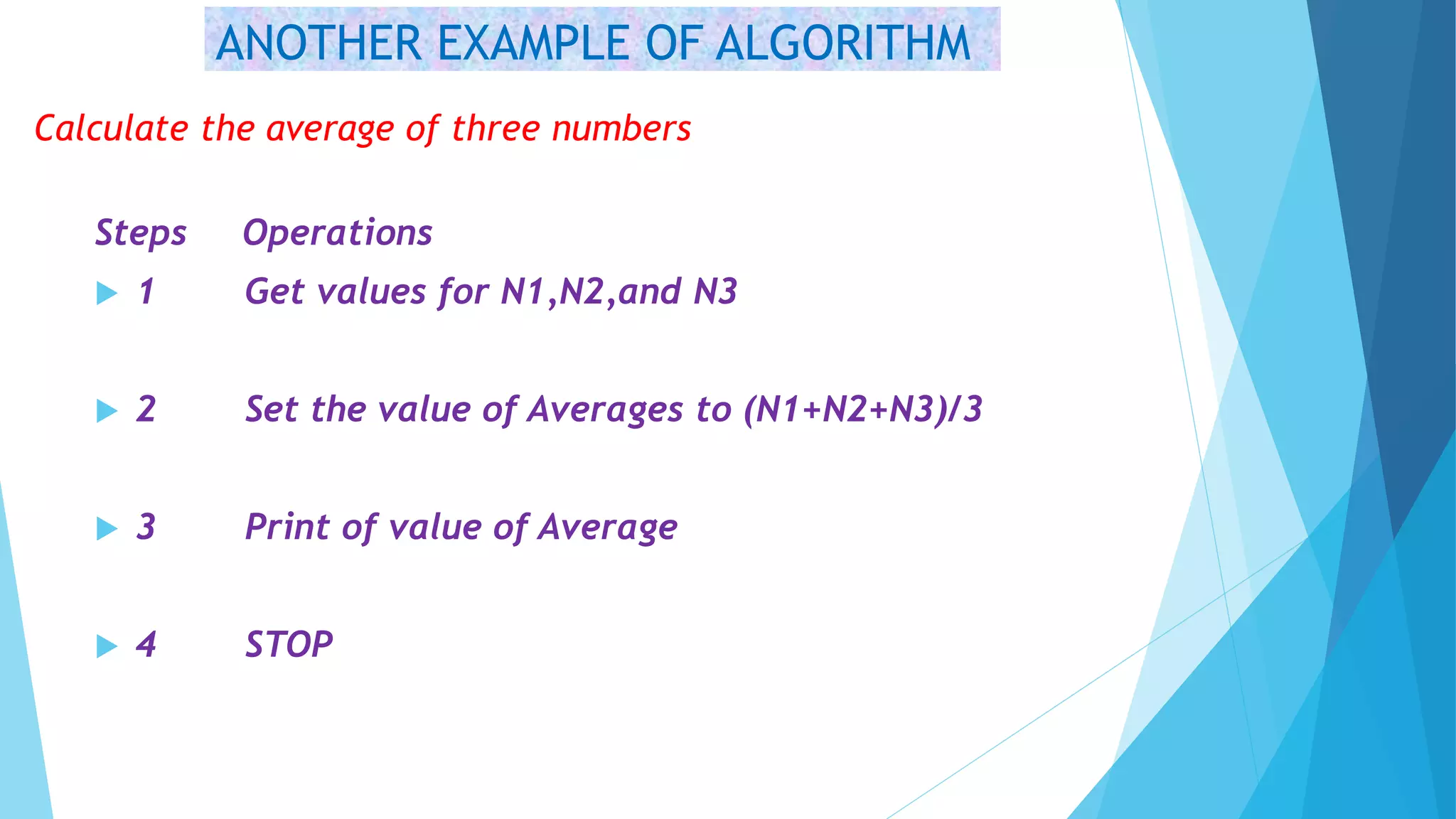
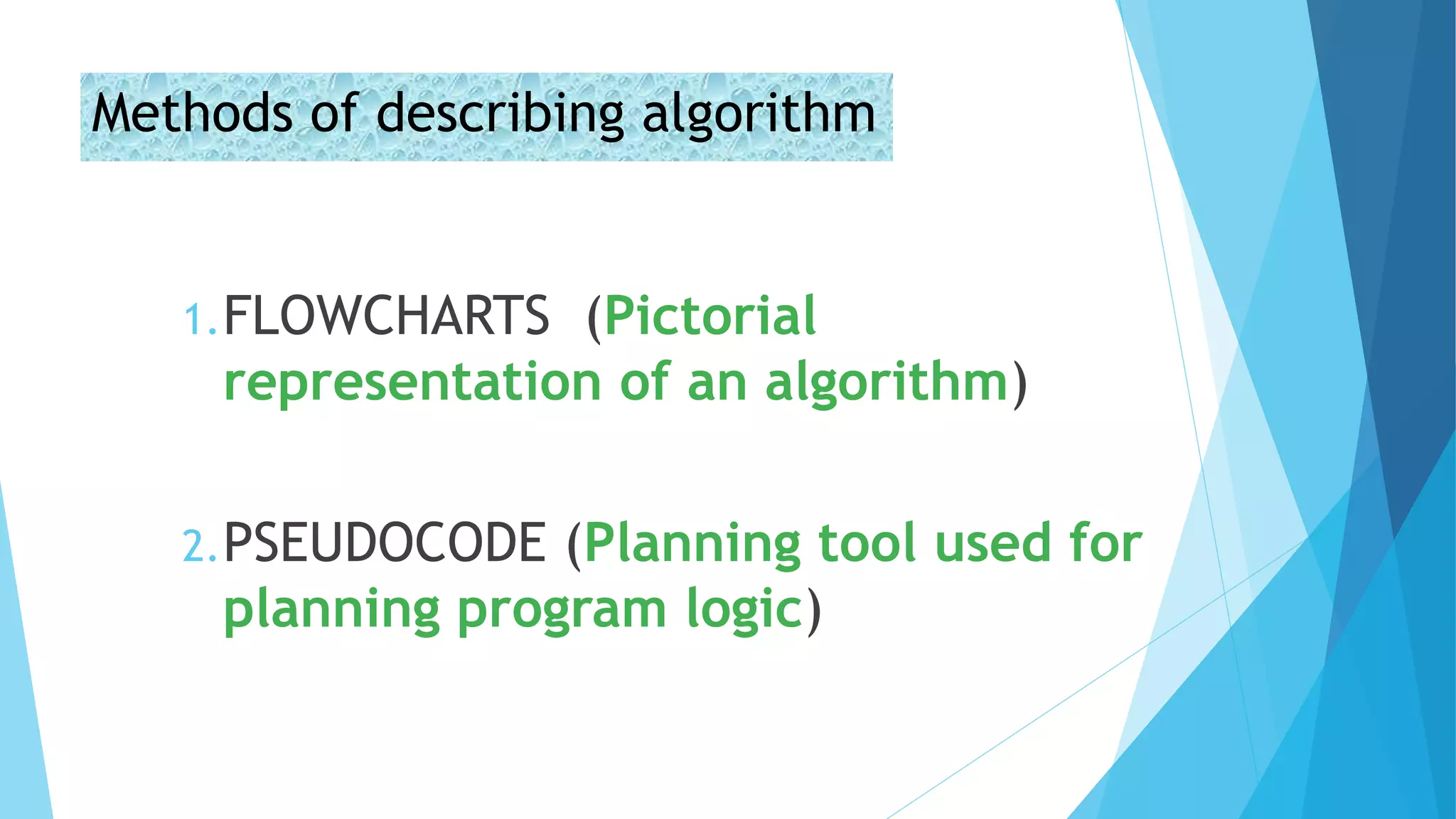
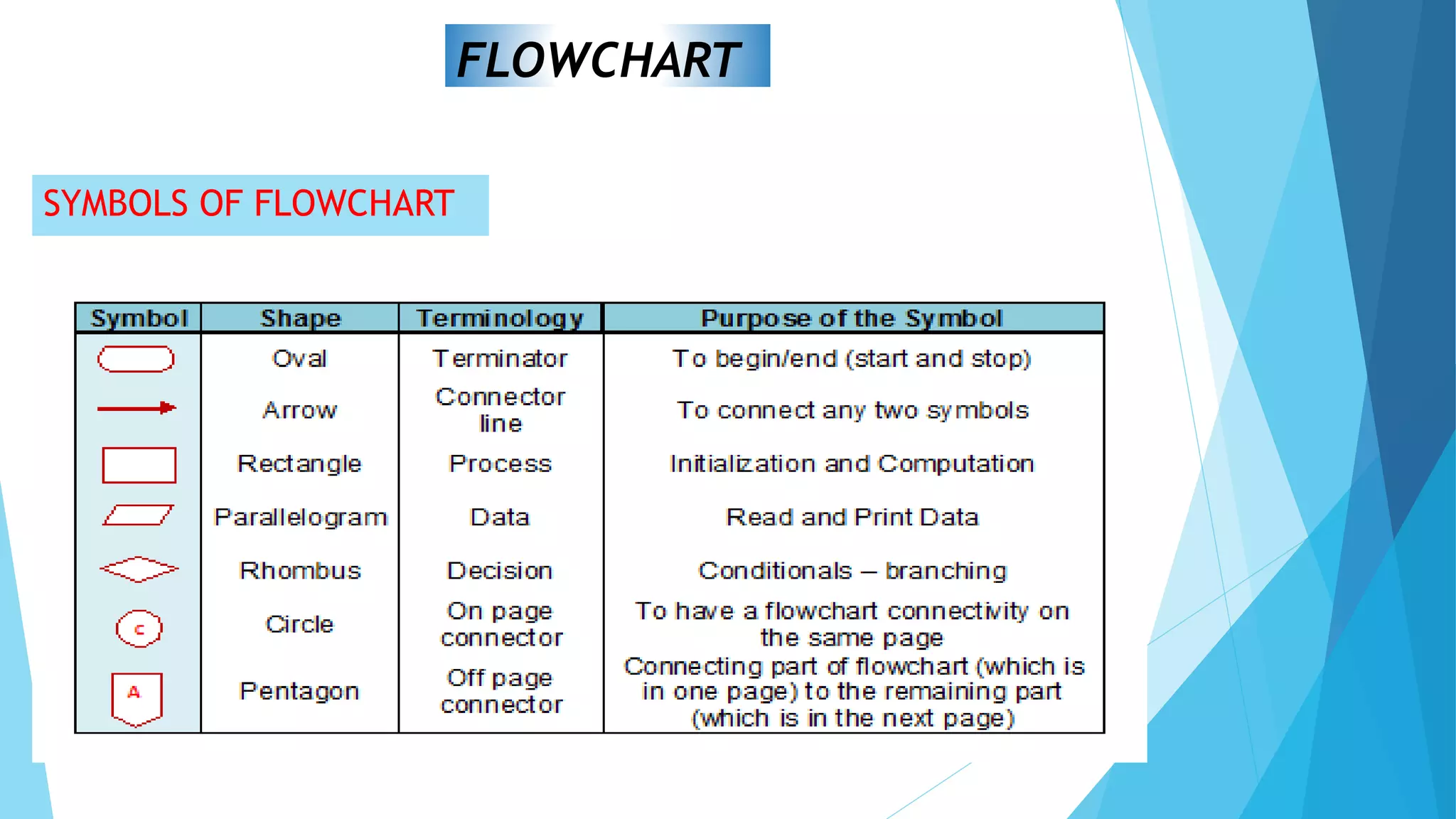
