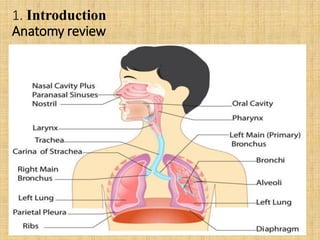
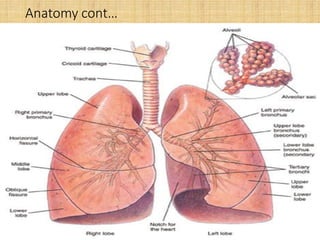
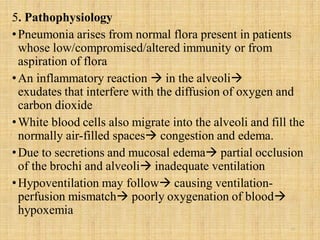
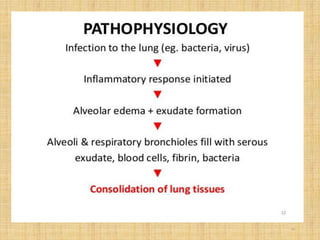
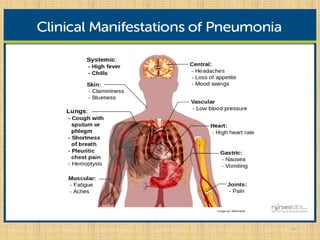
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It affects millions of people annually and can sometimes be fatal. The document discusses the epidemiology, classification, risk factors, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, complications, and nursing care plan for pneumonia patients. Key points include the different types of pneumonia based on location (community-acquired vs. hospital-acquired), causative agents, and patient risk factors. Proper diagnosis involves tests of sputum or other samples, along with chest imaging. Treatment focuses on antibiotics, respiratory support, fluids, rest, and patient education.