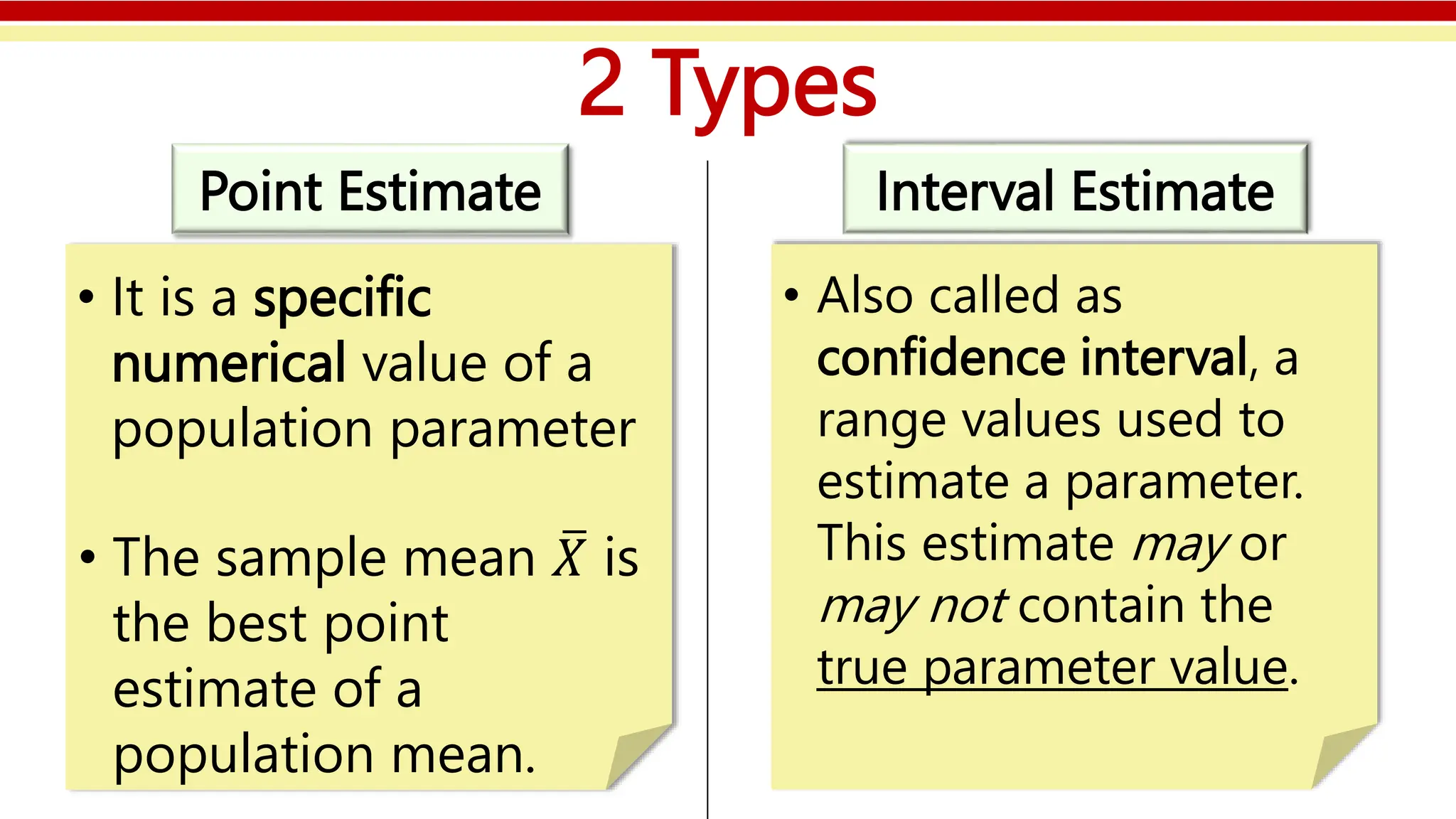
The document discusses the concepts of point and interval estimates in statistics, detailing how population parameters can be estimated from sample data. It explains two methods for calculating interval estimates: one when the population standard deviation is known, and another using the Student’s t-distribution when it is unknown. Additionally, the document includes examples and step-by-step procedures for finding point and interval estimates based on given sample data.




















![ESTIMATING SAMPLE SIZE
In order to determine the sample size we follow
the formula:
n = [
𝑍𝑎
2
σ
𝐸
]2
Where;
n = sample size
𝒁𝒂
𝟐
= Z values
E = margin error](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointandintervalestimate-240429044624-de7d83bd/75/Point-and-Interval-Estimate-by-regi-pptx-23-2048.jpg)
![ESTIMATING SAMPLE SIZE
In order to determine the sample size we follow
the formula:
n = [
𝑍𝑎
2
σ
𝐸
]2
Where;
n = sample size
𝒁𝒂
𝟐
= Z values
E = margin error](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointandintervalestimate-240429044624-de7d83bd/75/Point-and-Interval-Estimate-by-regi-pptx-24-2048.jpg)