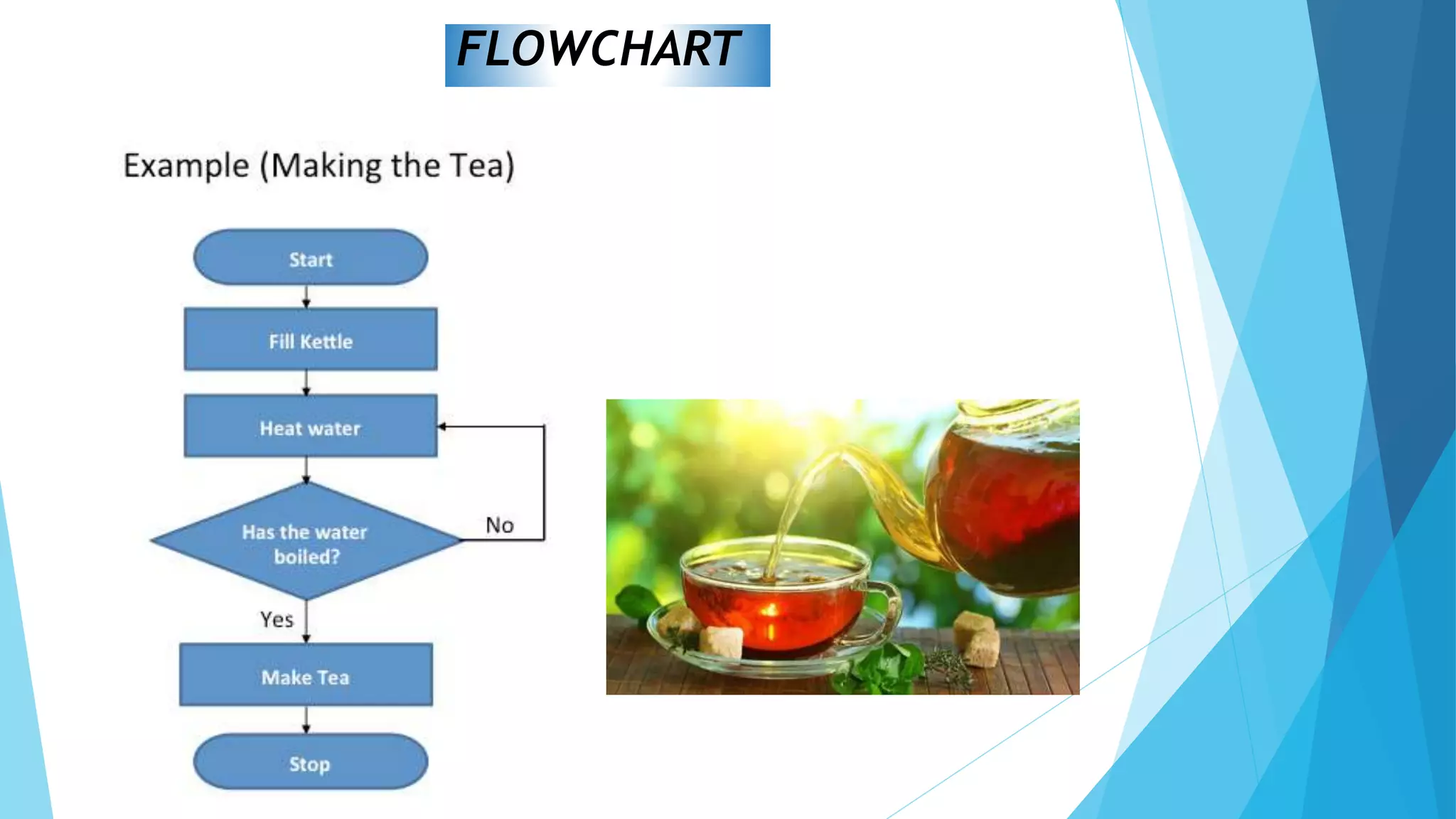
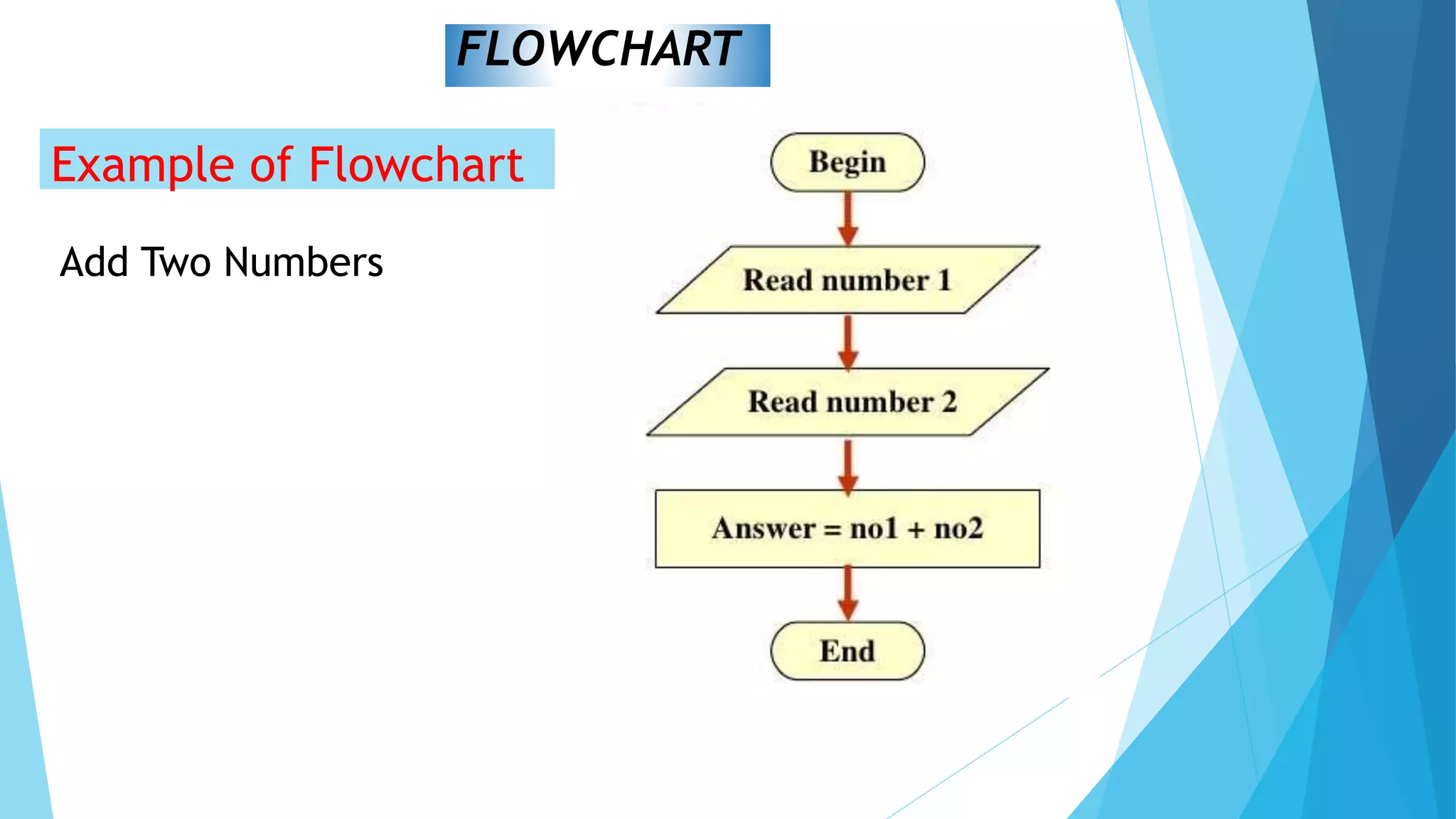
