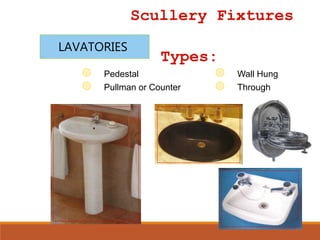
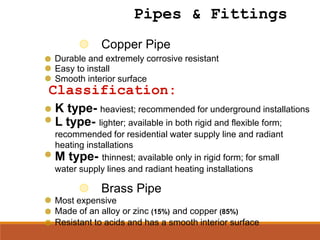
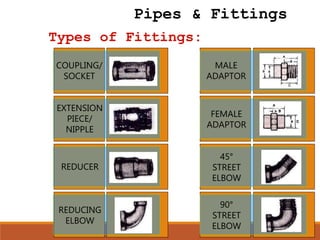
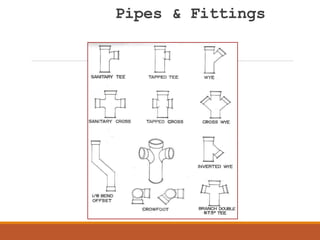
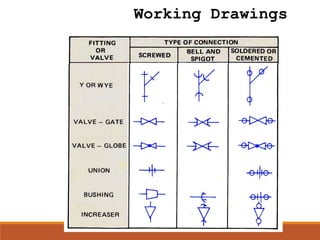
This document defines plumbing and provides a history and overview of plumbing practices in the Philippines. It discusses the definition of plumbing, key events in establishing plumbing codes and regulations, and the 22 basic principles of the plumbing code. It also describes common plumbing fixtures like water closets, urinals, kitchen sinks, and lavatories. Finally, it outlines the plumbing cycle and flow of water and waste through supply, distribution, use, collection, treatment and disposal.