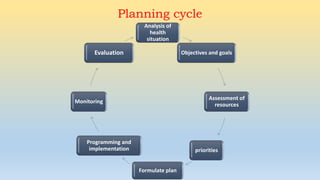
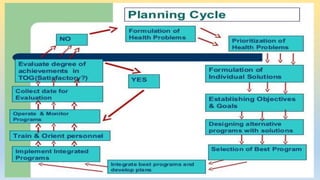
1) The document outlines the planning cycle for health programs which involves analyzing the health situation, establishing objectives and goals, assessing available resources, prioritizing issues, formulating plans, programming and implementing solutions, monitoring progress, and evaluating outcomes.
2) Major steps include analyzing population health data, setting specific and measurable targets, identifying available funding, staff and materials, prioritizing diseases and interventions, drafting detailed plans with inputs and outputs, assigning roles and supervision, tracking activities, and assessing the degree of objective fulfillment.
3) The cycle is intended to be continuous and adaptive to changing health needs with ongoing monitoring informing reprioritization.