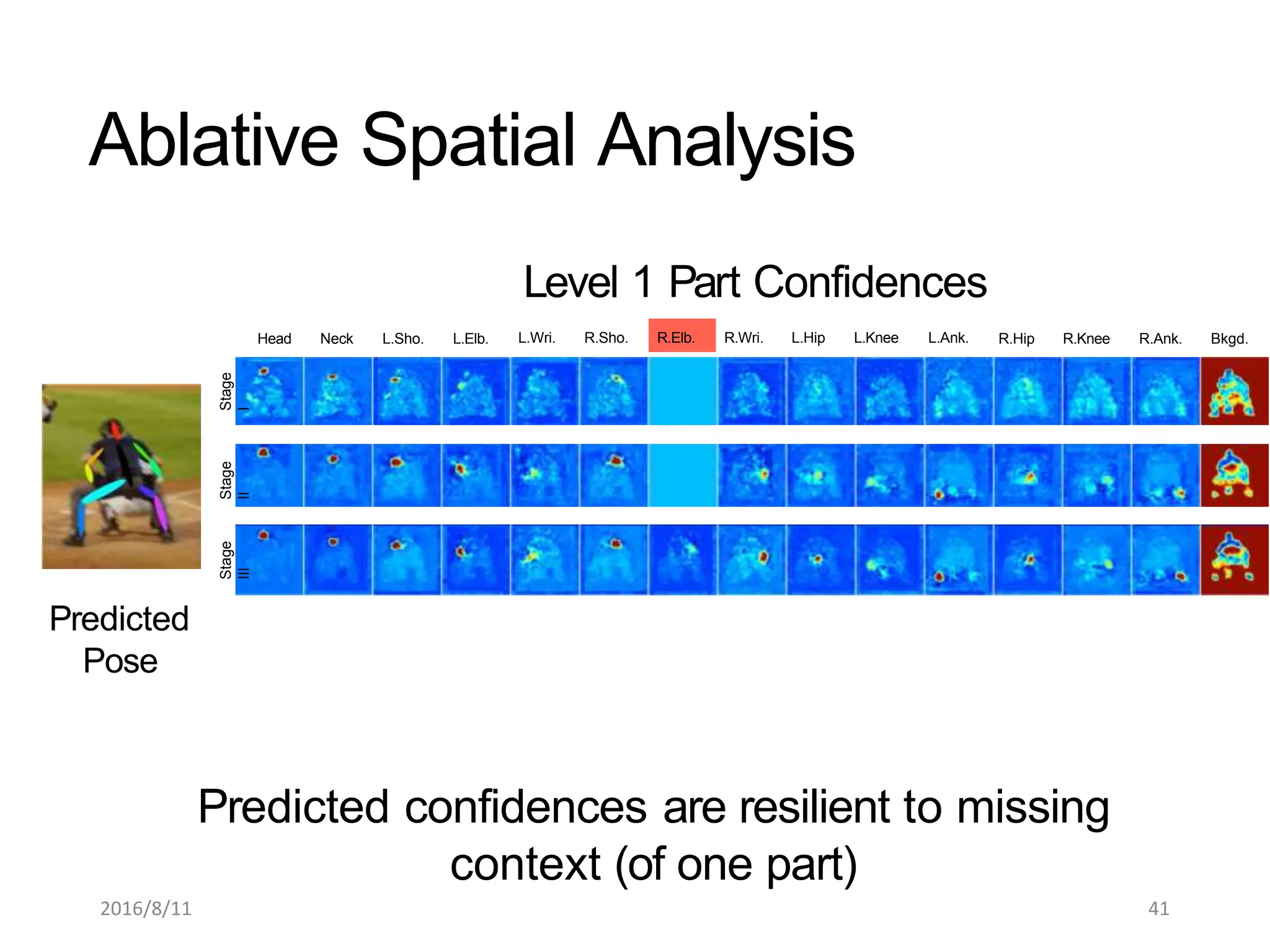
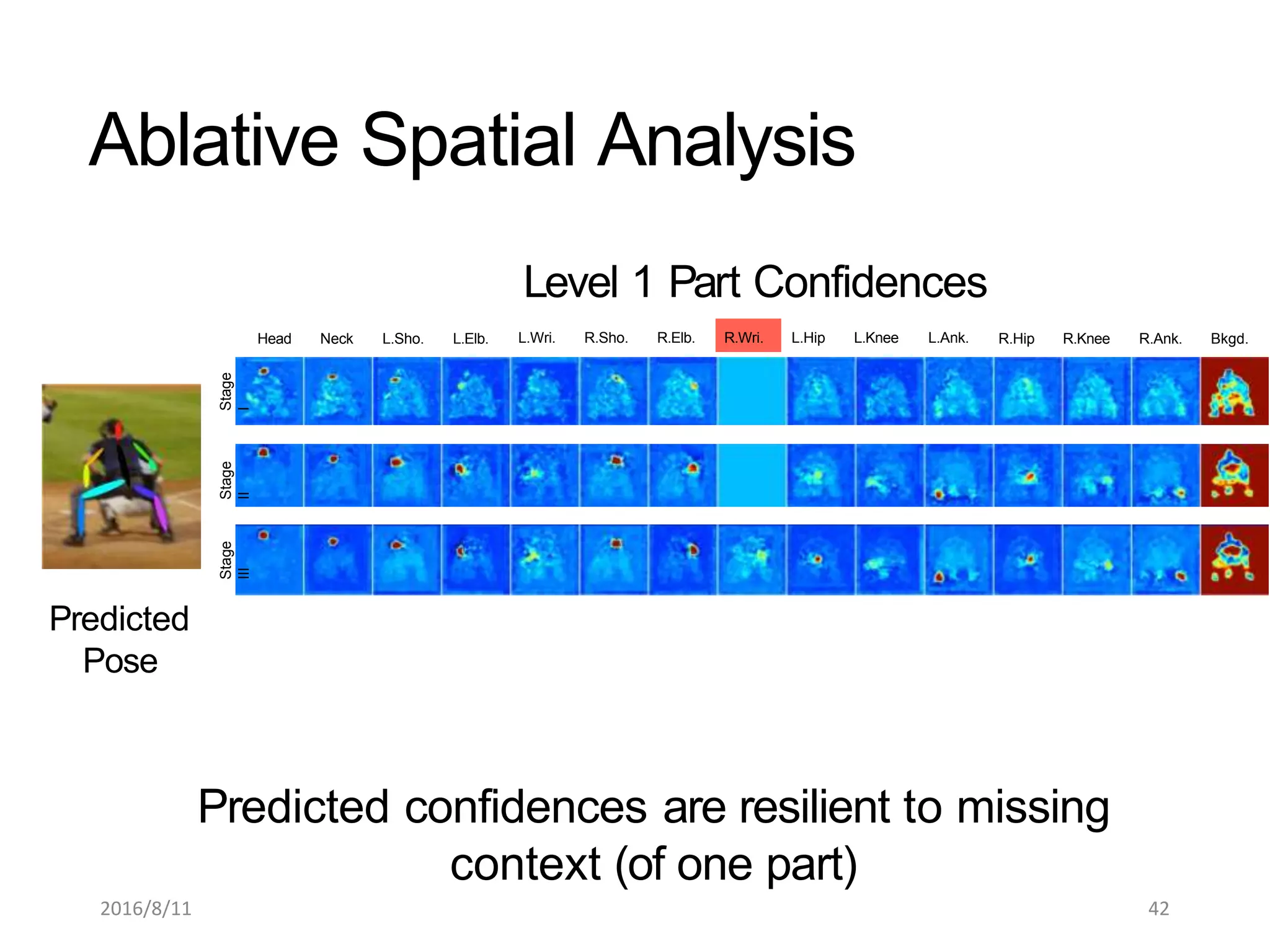
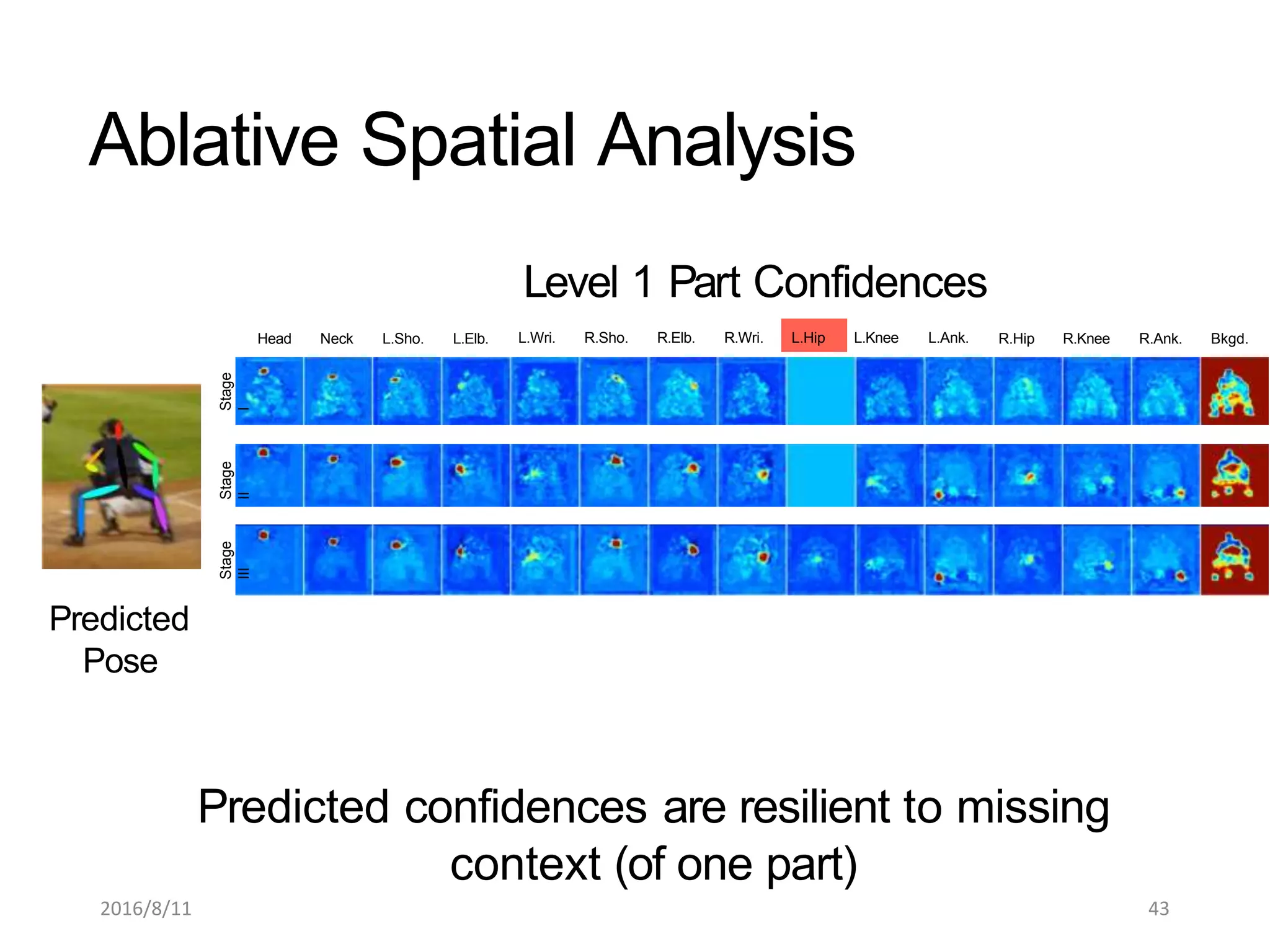
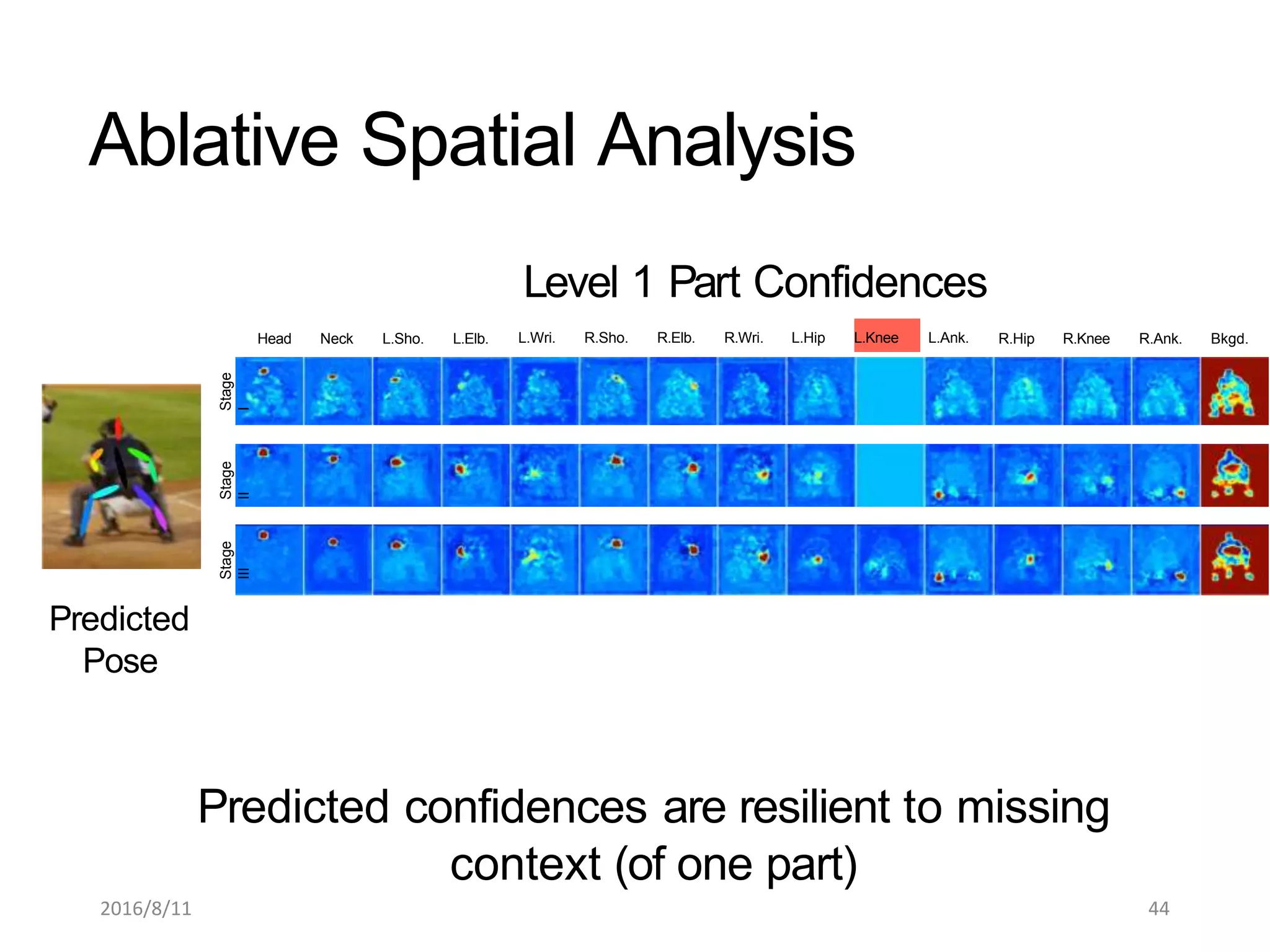
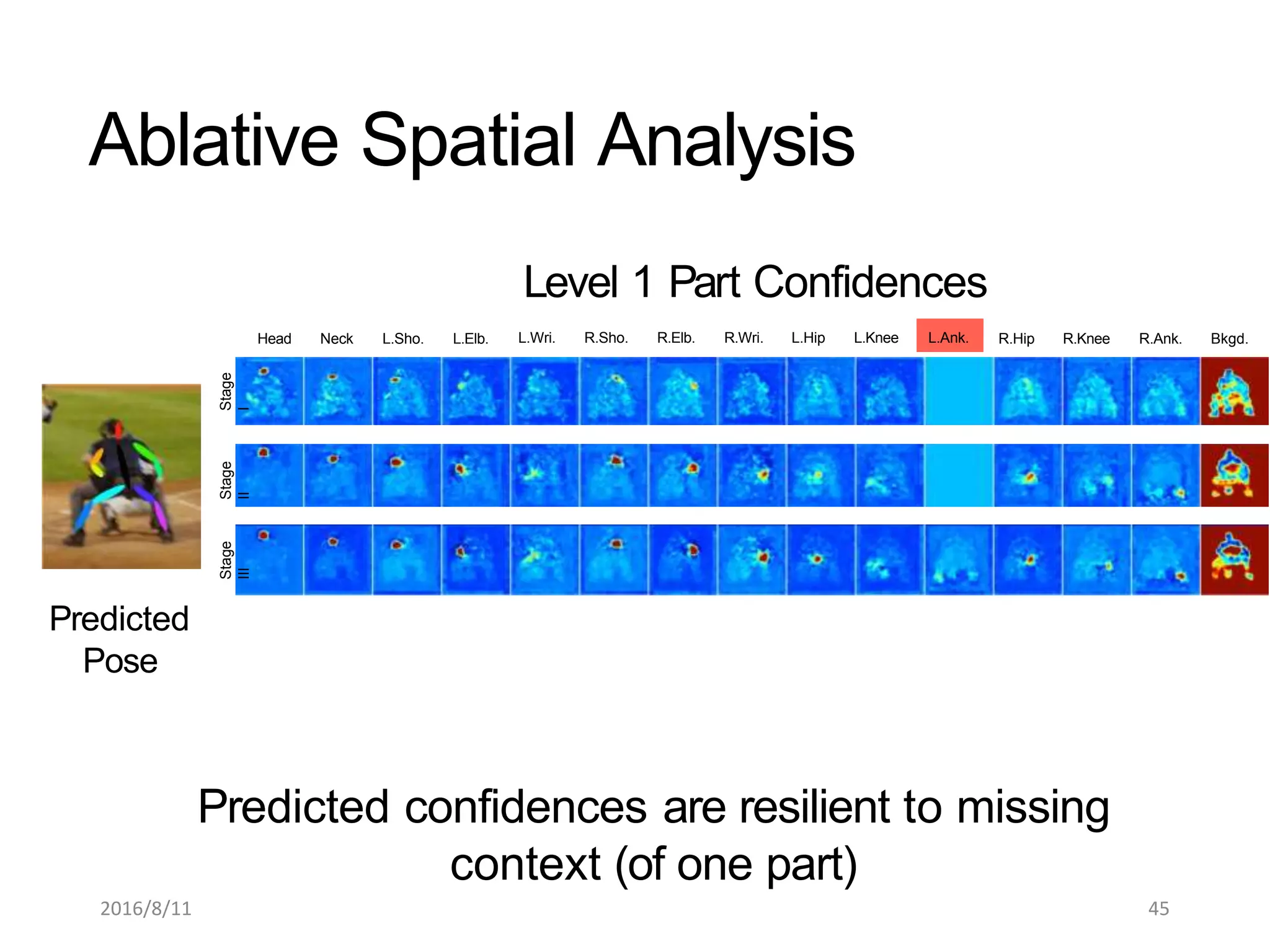
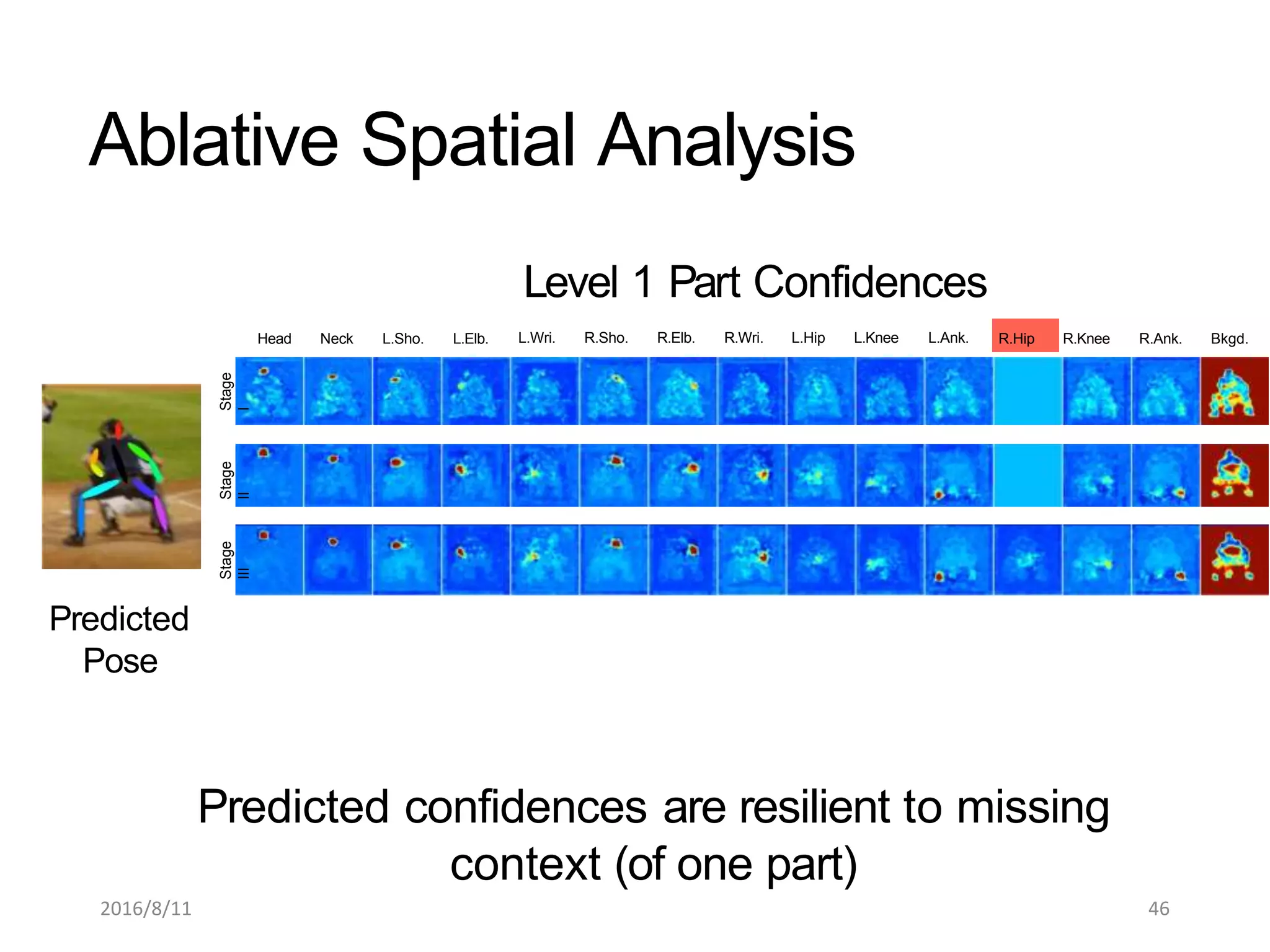
