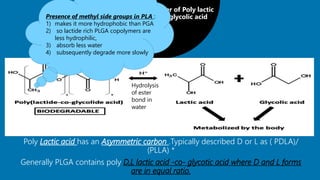
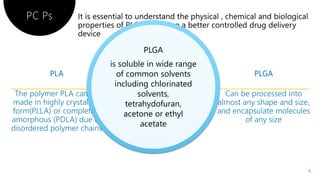
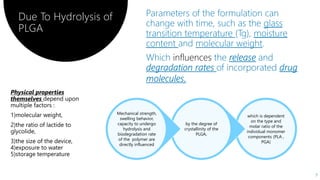
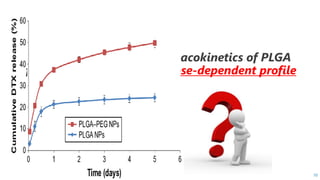
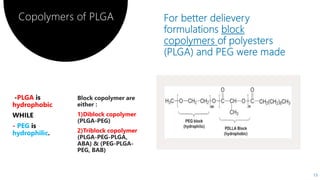
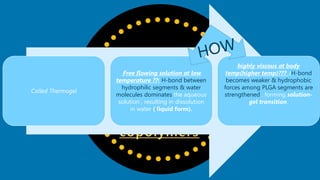
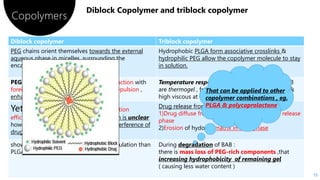
PLGA is a biodegradable and FDA-approved copolymer of poly lactic acid and poly glycolic acid. It is commonly used as a carrier for drug delivery due to its biodegradability and ability to tune degradation kinetics by adjusting the lactic acid to glycolic acid ratio. The document discusses the types of biodegradable polymers including synthetic polymers like PLGA and natural polymers. It explains that PLGA degradation is dependent on hydrolysis and factors like crystallinity and molecular weight that influence properties. The pharmacokinetics of PLGA is non-linear and dose-dependent, and PLGA has been shown to accumulate in organs like the liver and spleen. Surface modification with polymers like PEG can