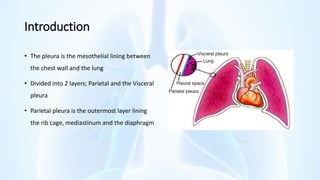
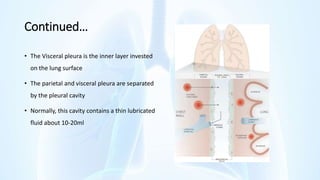
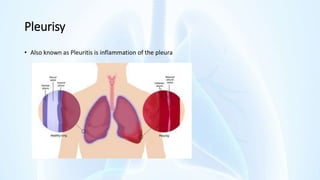
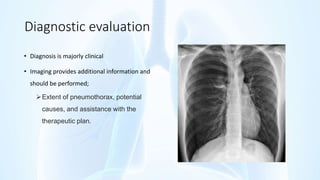
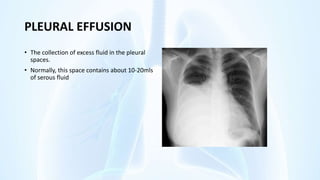
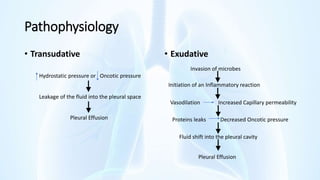
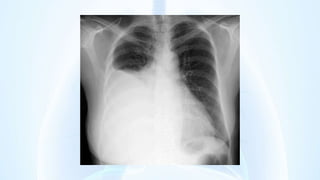
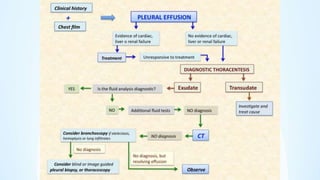
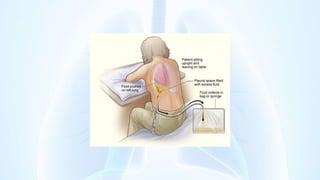
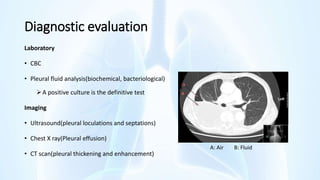
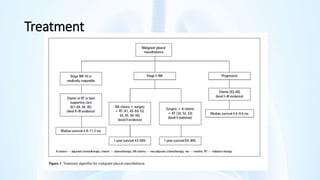
The document provides an overview of pleural diseases, specifically discussing pleurisy, pneumothorax, pleural effusion, empyema, and mesothelioma. It outlines the clinical presentations, diagnostic evaluations, and management strategies for these conditions, highlighting the importance of identifying underlying causes and appropriate treatments. Additionally, it covers the pathology, types, and complications associated with pleural disorders.