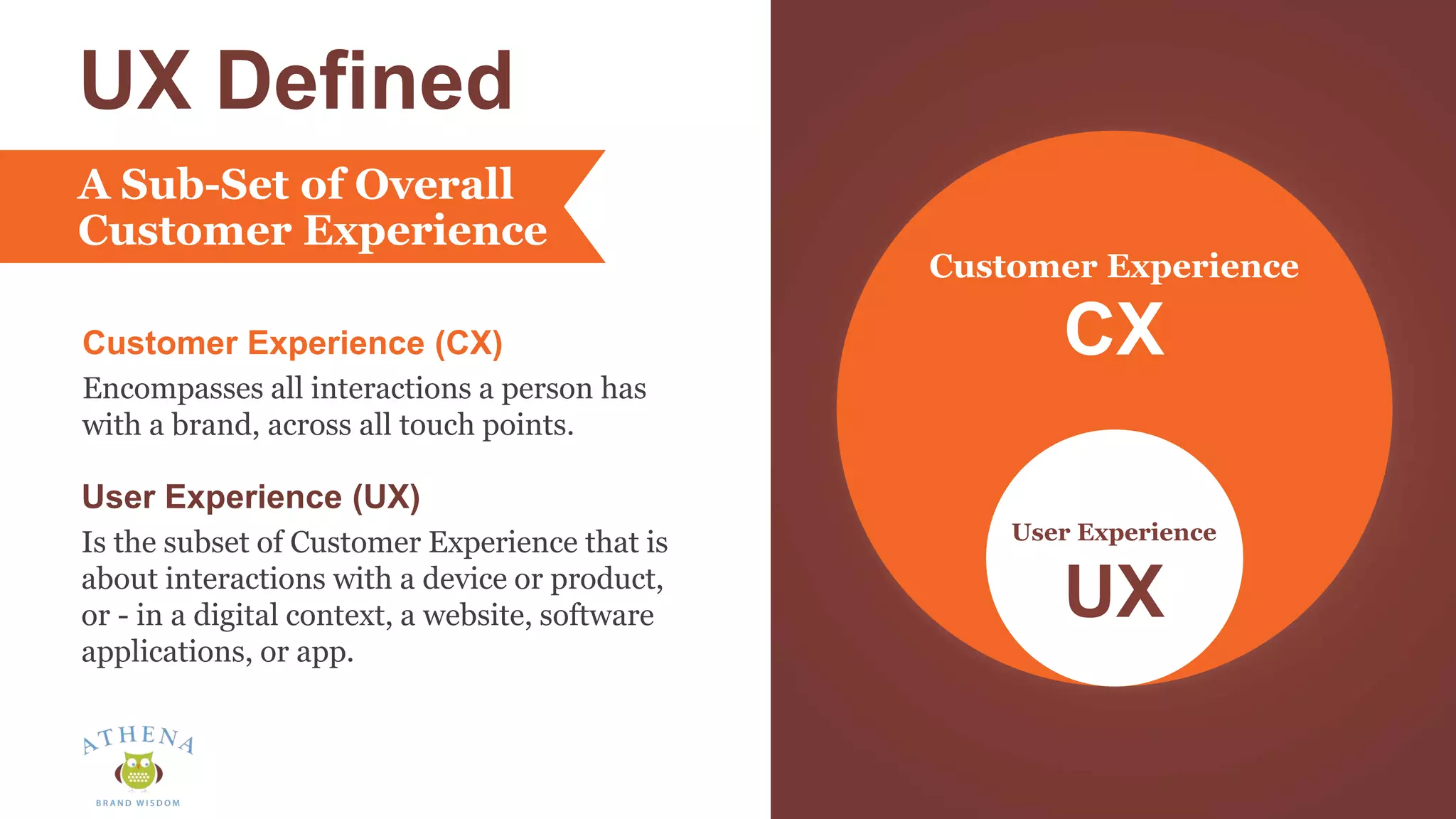
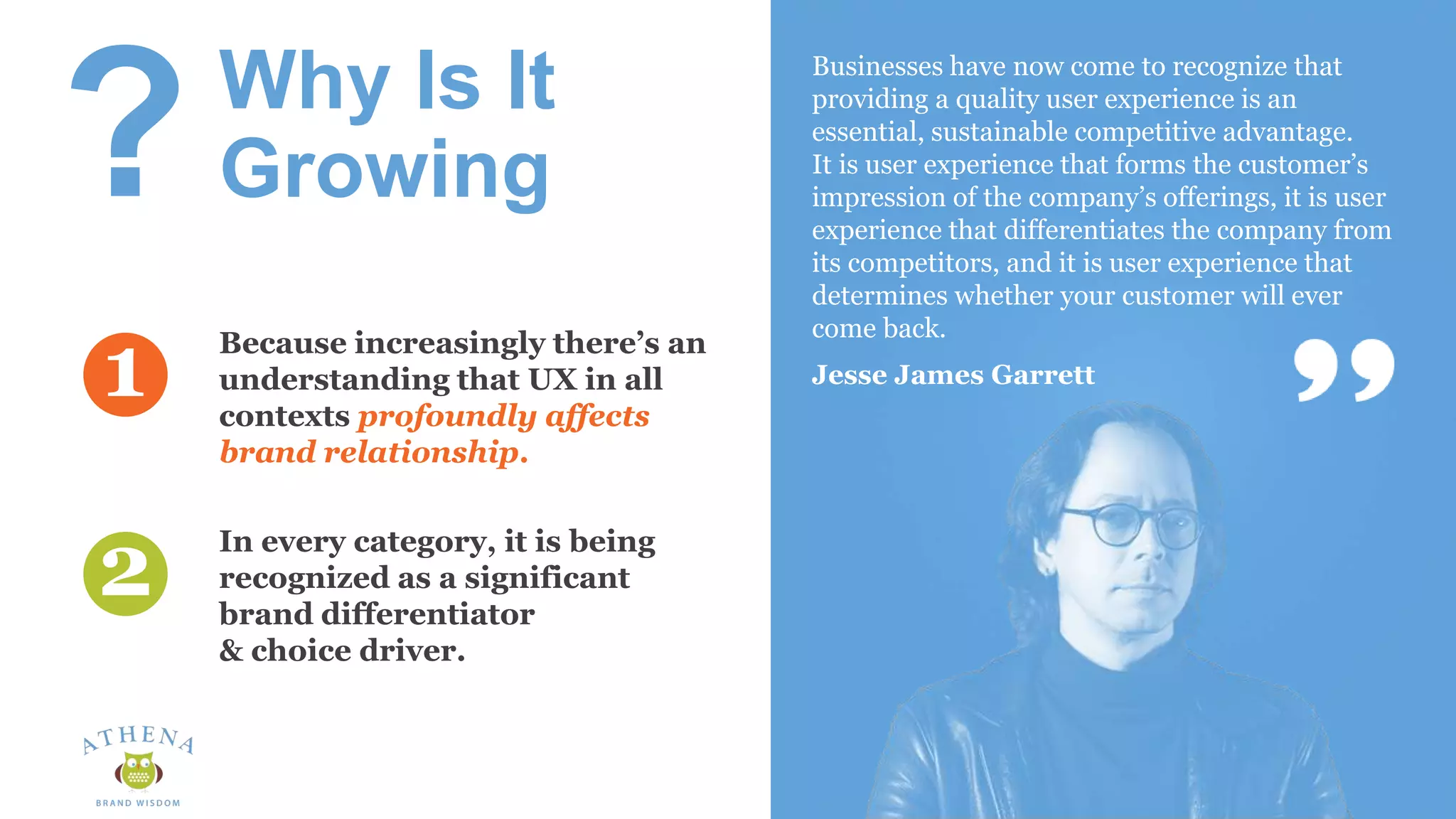
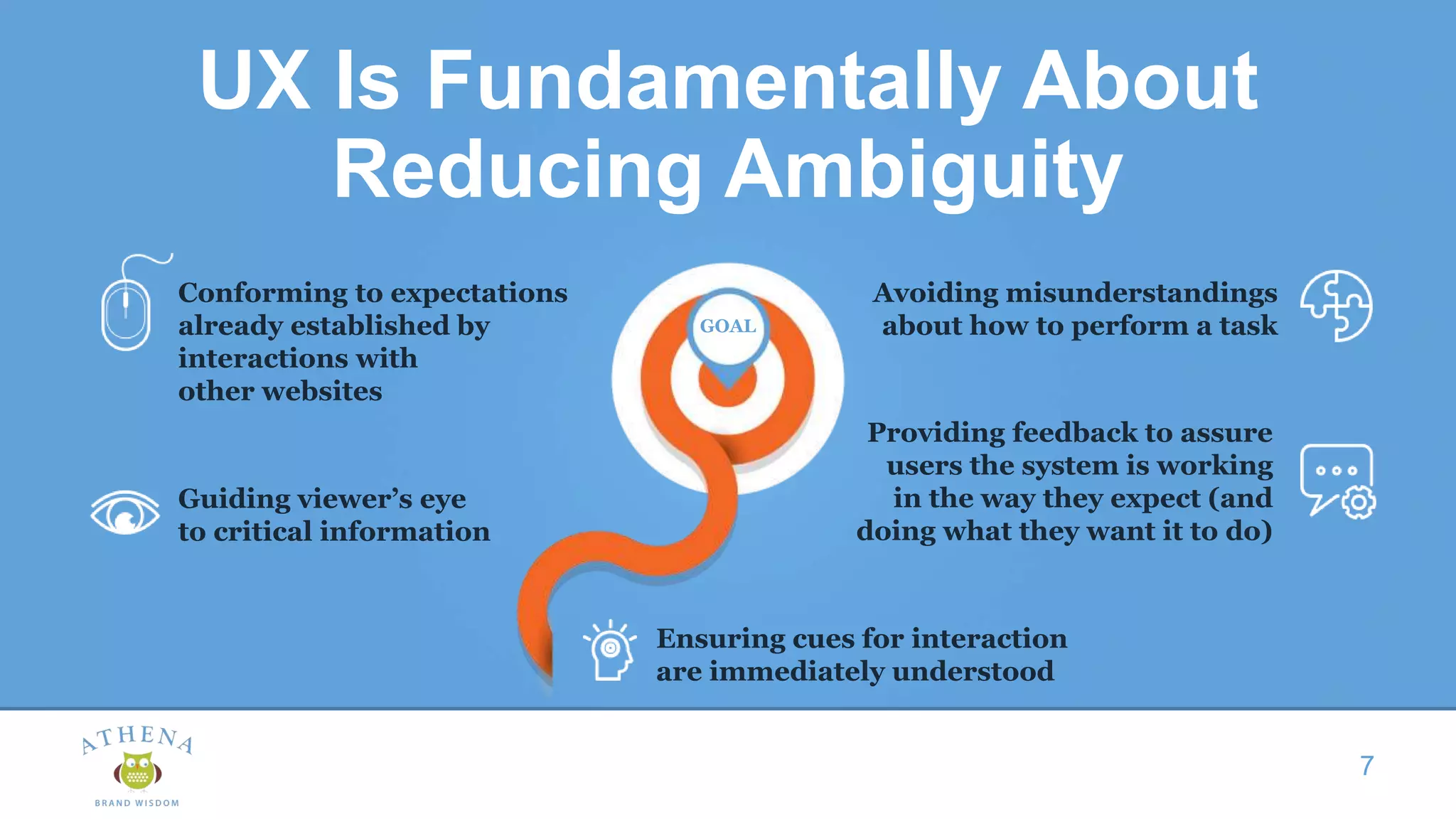
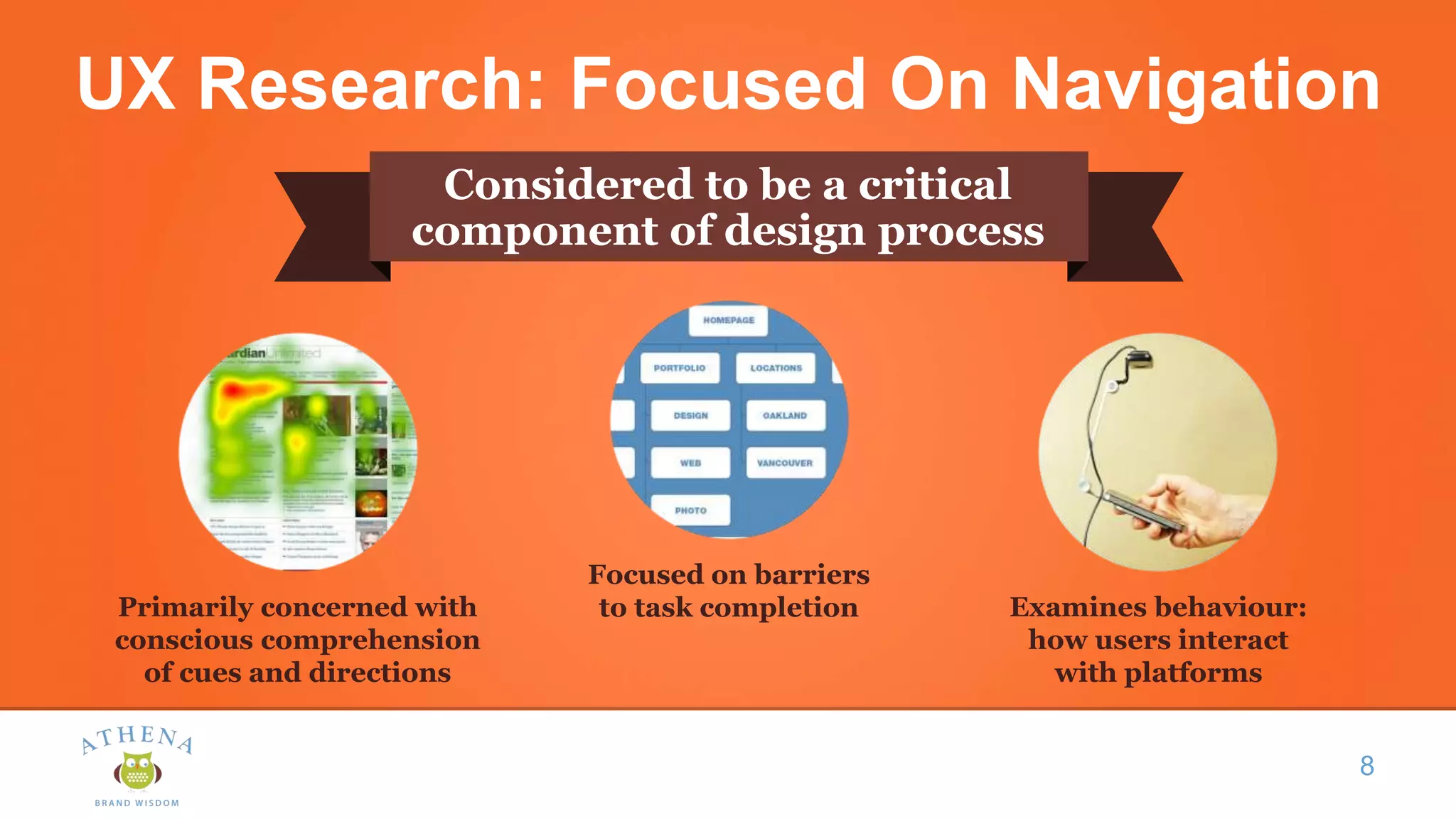
