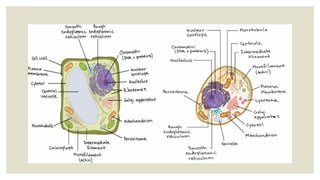
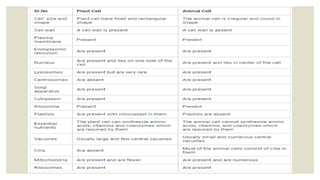
This document summarizes the key organelles and structures found within plant and animal cells. It describes the cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles, lysosomes, ribosomes, and plastids. The cell membrane forms the boundary of the cell and regulates what enters and exits. The nucleus contains DNA and directs cell activities. Mitochondria generate energy through respiration. Other organelles modify and transport cellular materials or store waste. While plant and animal cells share many structures, plant cells also contain a cell wall for protection and shape.