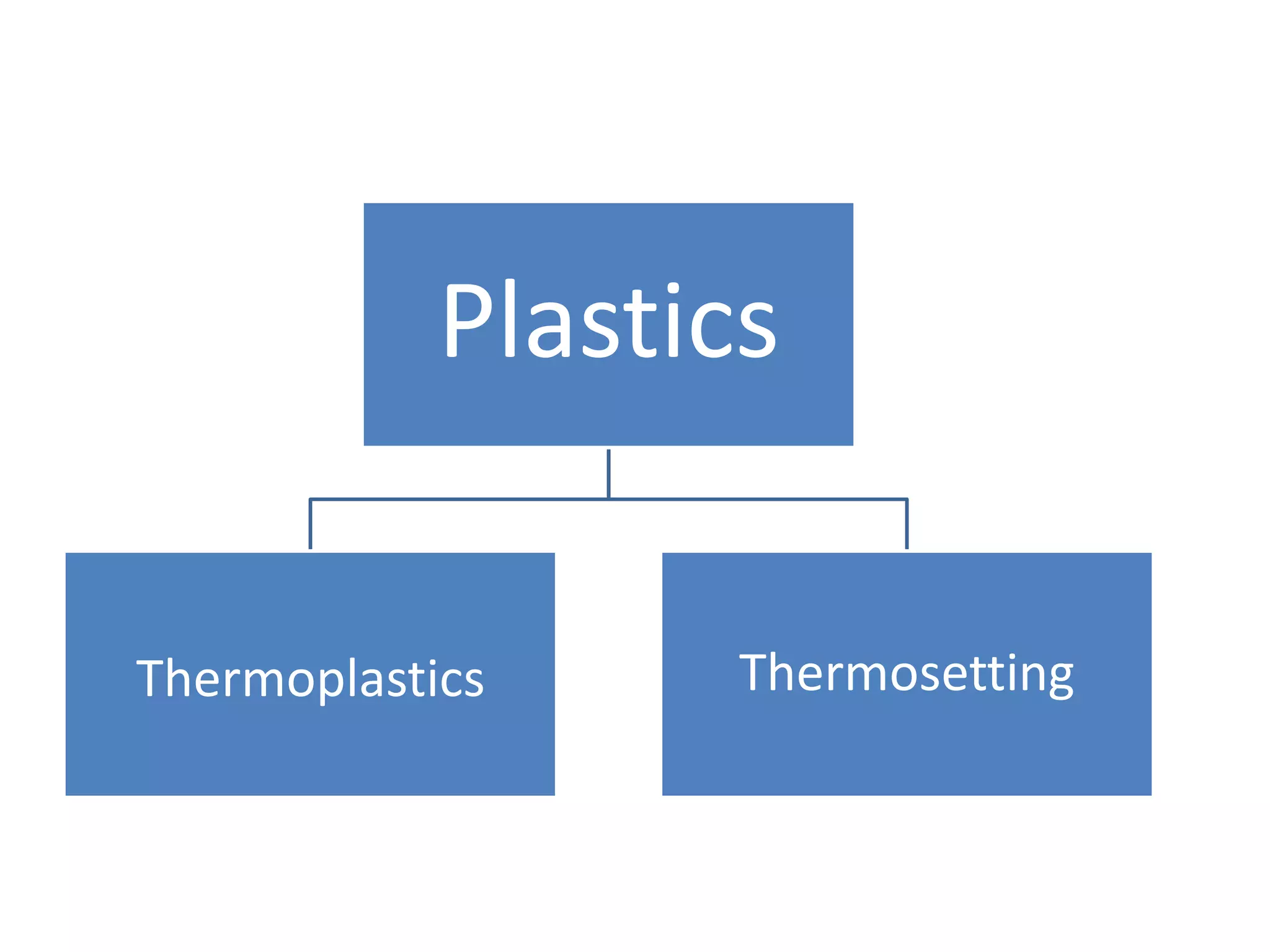
Synthetic plastics are primarily derived from crude oil and natural gas. Crude oil is refined to produce monomers like ethylene and propylene, which are linked together through polymerization to form polymers like polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, and polypropylene. Thermoplastics, like polyethylene, can be softened with heat and reshaped multiple times, while thermosetting plastics, like polyurethane and melamine formaldehyde, permanently harden after heating and shaping. Plastics and rubbers have a wide variety of applications due to their lightweight, durable, and moldable properties.