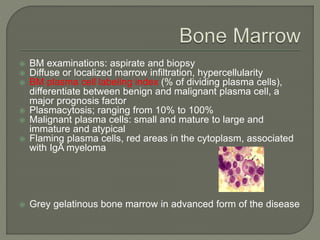
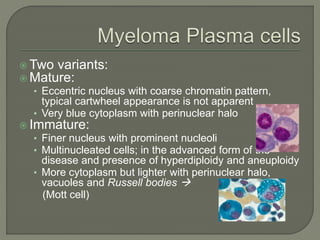
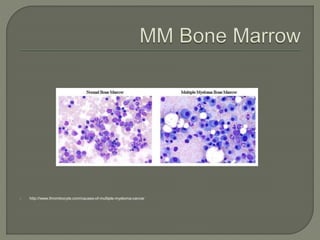
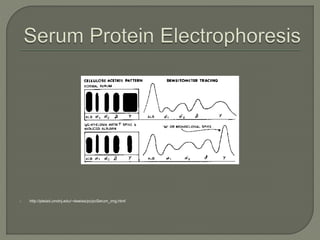
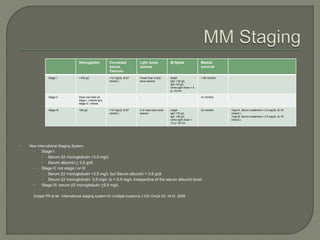
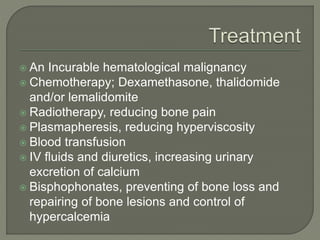
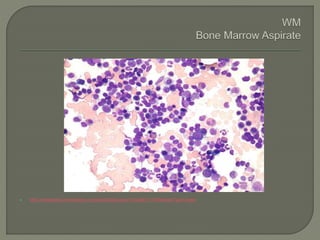
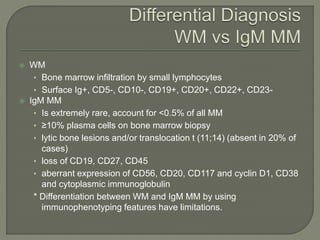
The document provides a comprehensive overview of multiple myeloma, detailing the abnormal proliferation of plasma cells, the types of immunoglobulins produced, related symptoms, and the disease's progression. It discusses diagnostic criteria, genetic factors, treatment options, and associated risk factors. Additionally, it highlights various forms of the disease, including heavy chain disease and Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, along with their clinical presentations and prognosis.