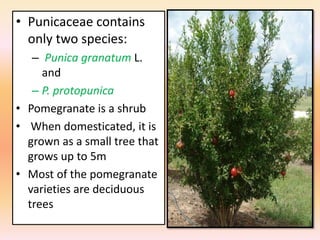
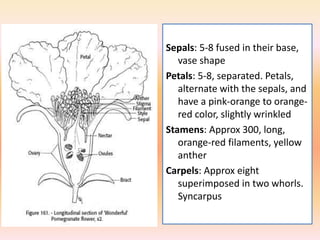
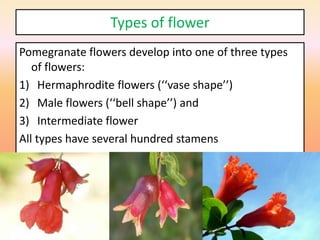
The document summarizes the morphology of pomegranate flowers. Pomegranate flowers can be solitary, paired, or clustered on branches. They are odorless but colorful, ranging from 5-9cm in length. There are three types of pomegranate flowers: hermaphrodite flowers which are fertile and self-pollinating; male flowers which are infertile and drop without fruit set; and intermediate flowers which have variable fertility. The percentage of hermaphrodite flowers impacts fruit yield potential, with Indian cultivars ranging from 53-80% hermaphrodite flowers. Pomegranate flower drop can occur due to pollination, pests, disease, environmental stresses like