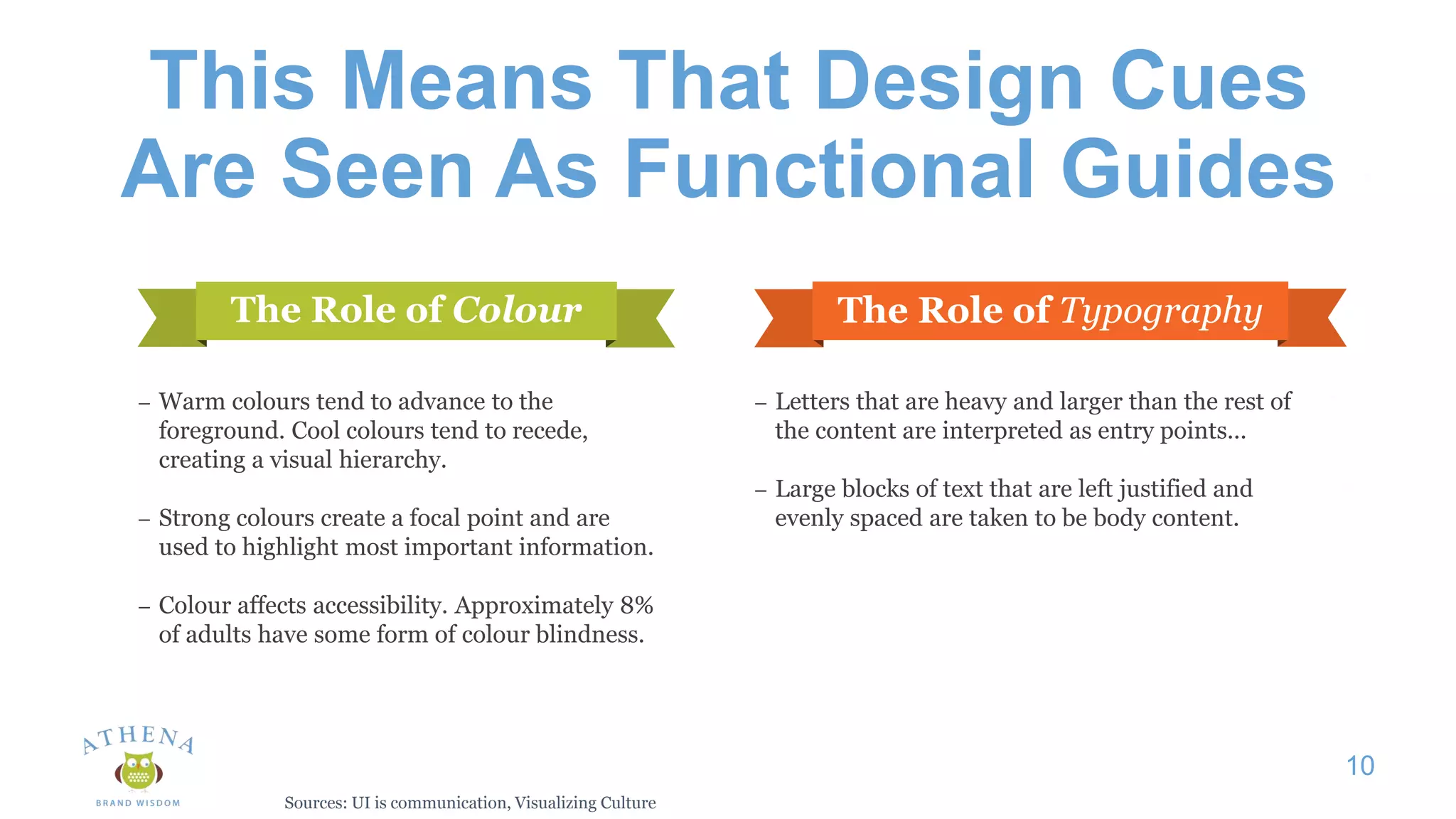
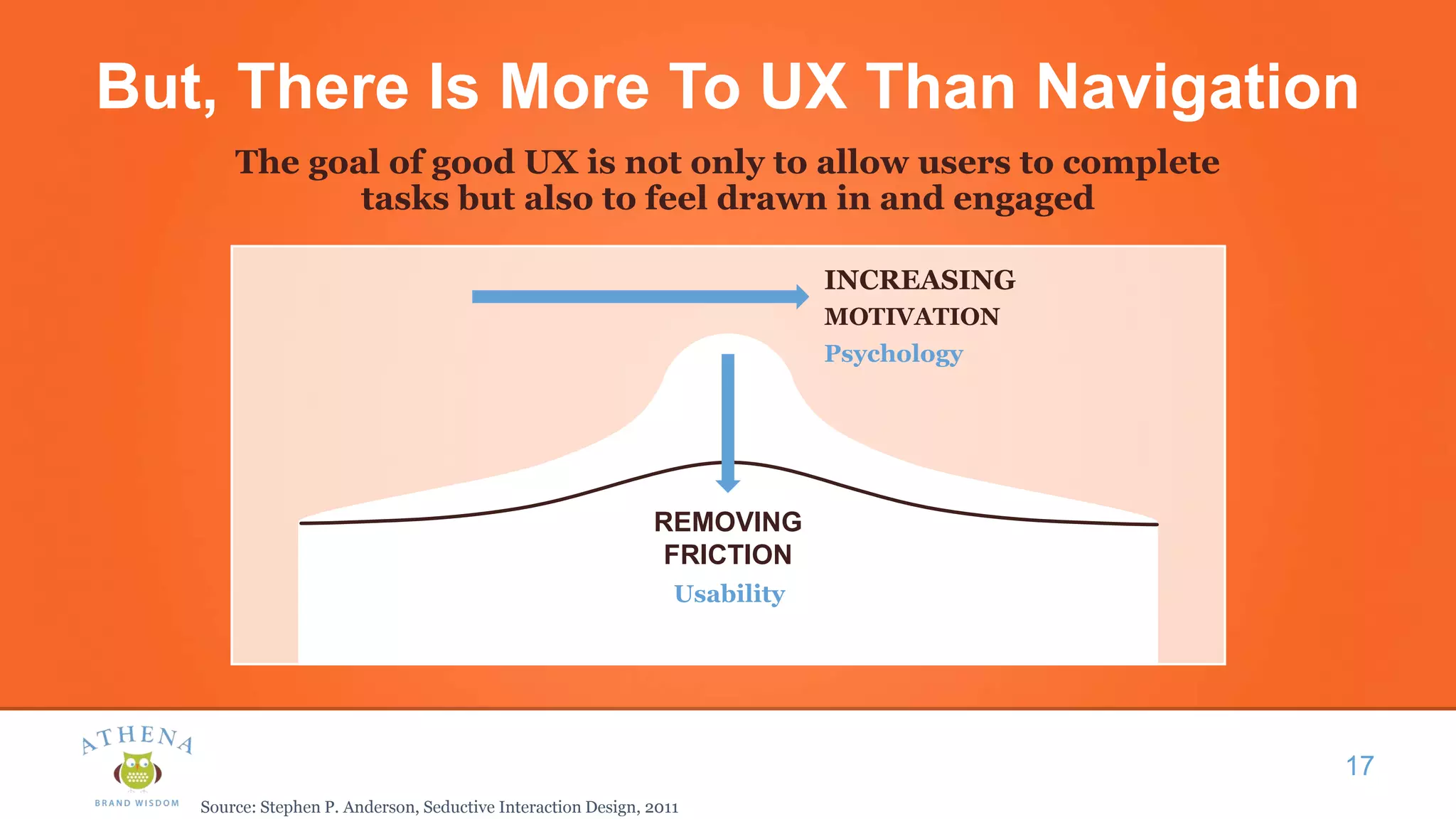
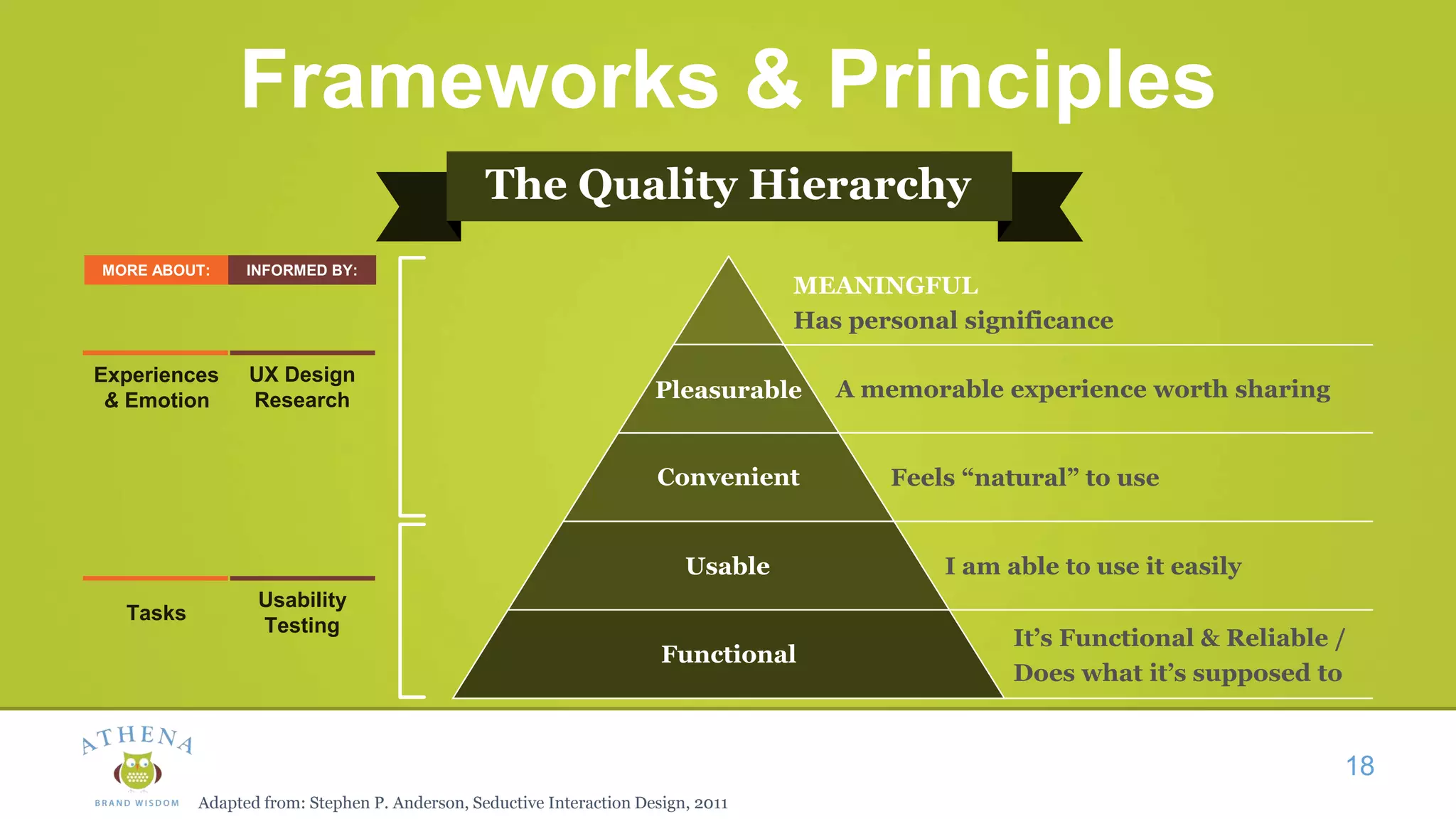
