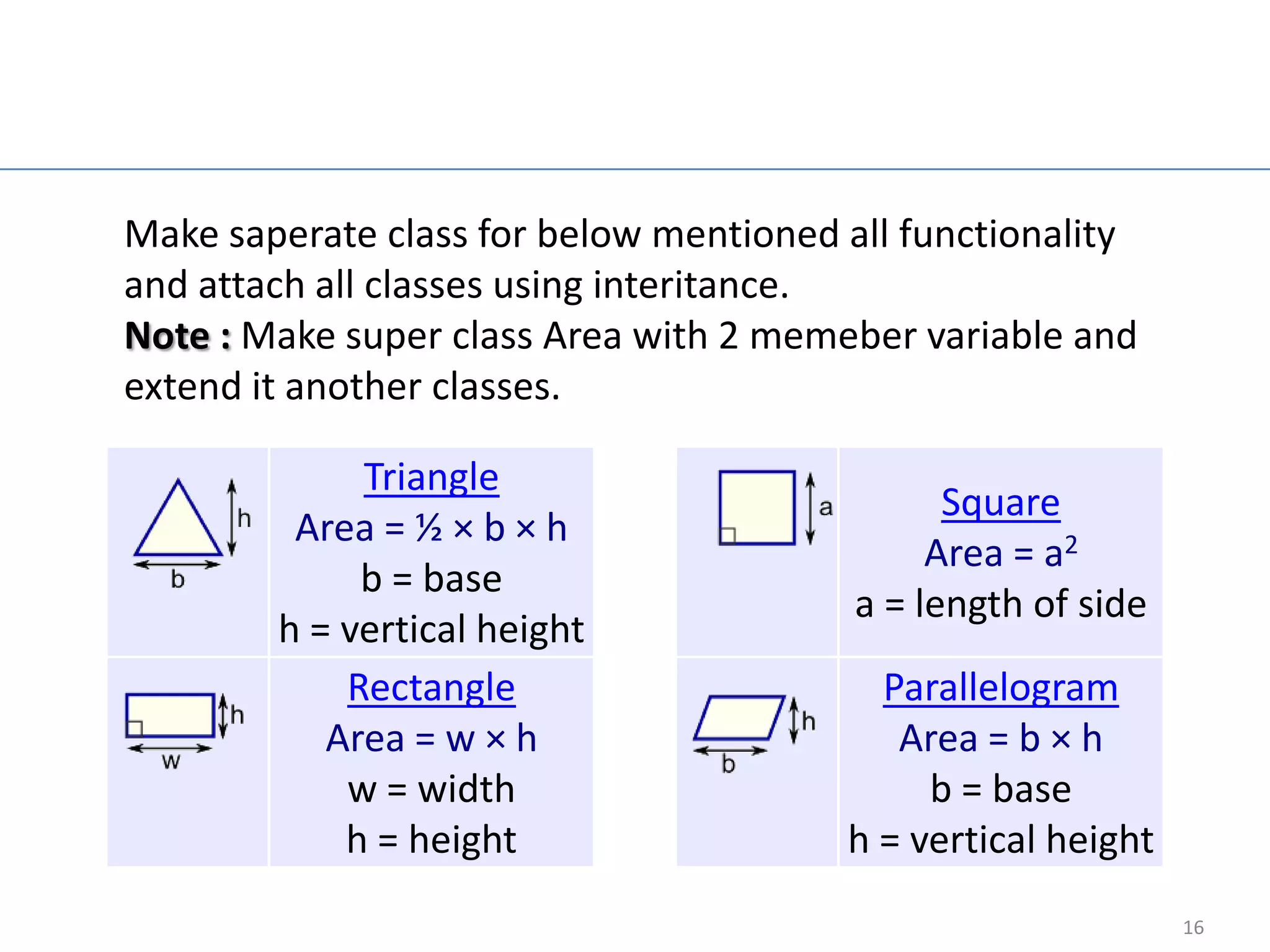
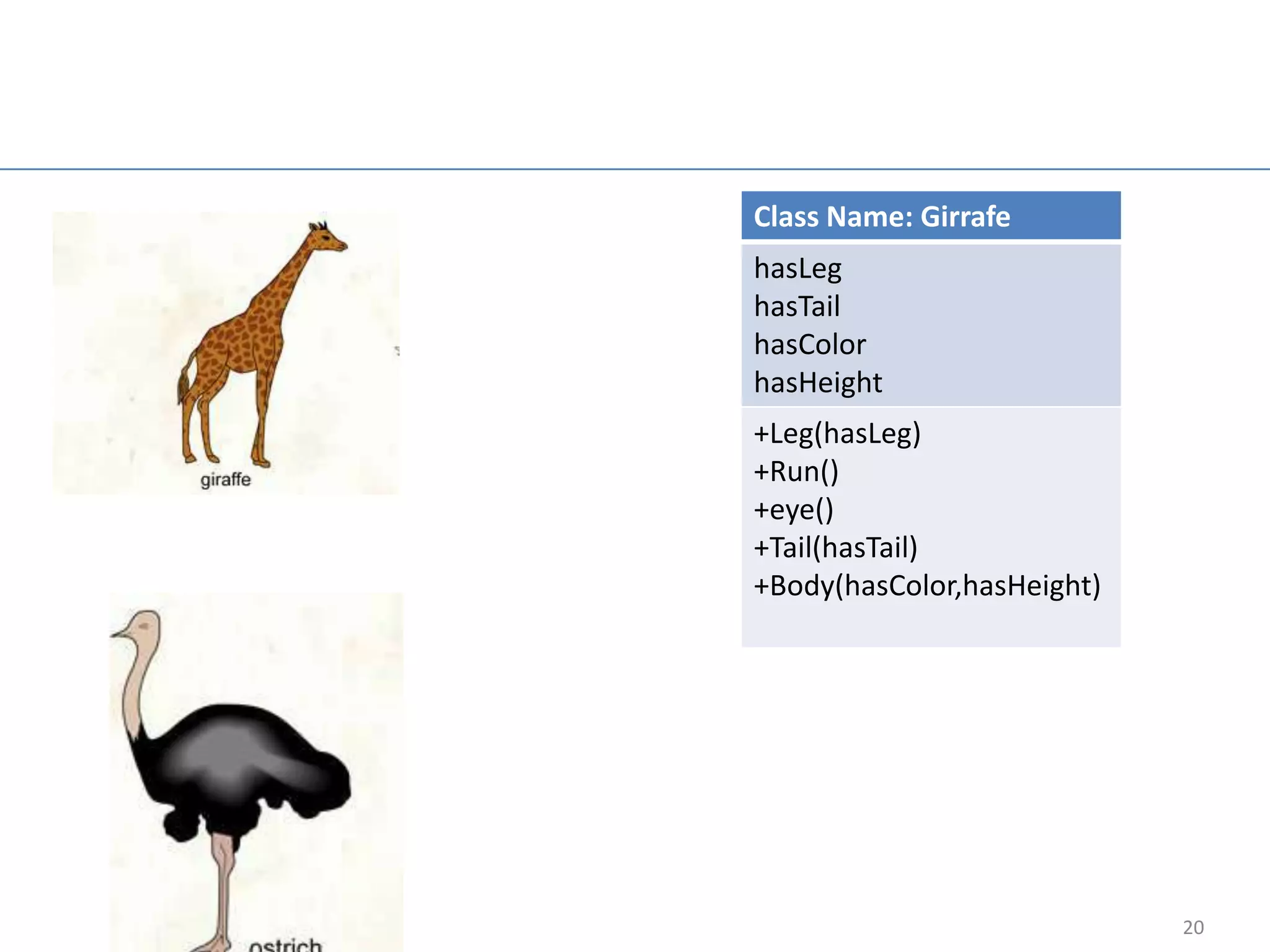
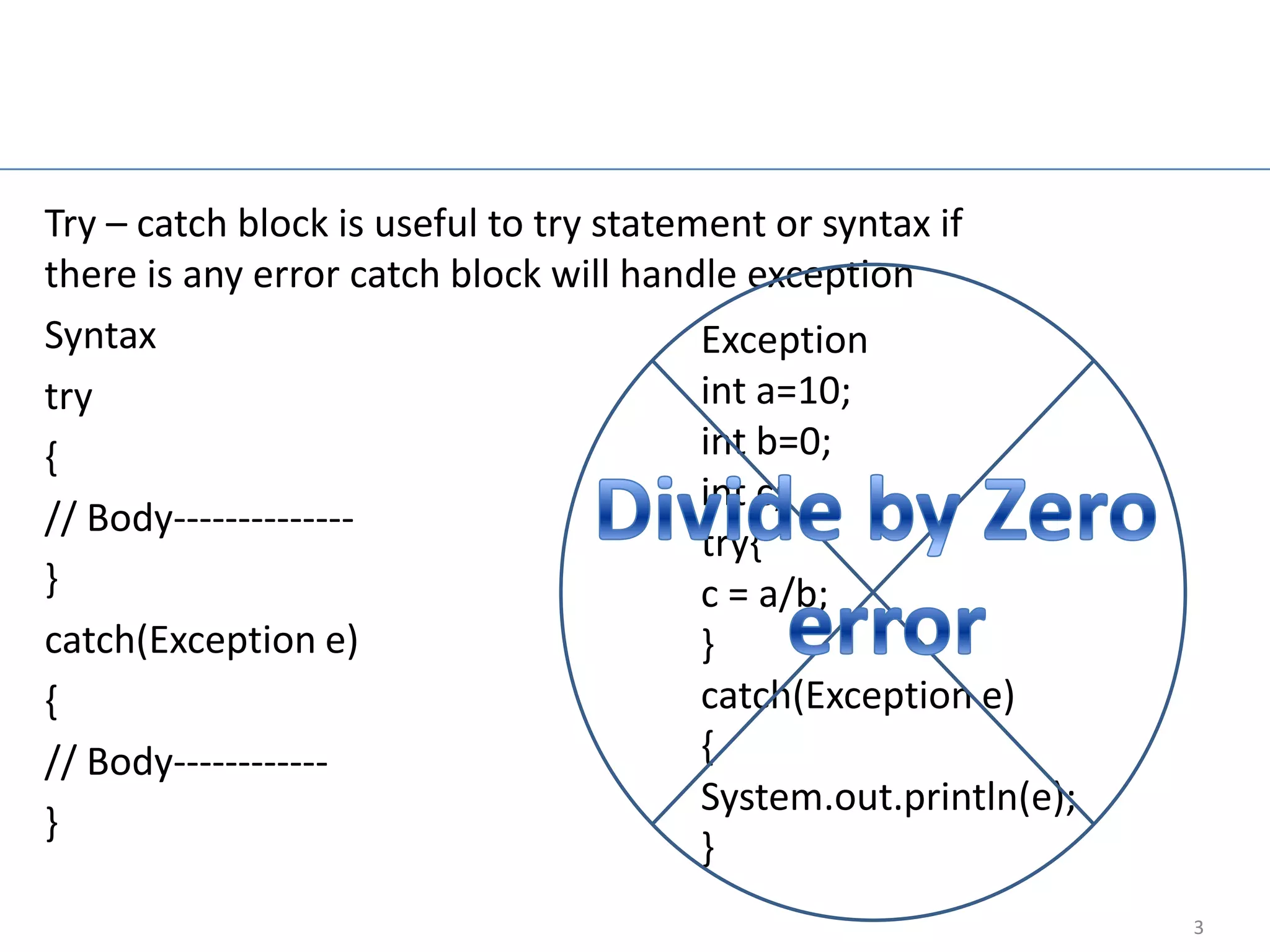
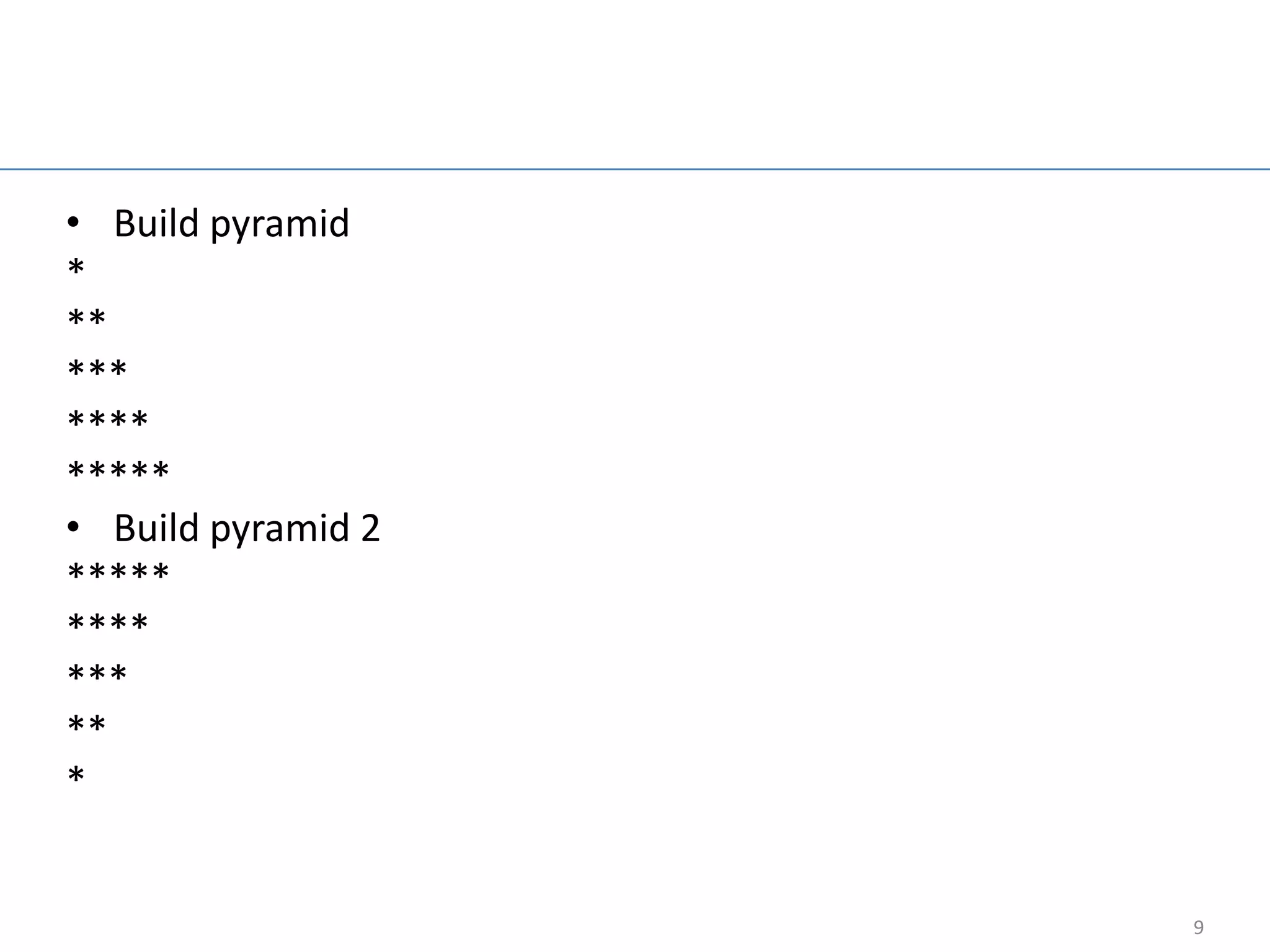
The document provides an overview of core Java concepts including try-catch blocks, reading input from the keyboard, control flow statements like if-else and switch, looping with for, while, and do-while loops, arrays, inheritance, overriding, abstract classes, interfaces, and packages. It includes code examples and discusses concepts like exception handling, control flow, looping, arrays, object-oriented programming principles of inheritance and polymorphism.











![Array in Java
Syntax
dataType[] arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraySize];
dataType[] arrayRefVar = {value0, value1, ..., valuek};
Example
Double[] myList = new double[10];
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-121122193907-phpapp01/75/Core-java-14-2048.jpg)