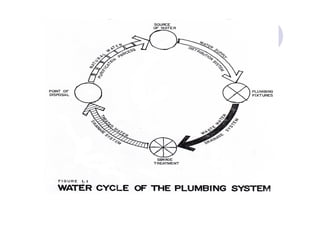
The document discusses the key elements of plumbing systems, including definitions of plumbing, plumbing systems, and their major components. It describes the roles of plumbers and the different categories of plumbers. It also outlines the National Plumbing Code of the Philippines, including its goals and 22 basic principles that govern plumbing design, installation, maintenance and sanitation requirements.