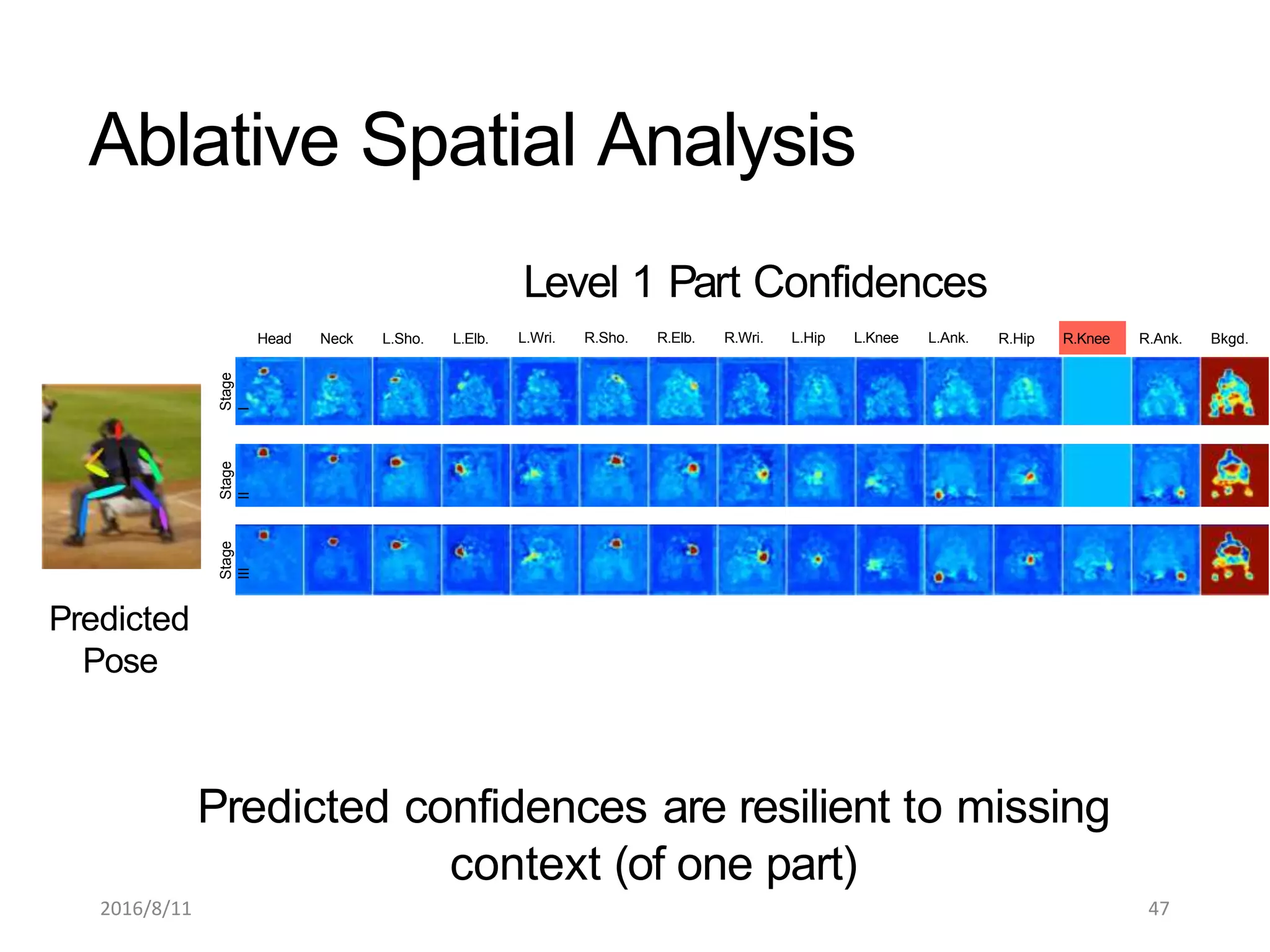
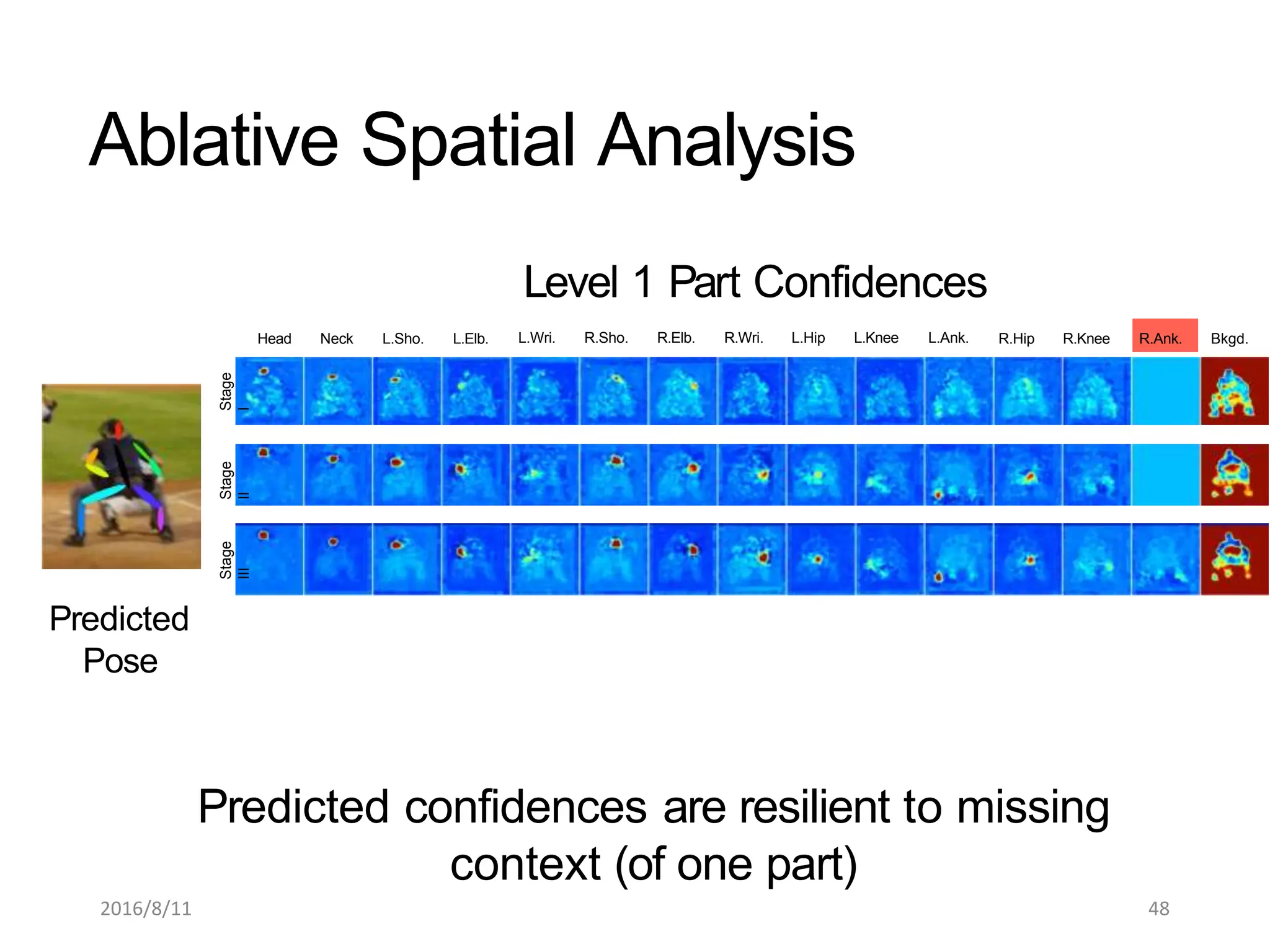
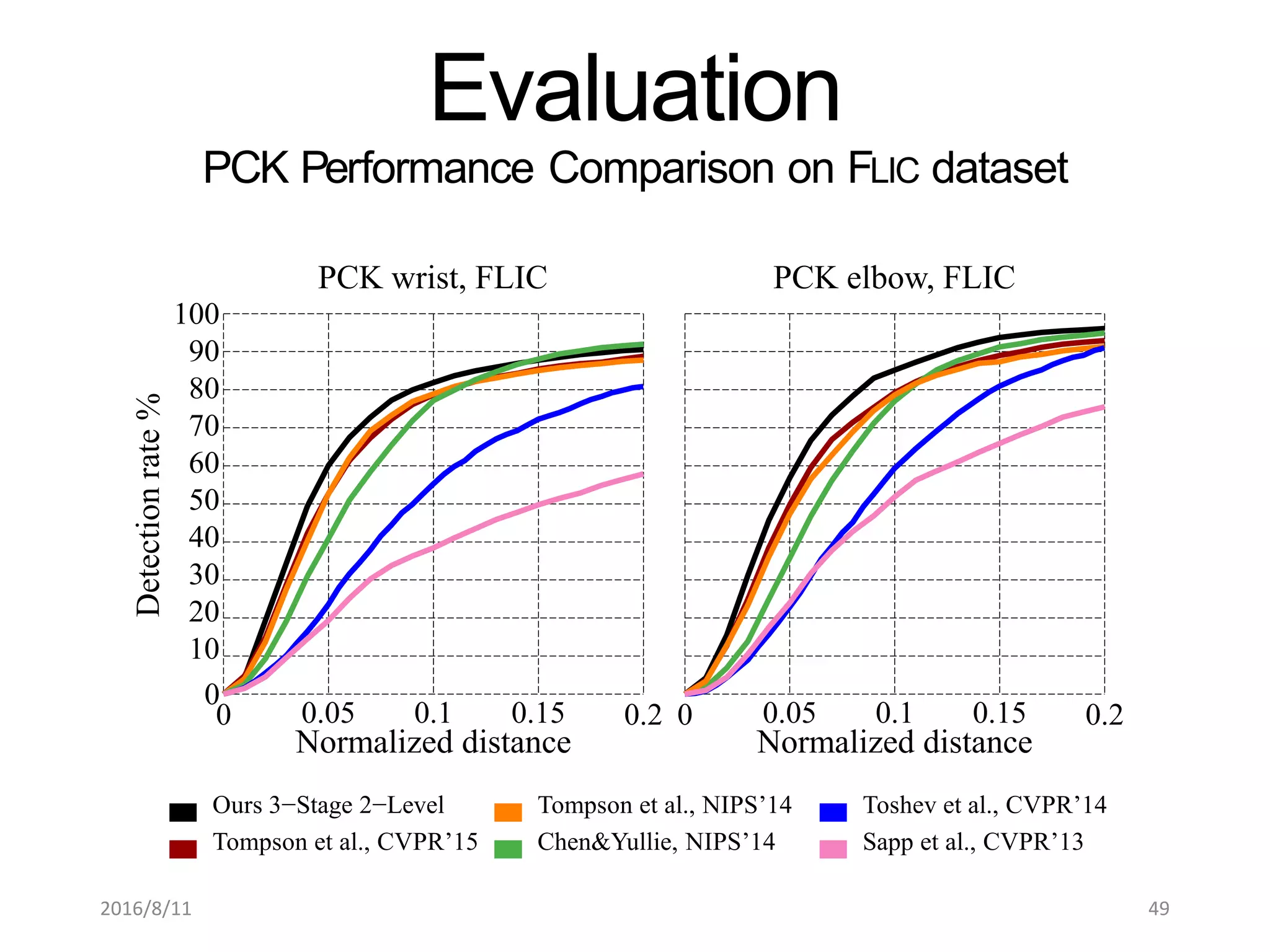
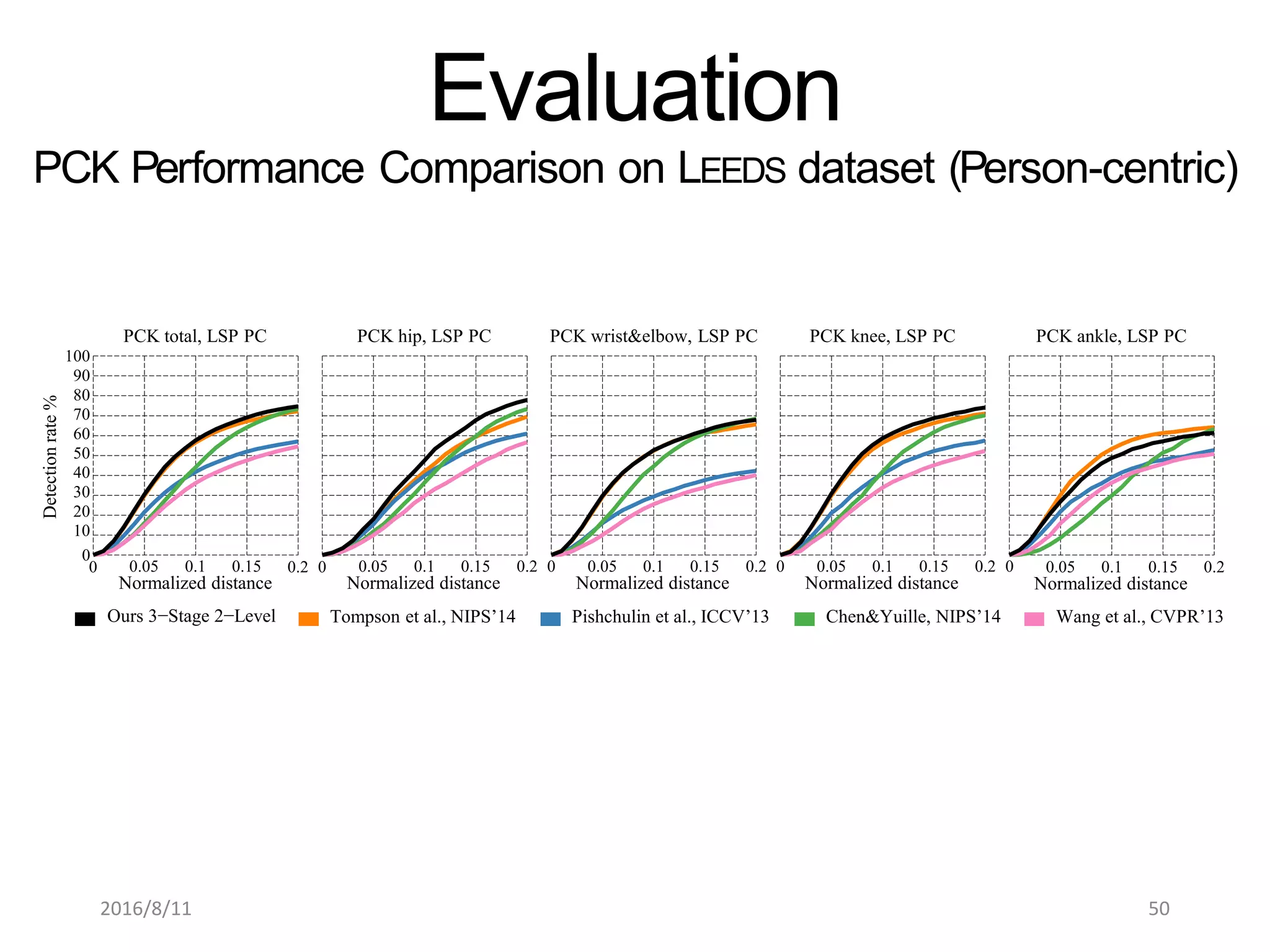
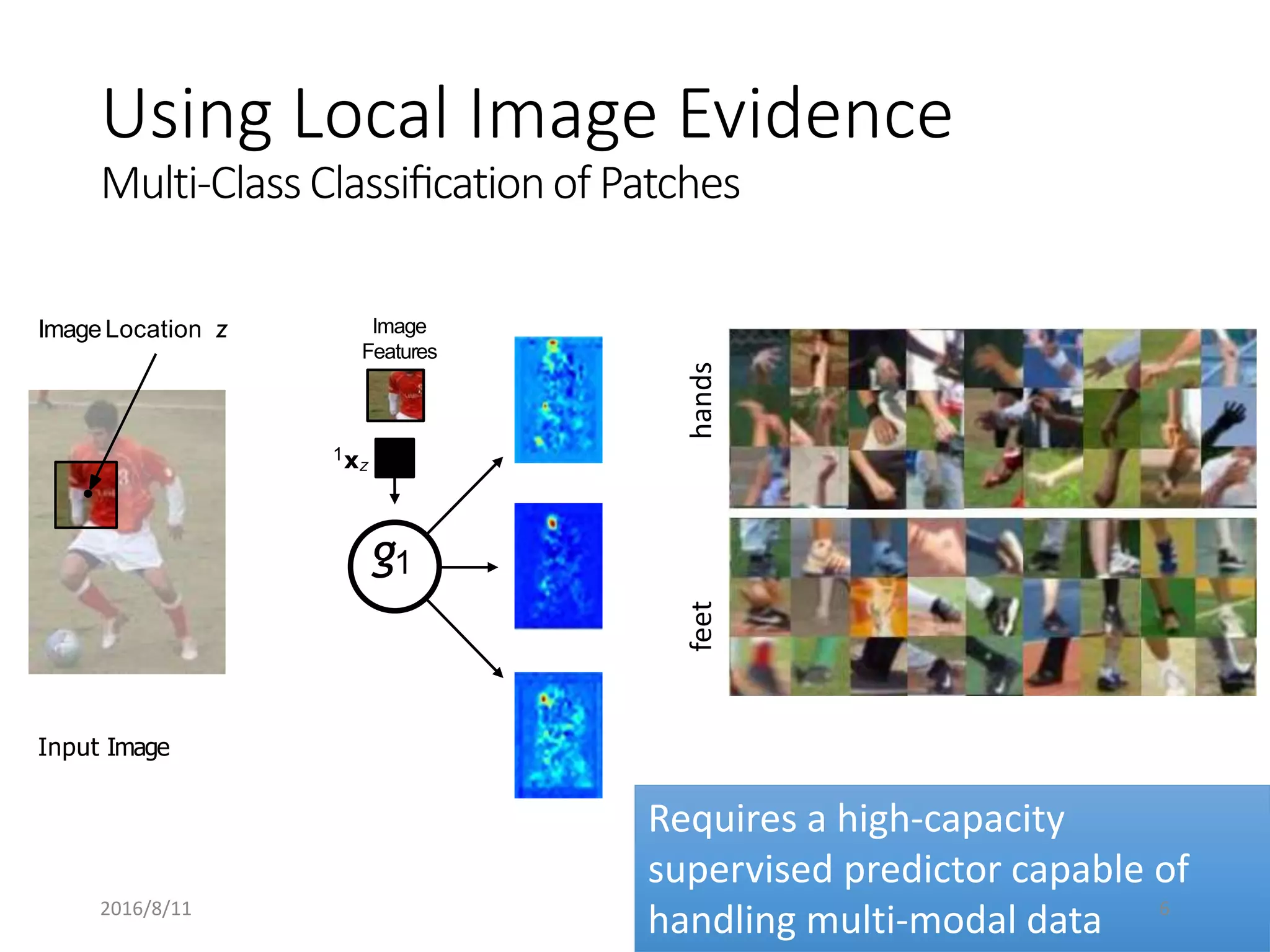
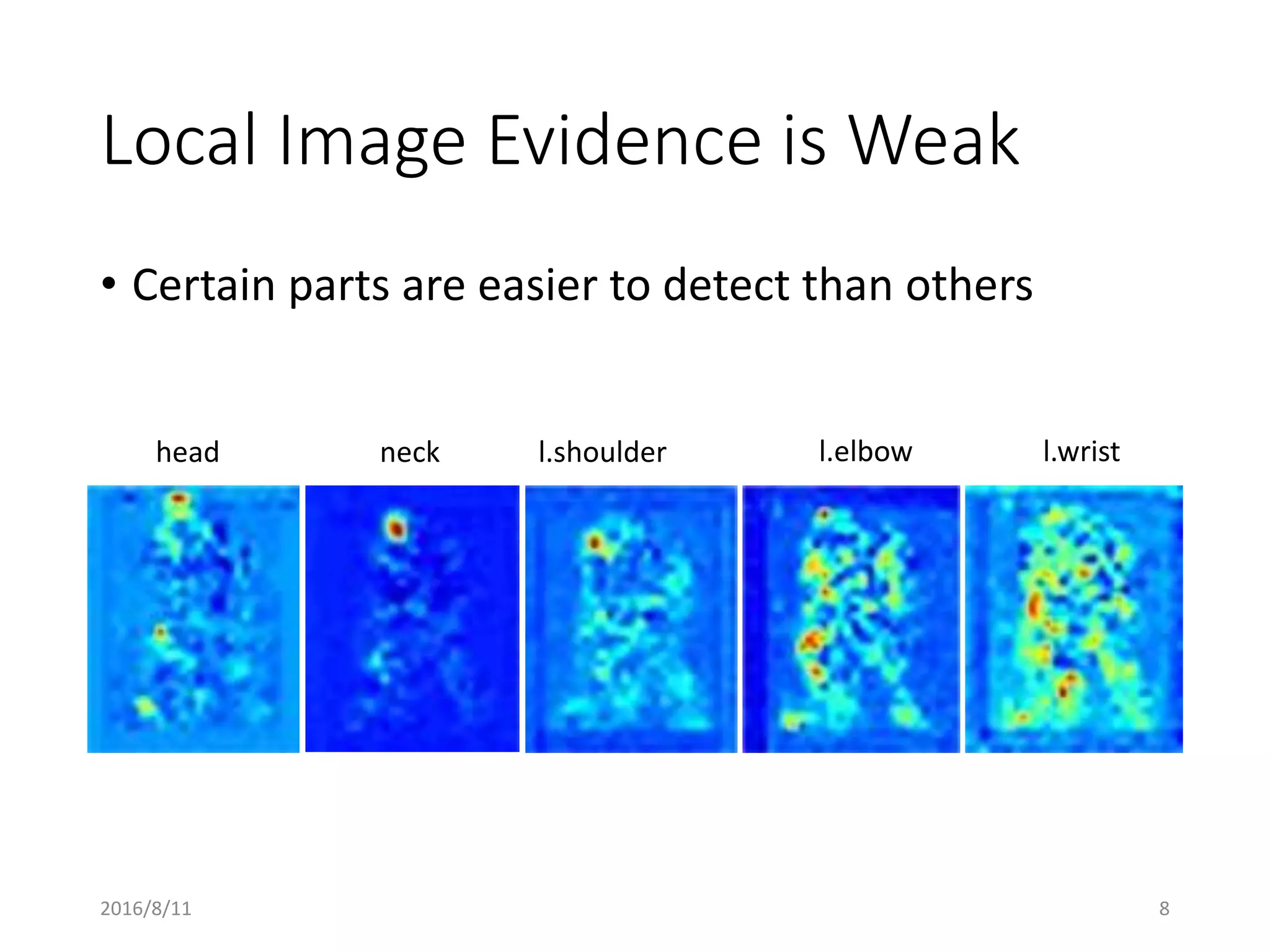
