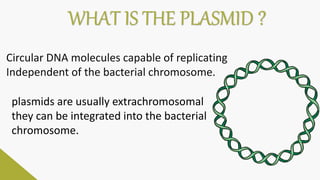
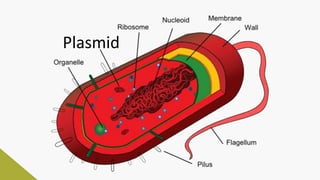
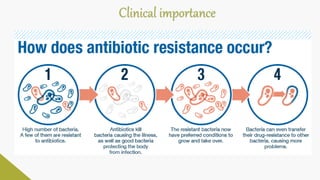
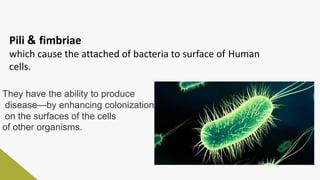
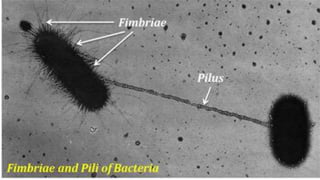
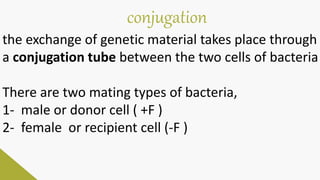
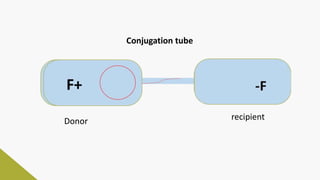
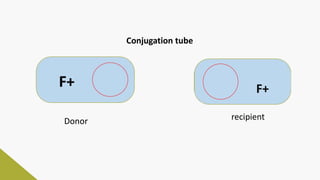
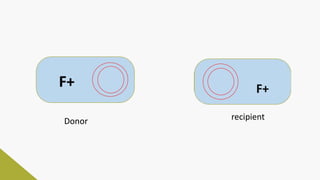
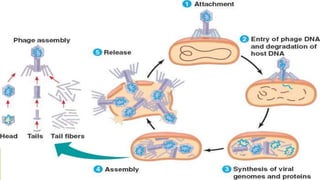
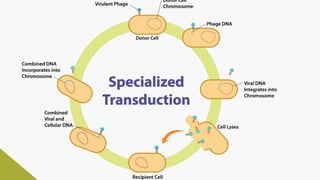
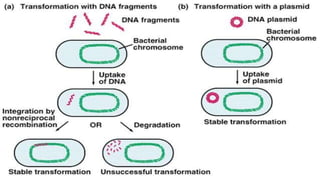
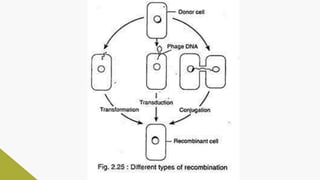
Plasmids are circular DNA molecules that can replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome. They are usually extrachromosomal but can sometimes integrate into the bacterial chromosome. Plasmids carry several genes that are medically important, including genes for antibiotic resistance, resistance to heavy metals and ultraviolet light, and production of bacteriocins, exotoxins, pili, and fimbriae. Mechanisms of bacterial genetic exchange include conjugation, transformation, and transduction, which allow for the horizontal transfer of plasmid DNA between bacteria.