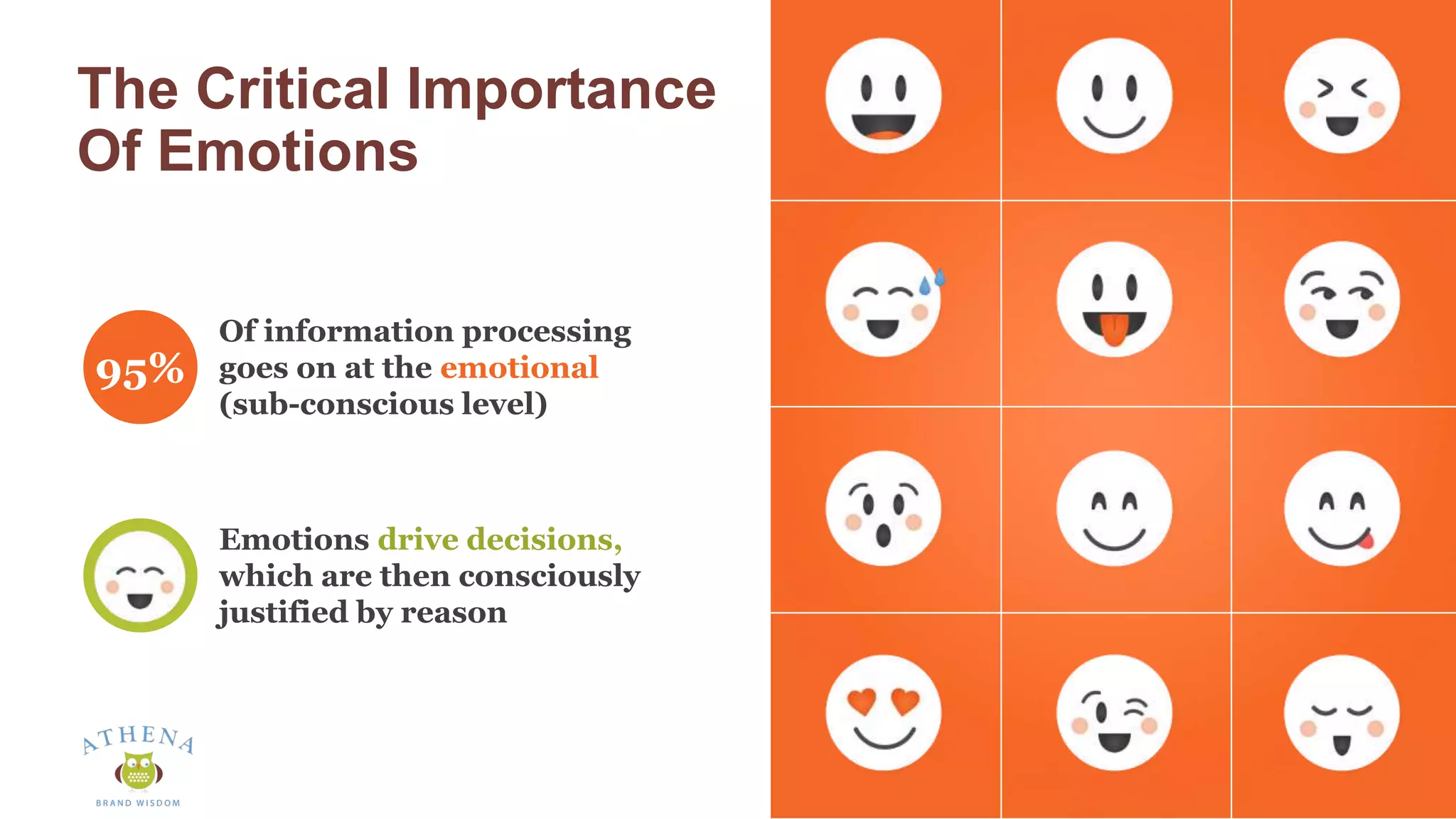
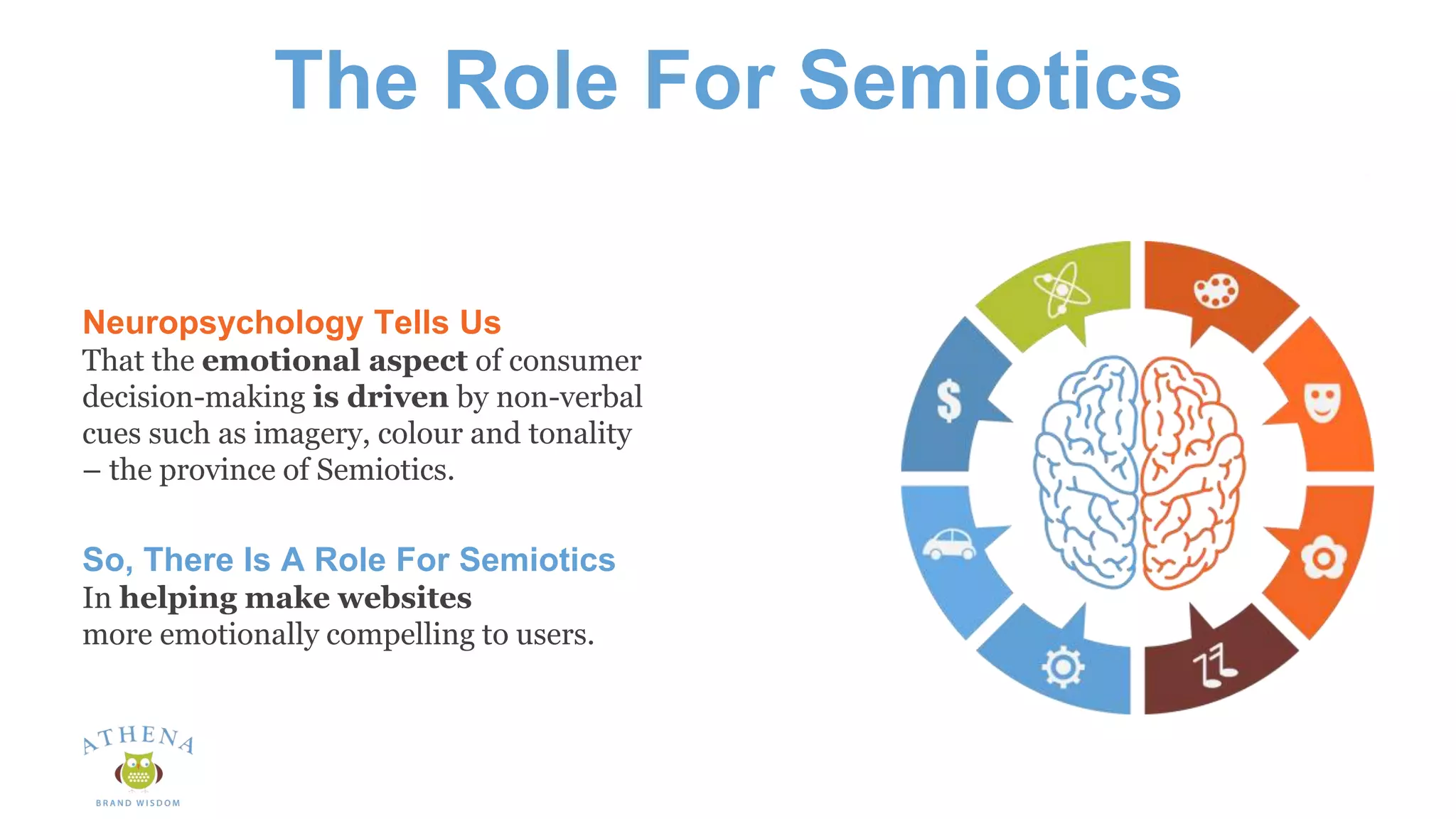
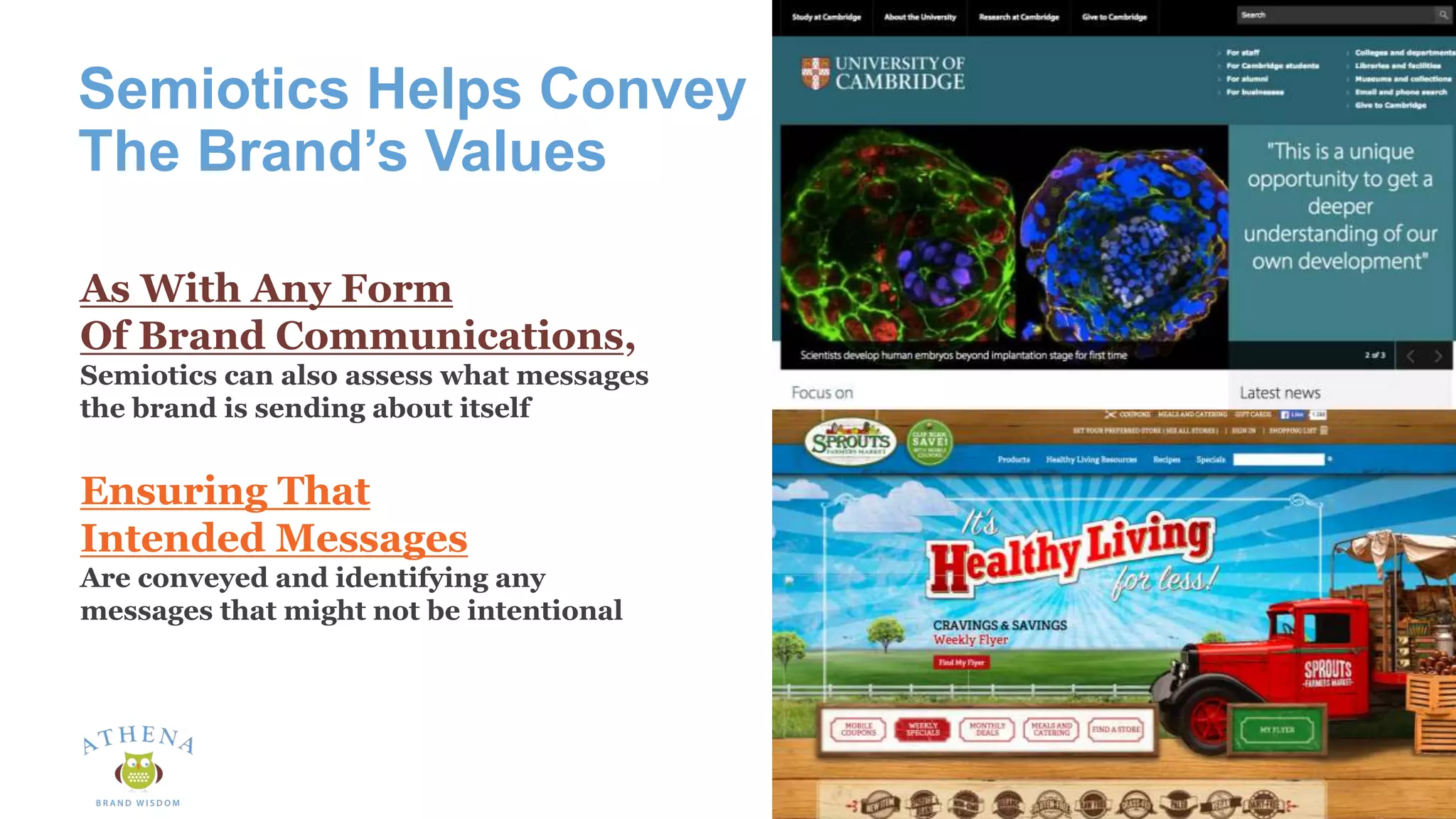
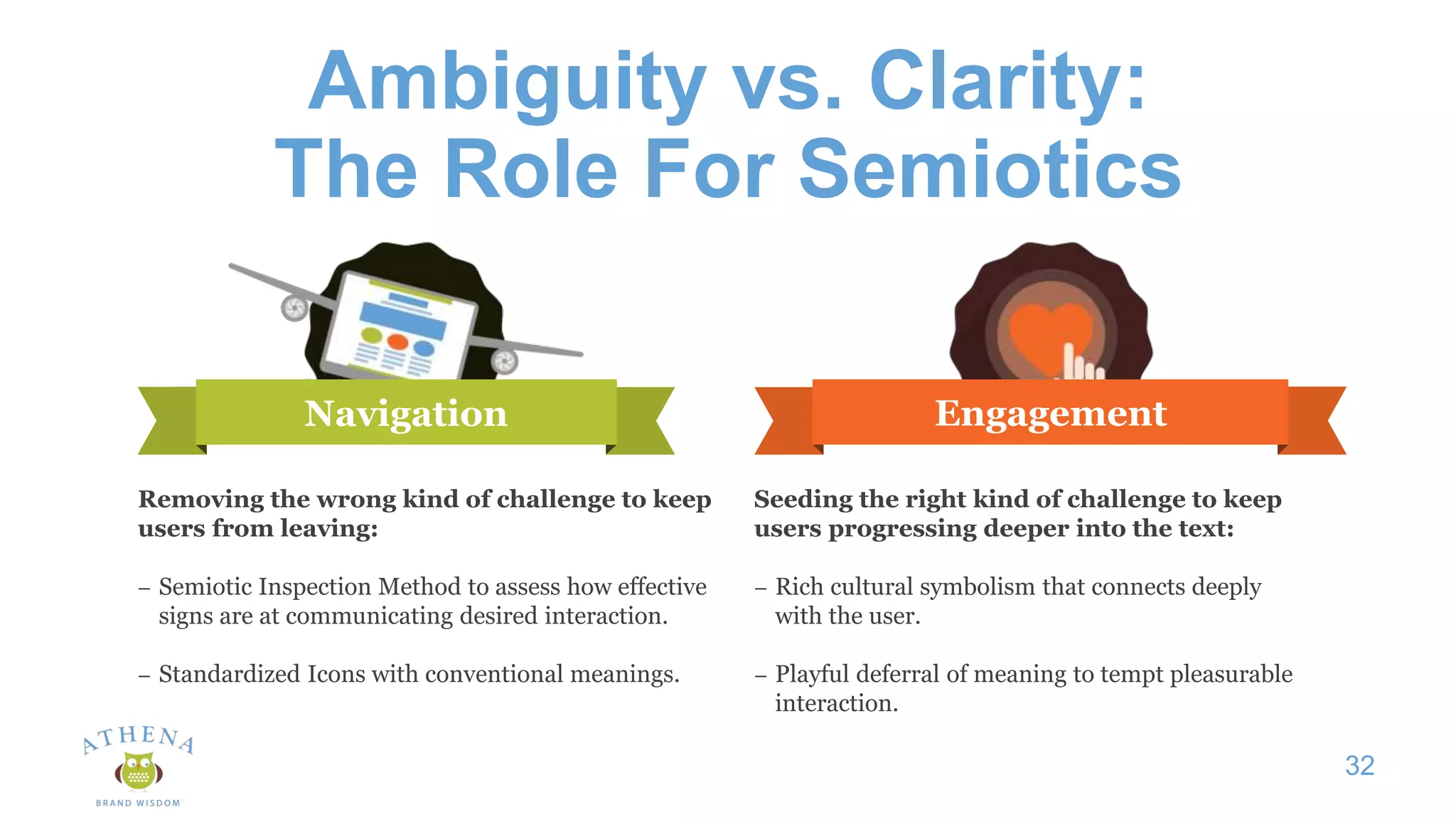