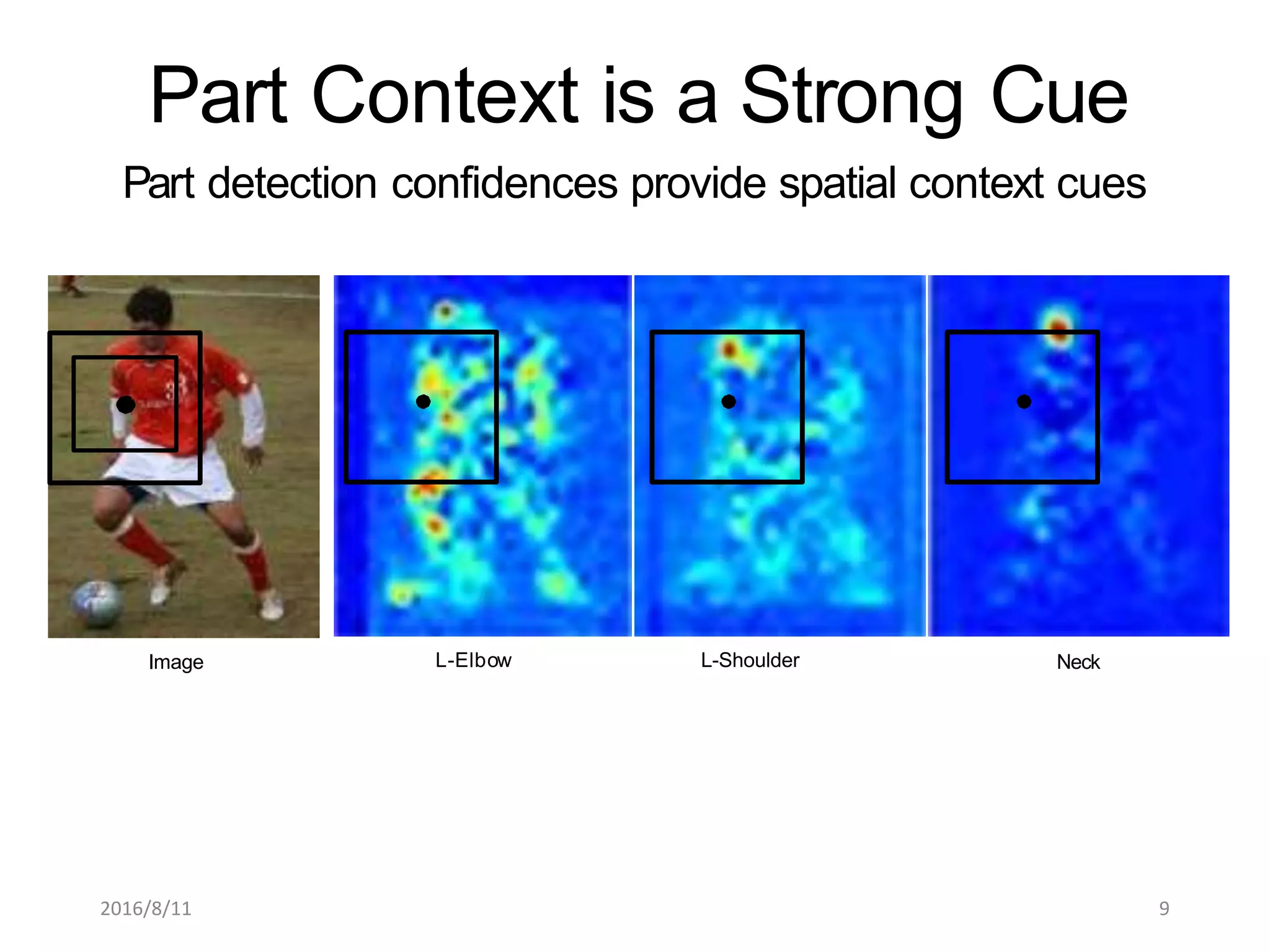
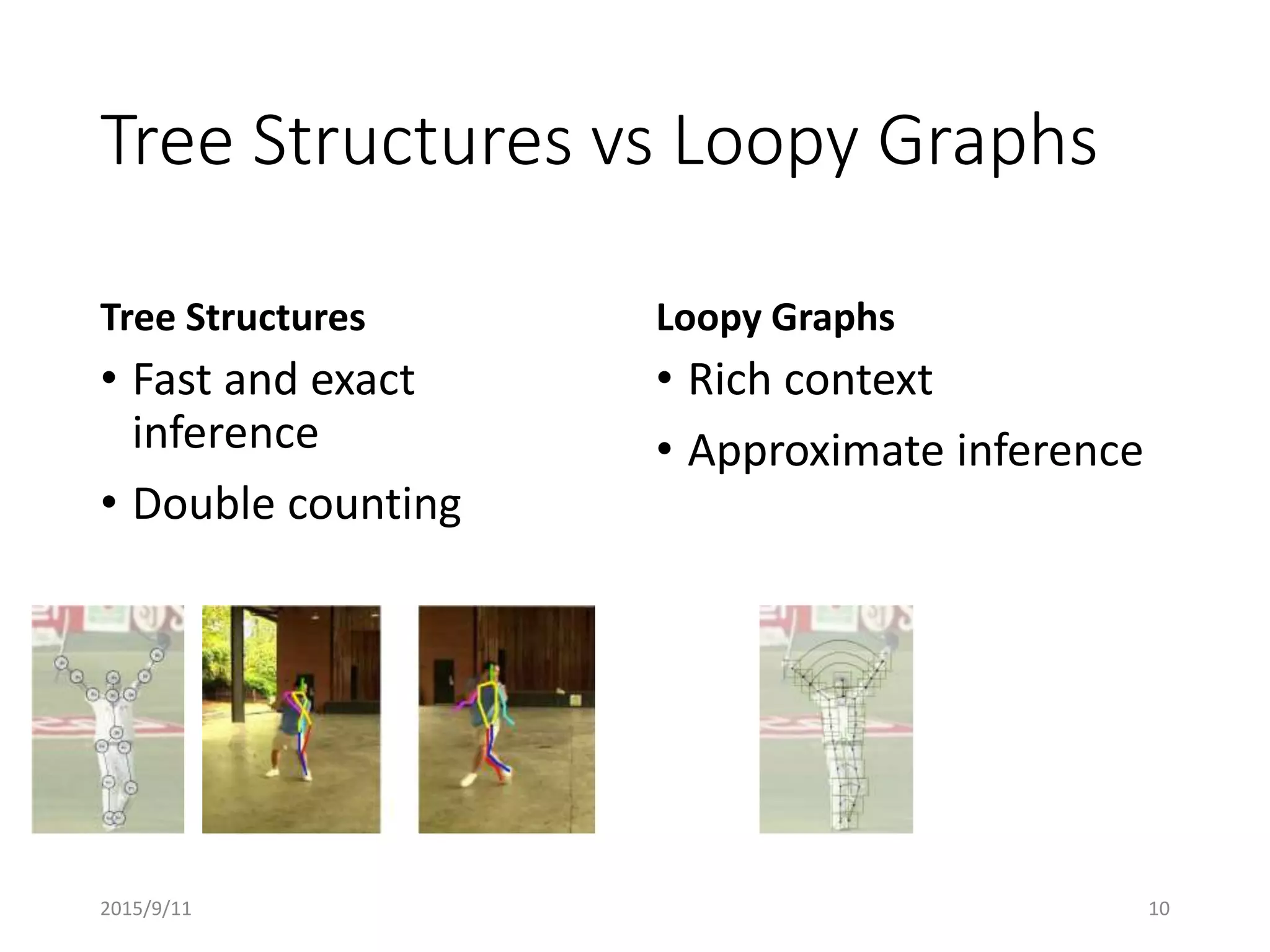
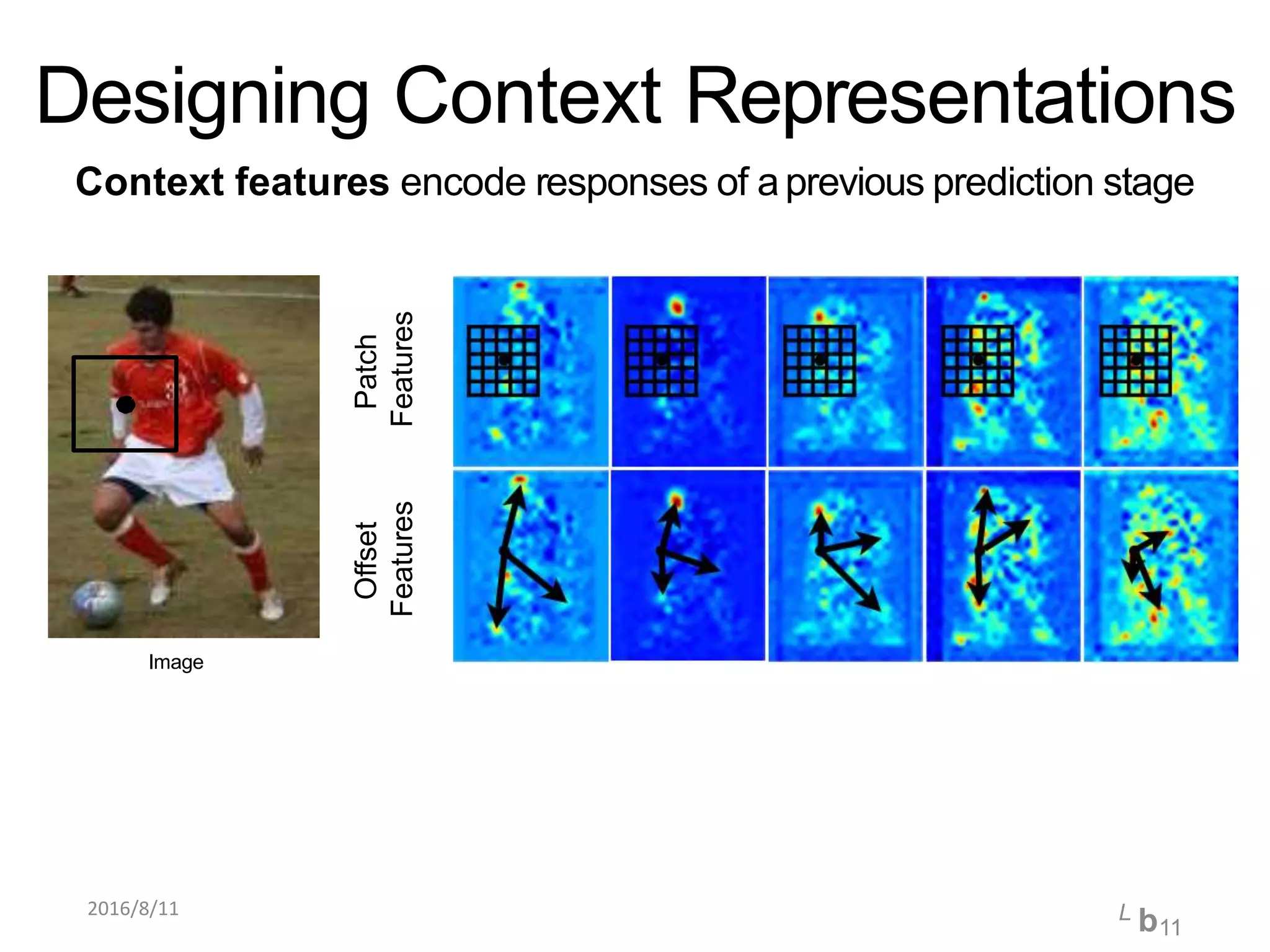
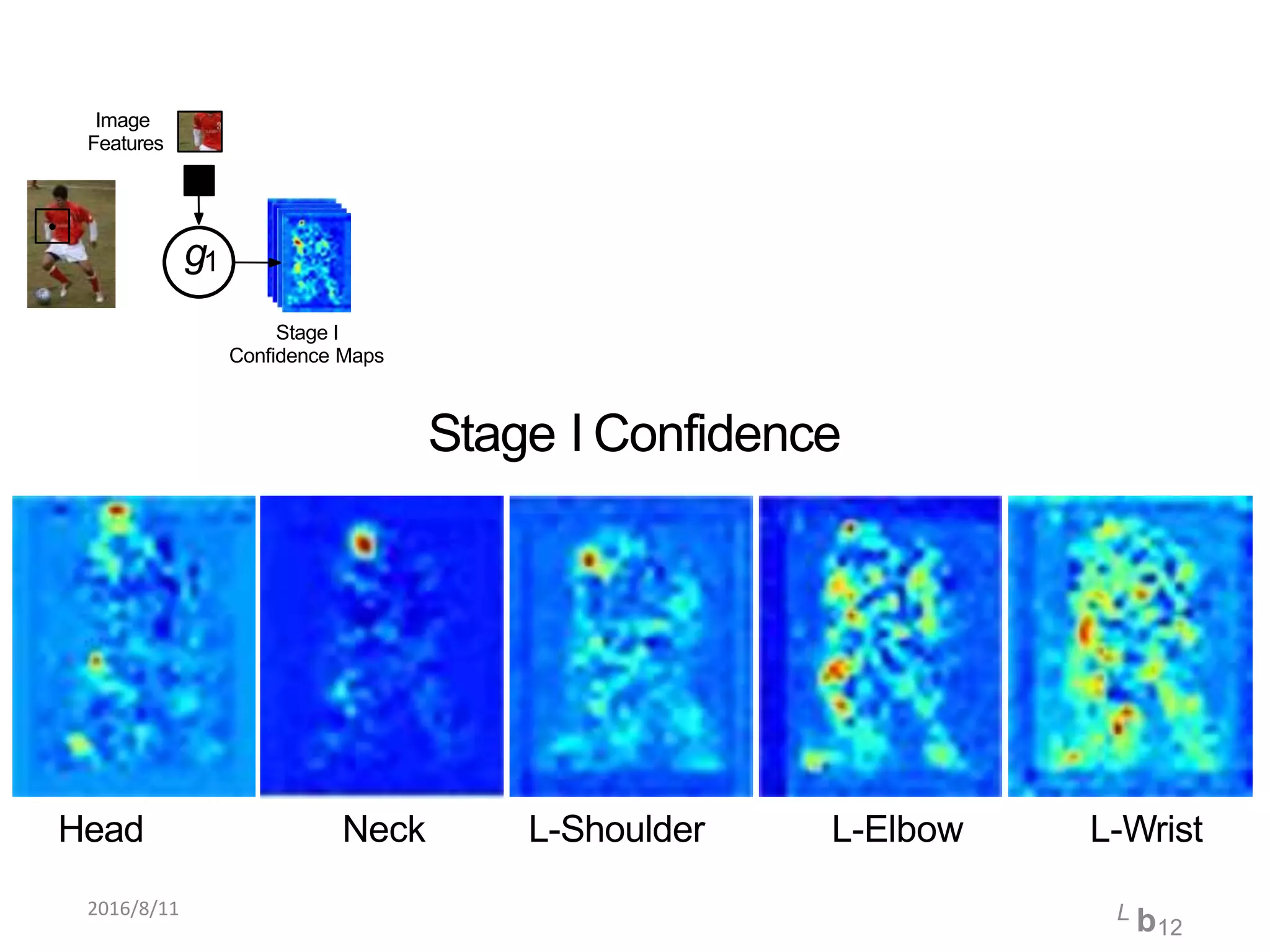
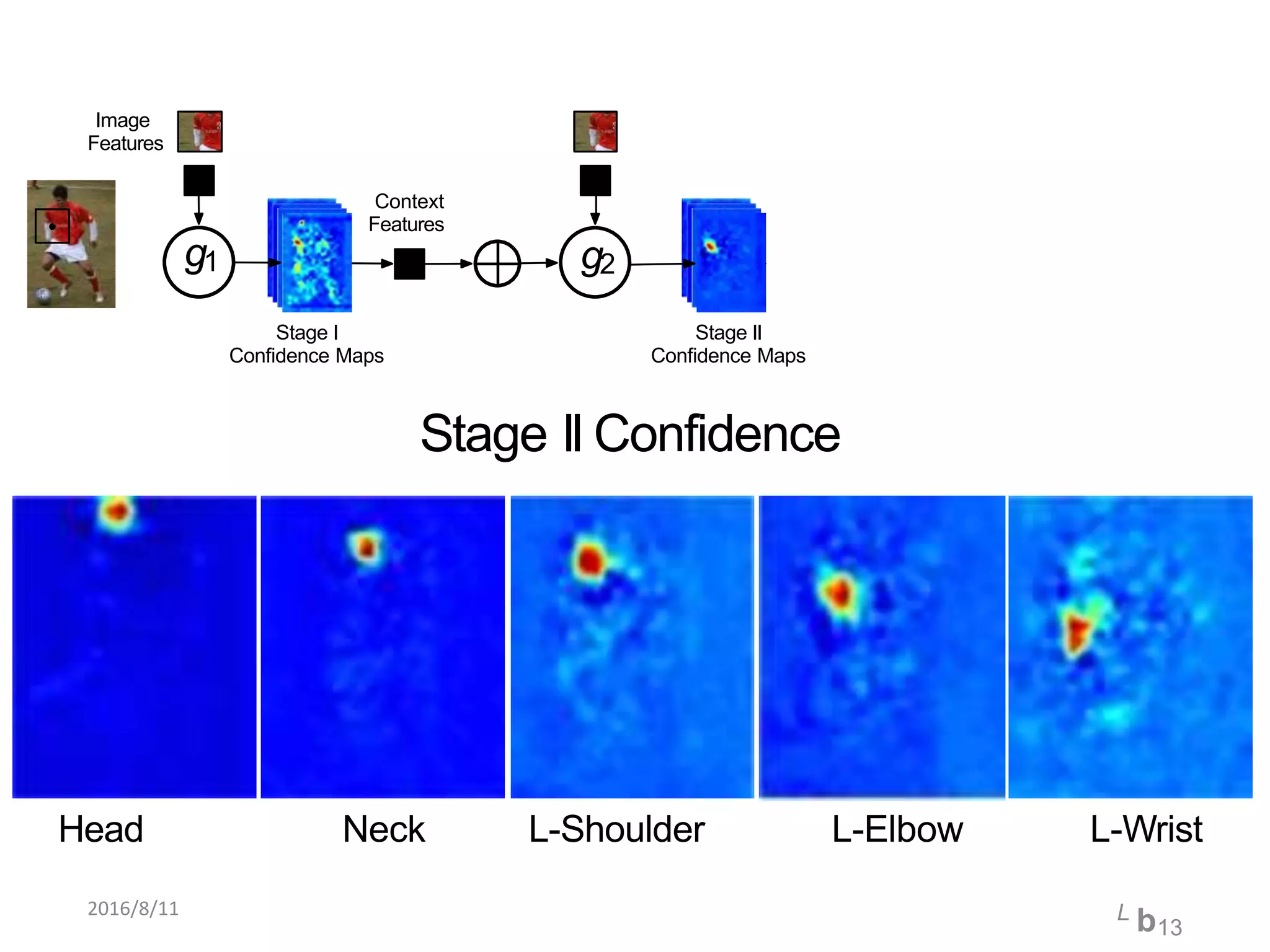
