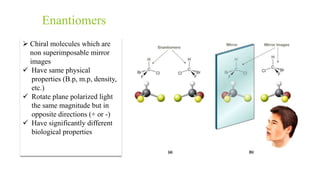
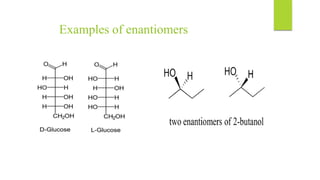
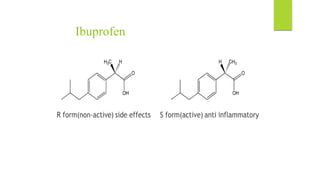
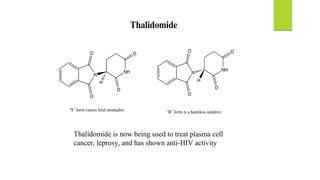
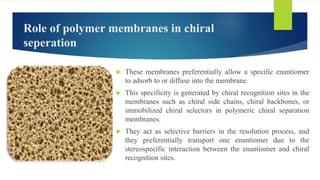
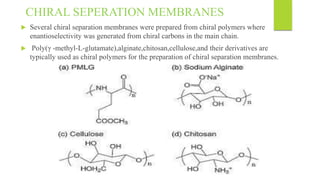
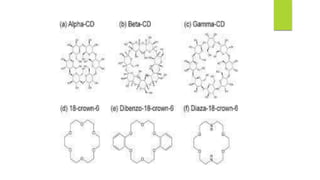
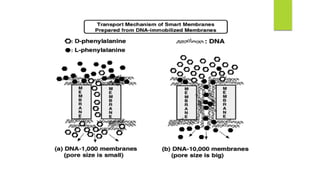
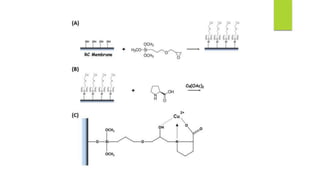
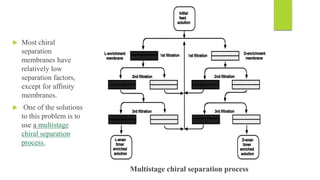
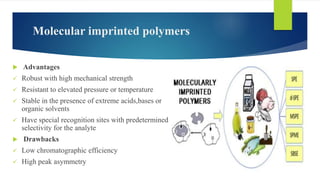
This document discusses separation of enantiomers using polymer membranes. It notes that enantiomers often have different biological properties and one may be active while the other causes side effects. Polymer membranes can separate enantiomers using chiral recognition sites. Common polymers used include poly(γ-methyl-L-glutamate) and cyclodextrins immobilized in the membrane. The document also discusses mechanisms of separation and examples of separating amino acids and drugs using membranes.