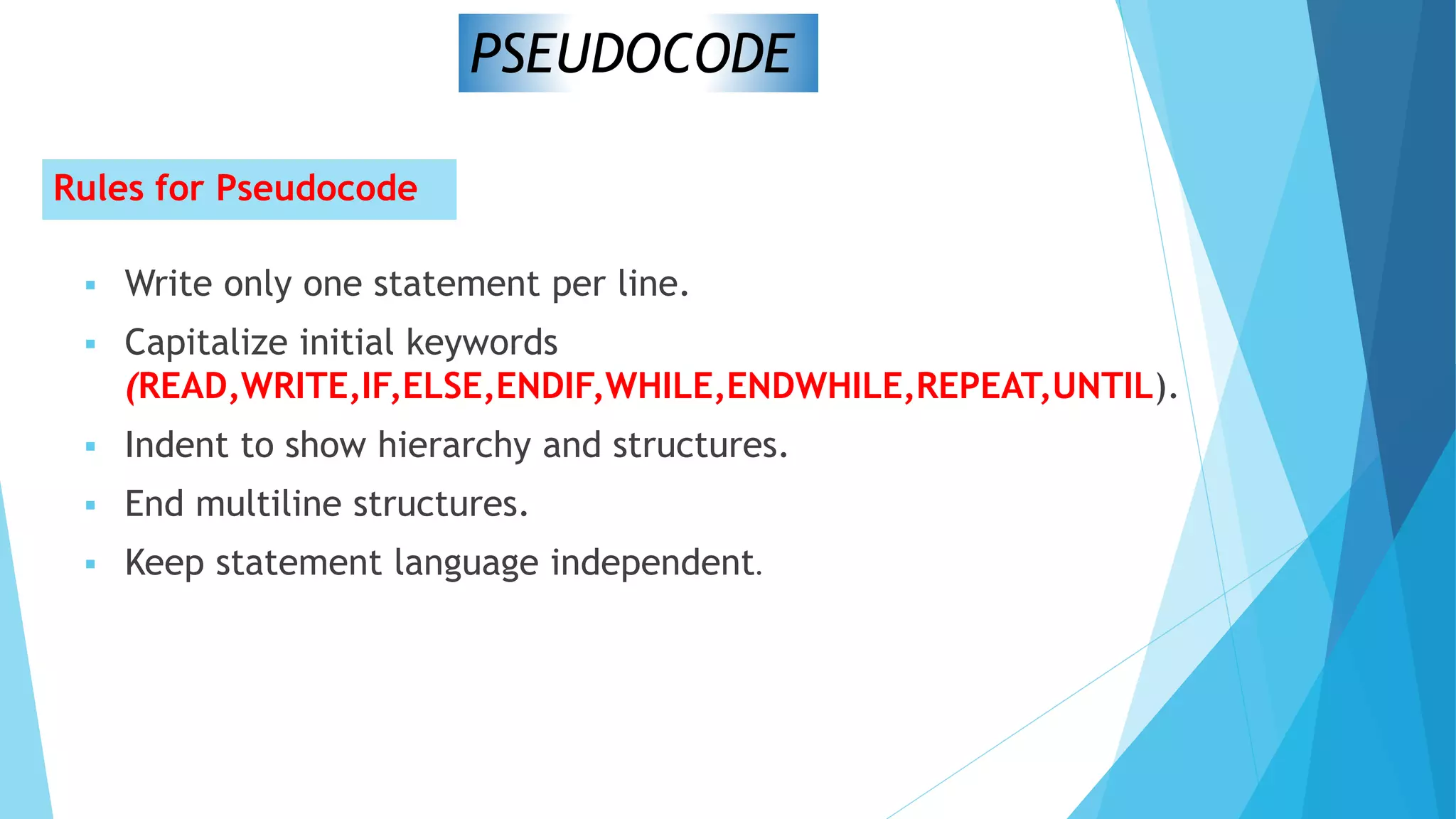
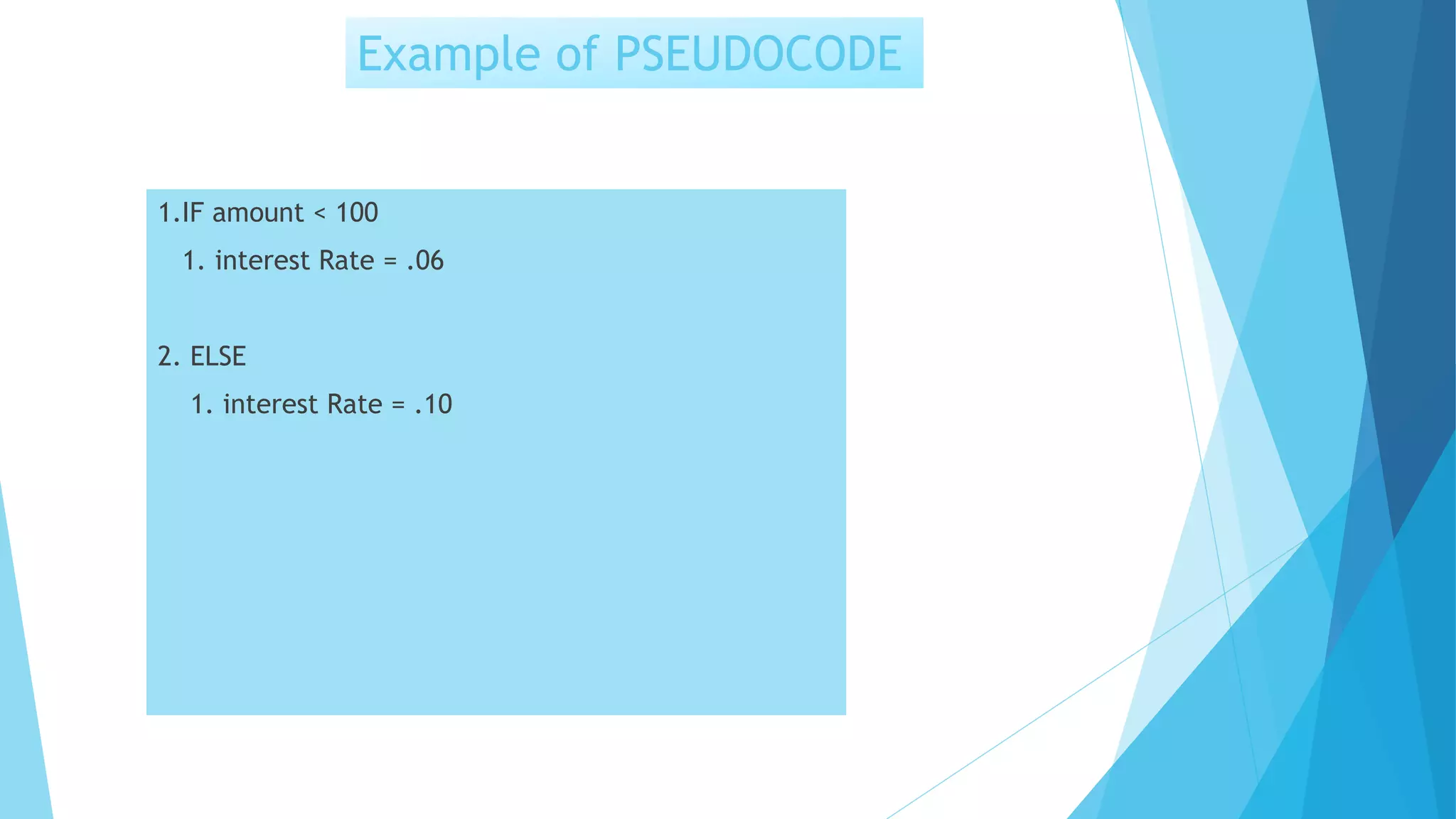
This document contains information about computer programs and programming concepts. It discusses that computer programs are lists of instructions written in a way that computers can understand. There are three main types of programs: operating systems, utilities, and applications. It also discusses the importance of planning for programming and defines algorithms and methods for describing algorithms like flowcharts and pseudocode.