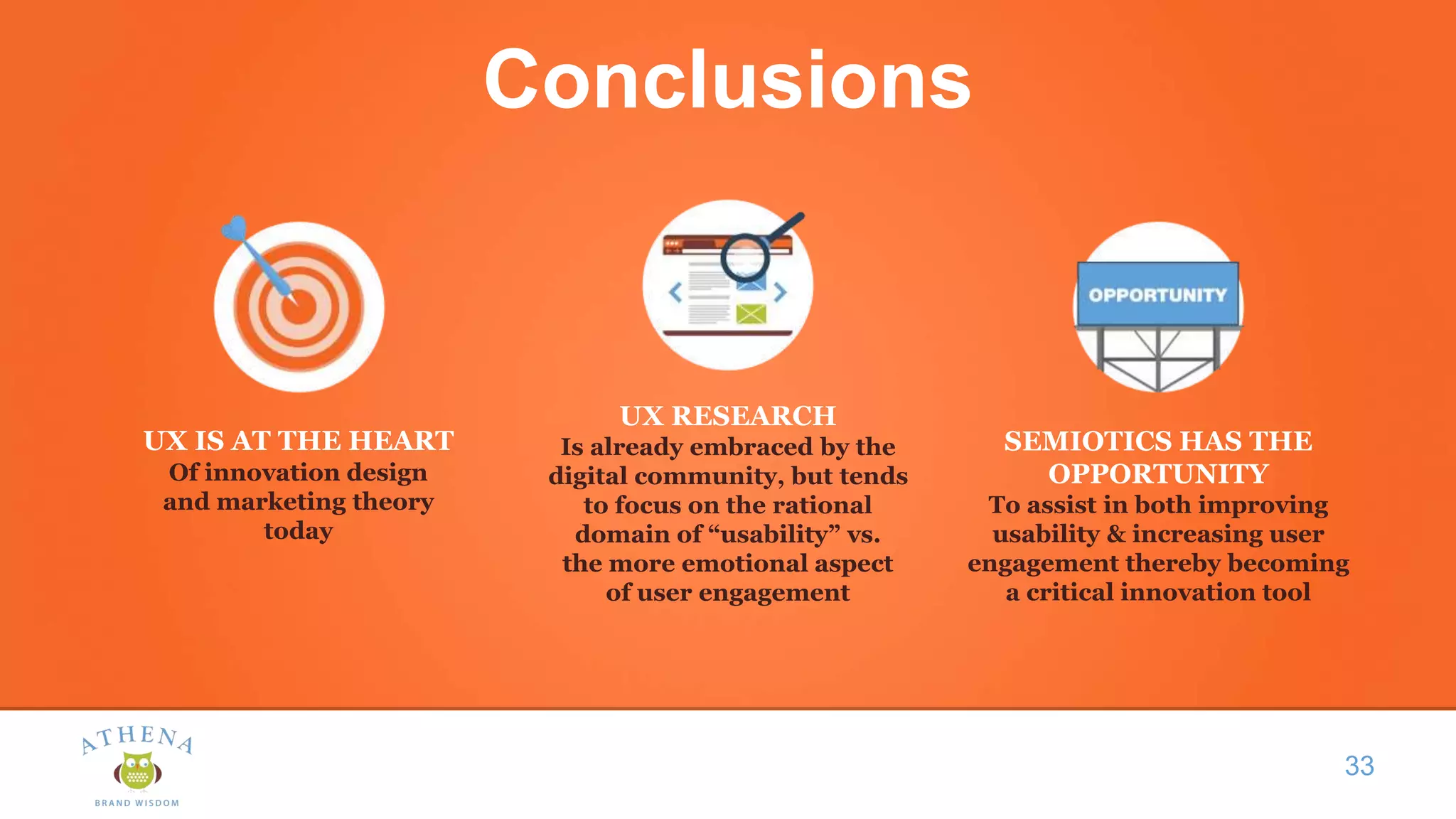
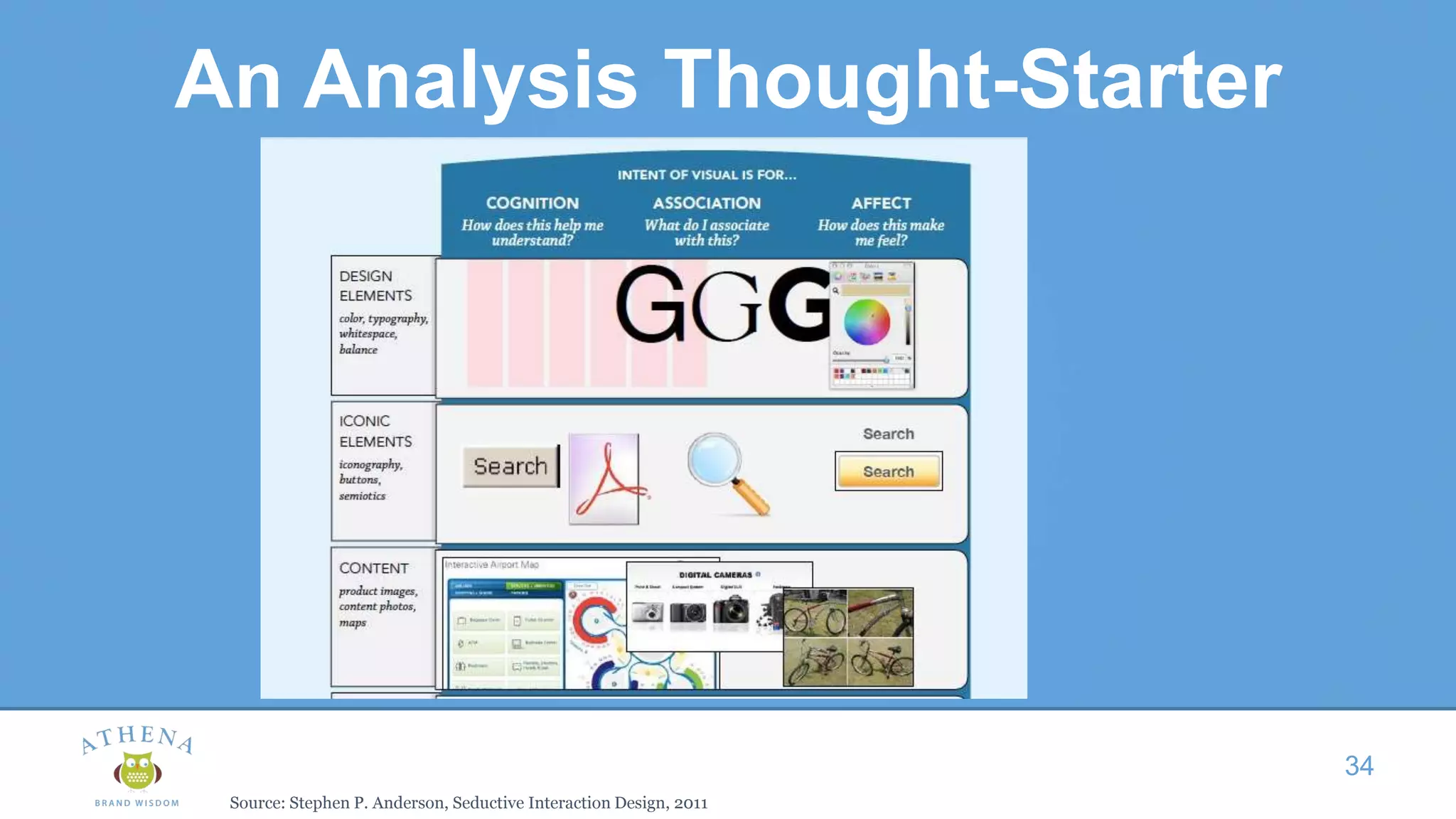
This document discusses the role of semiotics in digital user interface design. It begins by defining user experience (UX) and how UX focuses on reducing ambiguity and making interfaces self-evident. Semiotics can help evaluate how effectively interfaces communicate and convey culture. Navigation research examines user behavior and focuses on reducing barriers. However, good UX also aims to increase user engagement and motivation. Semiotics can help encode user personas and reflect cultural values to create a sense of play and pleasure in the interface. There is an interesting tension between ambiguity, which can create pleasure, and clarity, which is important for navigation.