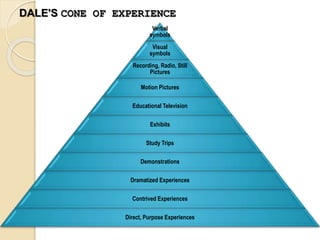
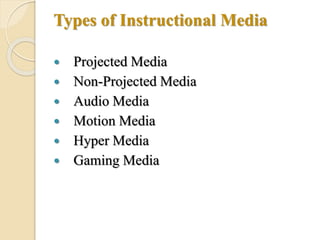
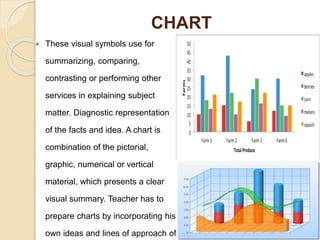
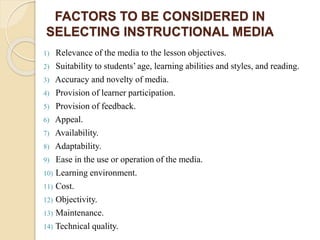
This document discusses instructional media and its role in teaching and learning. It defines instructional media as resources and physical means that an instructor can use to deliver instruction and facilitate student achievement of learning objectives. This may include traditional materials like chalkboards as well as newer technologies like computers and the internet. The document outlines various types of instructional media including projected, non-projected, audio, motion, hyper, and gaming media. It also discusses factors to consider when selecting instructional media and the benefits of using instructional media in the classroom, such as gaining and holding student attention and helping students visualize lessons.