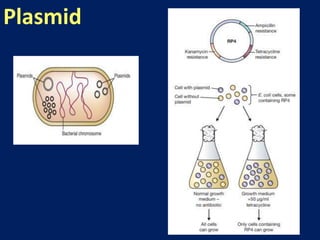
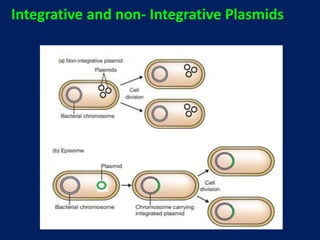
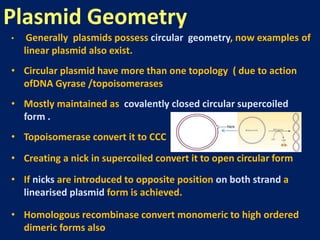
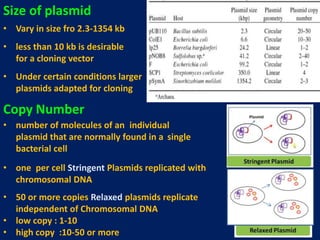
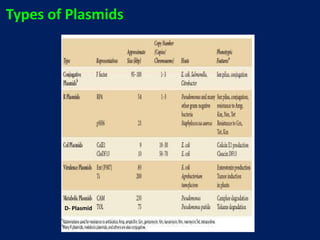
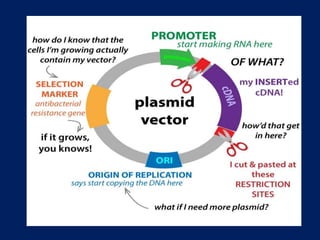
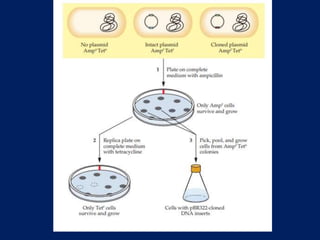
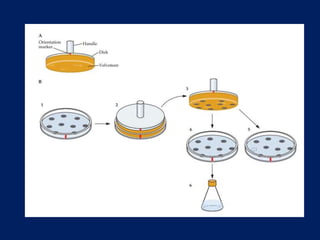
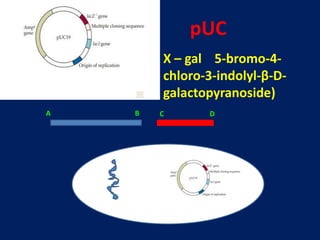
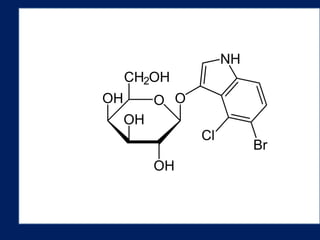
Plasmids are extra-chromosomal genetic elements important for bacterial diversity, capable of autonomous replication, and varying in size and type. They are categorized into conjugative and non-conjugative types, with conjugative plasmids facilitating the transfer between bacterial cells via tra genes. Over time, plasmid definitions have evolved, highlighting their circular geometry, copy number variations, and their role in providing genetic functions like antibiotic resistance.