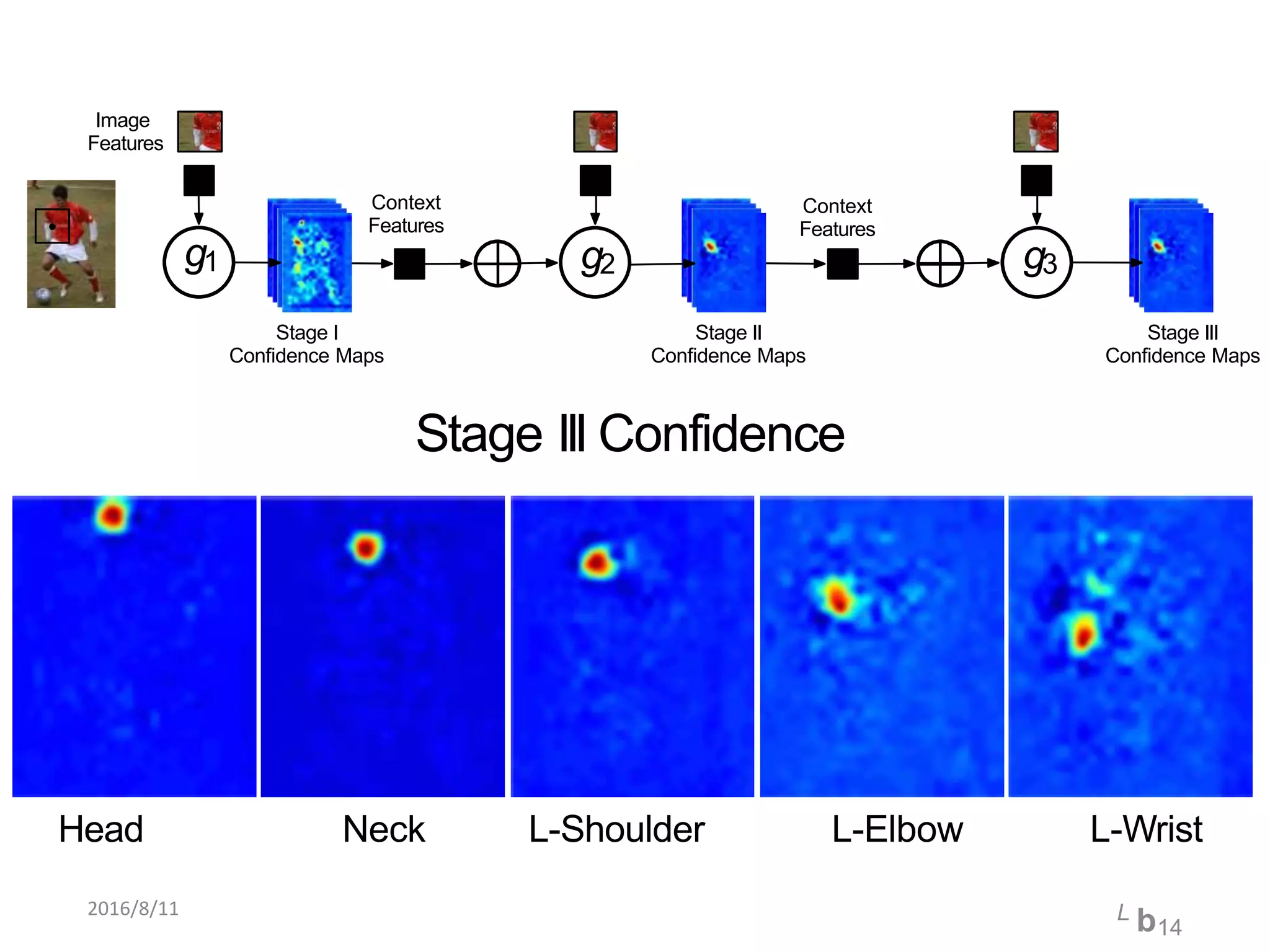
Pose Machines is a method for estimating articulated human pose from images using convolutional neural networks. It uses a multi-stage approach where each stage predicts confidence maps for body parts using features from the previous stage. This allows the model to incorporate strong contextual cues between related body joints across stages. Key aspects of the approach include using intermediate supervision to address vanishing gradients, large receptive fields to capture context, and hierarchical prediction of parts to leverage top-down cues. Evaluation on public datasets shows it achieves state-of-the-art performance for articulated human pose estimation from single images.





![Level 1 parts Level 2 poselet Level 3 full body
[Bourdev et al., CVPR2009][Sun et al., CVPR2012]
[Duan et al., BMVC 2012][Singh et al., ECCV2012]
[Pishchulin et al., CVPR2013] etc.
Top Down Cues are Helpful
Larger Composite Parts can be Easier to detect
2016/8/11 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tq68lz9qhyorqndxpv5w-signature-54f17826ed7e29e13653ed835b10fabd79d8e26ac84412798c7e96ef7d109006-poli-160811023645/75/Pose-Machine-15-2048.jpg)