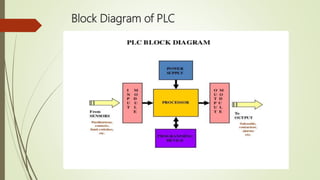
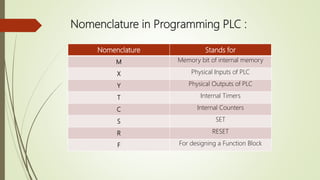
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), including their definition, functionality, and programming languages. It discusses the need for PLCs in automation, leading manufacturers, and both their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it highlights practical applications in various industries and explains various PLC components and logic structures.