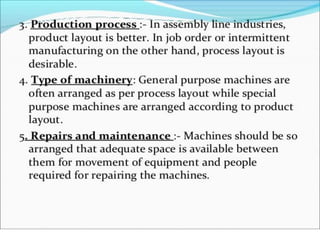
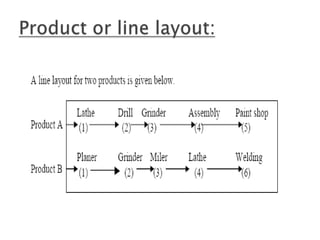
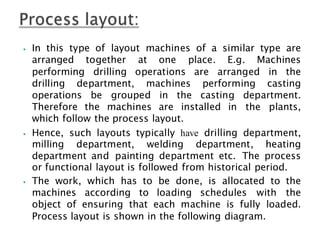
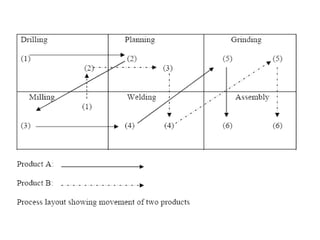
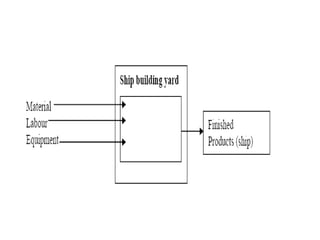
This document discusses different types of plant layouts used in manufacturing units. It describes product or line layouts, where machines are arranged in a line based on the sequence of operations. Process or functional layouts group similar machines together by department. Fixed position layouts do not move materials or products, but bring all facilities to a single work center location. Combined or group layouts incorporate elements of product, process, and fixed position layouts to suit manufacturing units with multiple product types or processes. The key objectives of plant layouts are to minimize costs and optimize the flow of materials through production.


















![⦁ Certain manufacturing units may require all three
processes namely intermittent process (job
shops), the continuous process (mass production
shops) and the representative process combined
process [i.e. miscellaneous shops].
⦁ In most of industries, only a product layout or
process layout or fixed location layout does not
exist. Thus, in manufacturing concerns where
several products are produced in repeated
numbers with no likelihood of continuous
production, combined layout is followed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/productionmanagementunit3-221114103849-2dc4687a/85/production-management-unit-3-pdf-23-320.jpg)