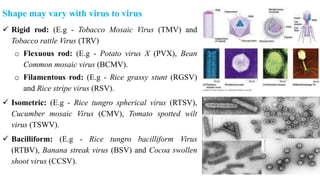
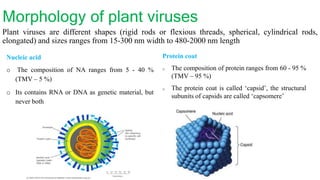
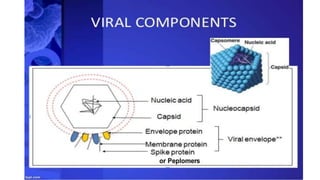
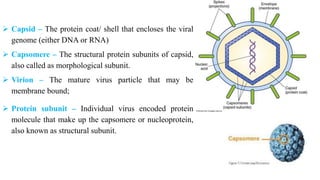
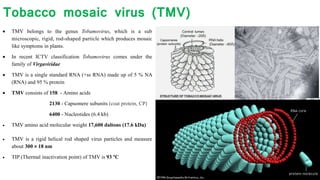
Plant viruses come in various shapes and sizes but generally contain RNA or DNA as their genetic material within a protein coat. They multiply only within living plant cells and can cause symptoms such as mosaic patterns, leaf curling, stunting, and chlorosis. The tobacco mosaic virus is a well-studied plant virus that is rigid and rod-shaped, containing RNA within a protein coat composed of 2130 subunits. It measures around 300 by 18 nm and can be inactivated by heat at 93 degrees Celsius.