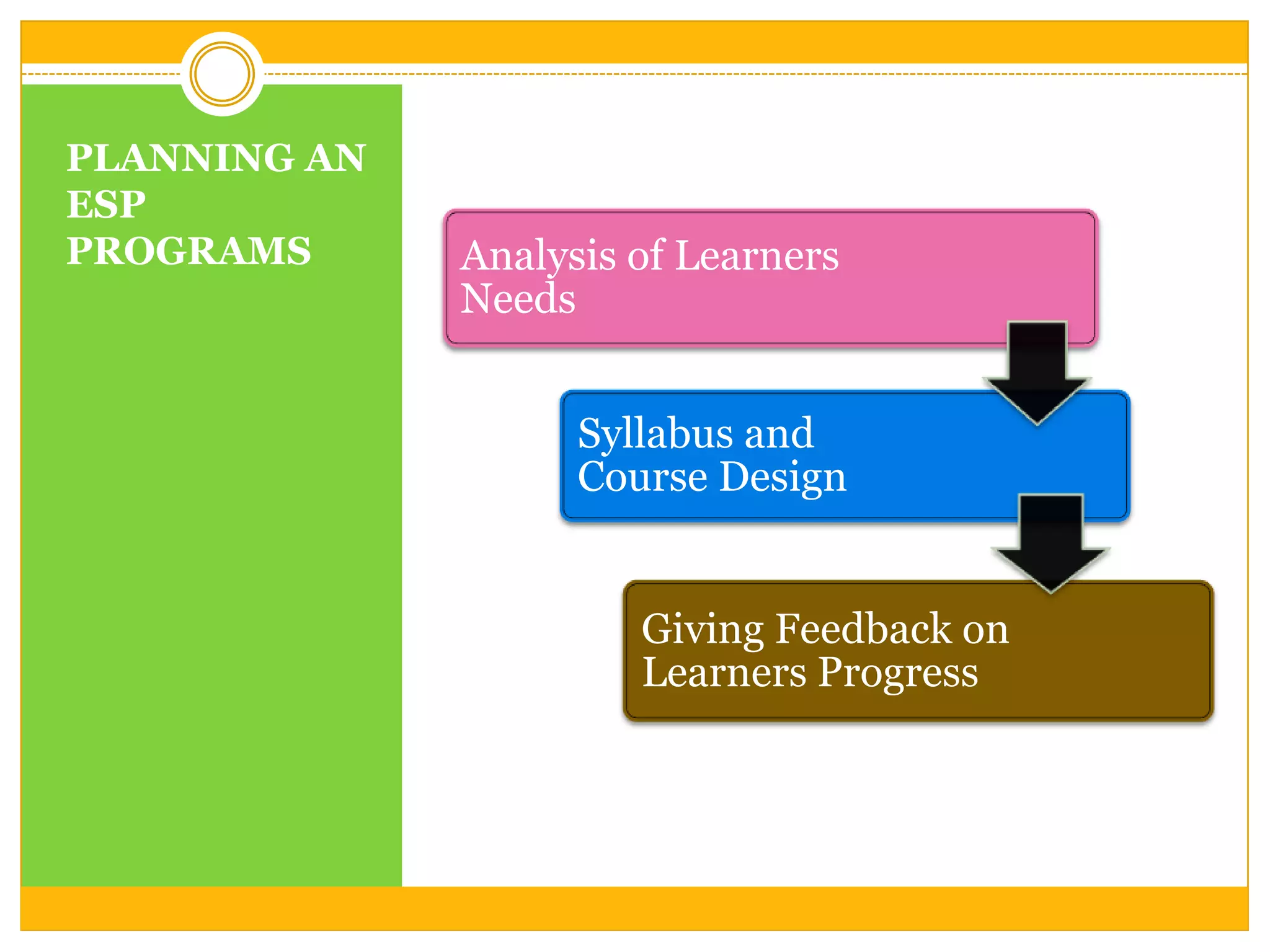
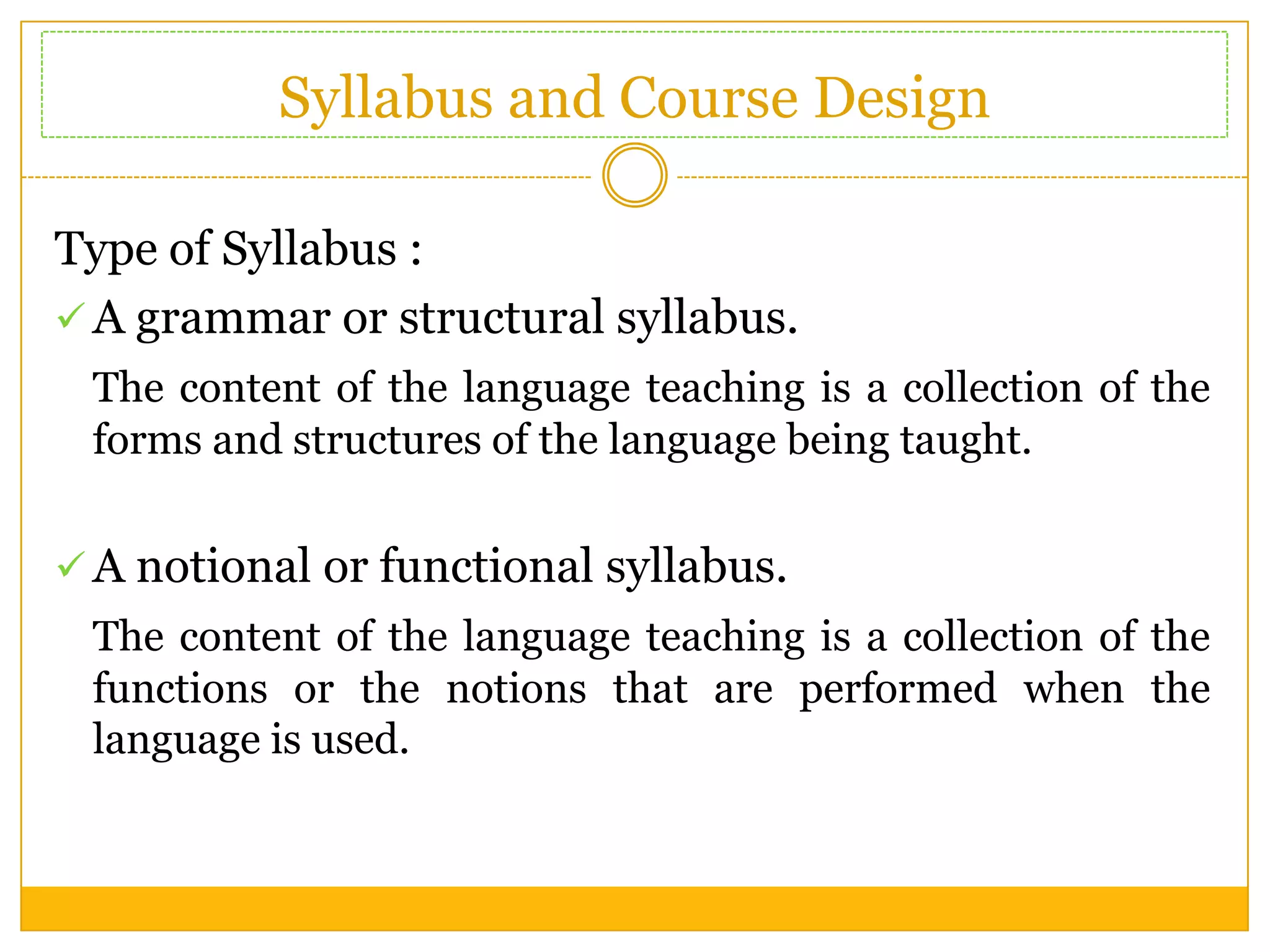
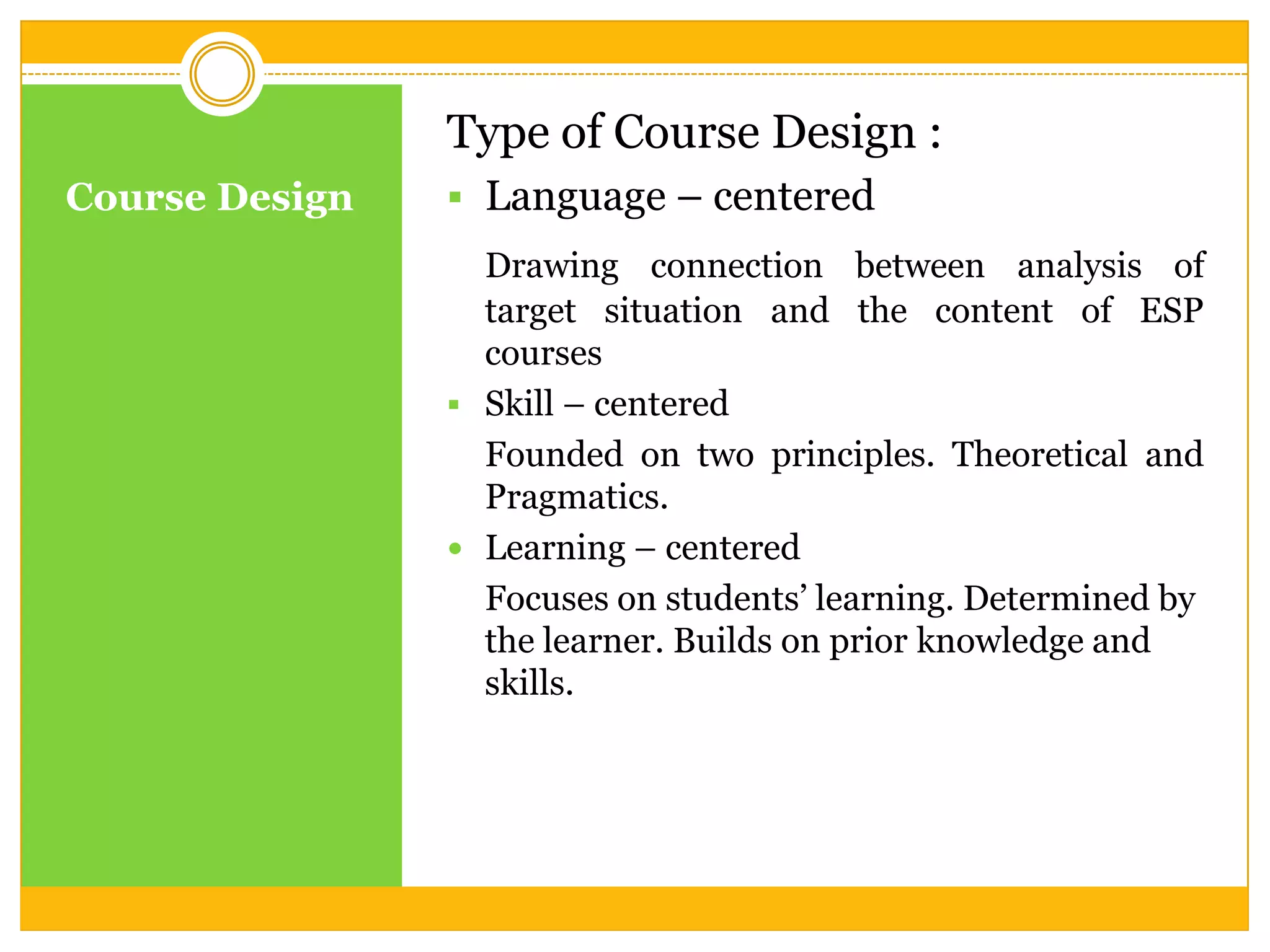
The document discusses planning and conceptualizing an English for Specific Purposes (ESP) program. It involves determining what students need to learn based on their needs and course purpose. The process also includes deciding what to include, emphasize, and how to organize content. Planning an ESP program involves analyzing learner needs to establish objectives and course content. It also involves designing a syllabus that can be grammar-based, functional, situational, skill-based, task-based, or content-based. The course design can be language-centered, skill-centered, or learning-centered. Finally, the document discusses giving feedback on learner progress by suggesting improvements, balancing positive and negative comments, and allowing discussion.