The document provides an index and descriptions of various topics related to web development including:
1. The modulus operator and examples of using it to check for divisibility.
2. Relational and logical operators like greater than, less than, equal to and examples of using them in code.
3. Descriptions of do-while and for loops with examples.
4. An example using a parameterized constructor to initialize cube dimensions.
5. Examples of string methods like startsWith, length, and trim.
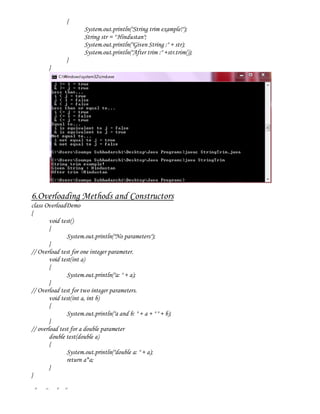
6. Descriptions and examples of overloading methods and constructors.
7. An example of inheritance with overriding methods.
8. An interface example with animal classes

![1. Modulus Operator Description
class Remainder
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
int i = 12;
int j = 4;
int k = 0;
System.out.println("i is " + i);
System.out.println("j is " + j);
k = i % j;
System.out.println("Its Remainder is " + k);
}
}
class Divisor
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 10;
int b = 2;
if ( a % b == 0 )
{
System.out.println(a + " is divisible by "+ b);
}
else
{
System.out.println(a + " is not divisible by " + b);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samwdprograms-111126074750-phpapp01/85/Sam-wd-programs-3-320.jpg)
![2. Relational and Logical Operators
class RelationalProgram
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{ //a few numbers
int i = 3;
int j = 4;
int k = 4;
System.out.println("Greater than..."); //greater than
System.out.println(" i > j = " + (i > j)); //false
System.out.println(" j > i = " + (j > i)); //true
System.out.println(" k > j = " + (k > j)); //false(equal) //greater than or equal to
System.out.println("Greater than or equal to...");
System.out.println(" i >= j = " + (i >= j)); //false
System.out.println(" j >= i = " + (j >= i)); //true
System.out.println(" k >= j = " + (k >= j)); //true
//less than
System.out.println("Less than...");
System.out.println(" i < j = " + (i < j)); //true
System.out.println(" j < i = " + (j < i)); //false
System.out.println(" k < j = " + (k < j)); //false
//less than or equal to
System.out.println("Less than or equal to...");
System.out.println(" i <= j = " + (i <= j)); //true
System.out.println(" j <= i = " + (j <= i)); //false
System.out.println(" k <= j = " + (k <= j)); //true
//equal to
System.out.println("Equal to...");
System.out.println(" i is equivalent to j = " + (i == j));
System.out.println(" k is equivalent to j = " + (k == j));
//not equal to
System.out.println("Not equal to...");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samwdprograms-111126074750-phpapp01/85/Sam-wd-programs-4-320.jpg)
![System.out.println(" i not equal to j = " + (i != j)); //true
System.out.println(" k not equal to j = " + (k != j)); //false
}
}
class ConditionalOperator
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 2;
int y = 20, result=0;
boolean bl = true;
if((x == 5) && (x < y))
{
System.out.println("value of x is "+ x);
}
if((x == y) || (y > 1))
{
System.out.println("value of y is greater than the value of x");
}
result = bl ? x : y;
System.out.println("The returned value is "+ result);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samwdprograms-111126074750-phpapp01/85/Sam-wd-programs-5-320.jpg)
![3. Do while and For loop presentation
class DoWhile
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int count = 1;
do
{
System.out.println("Count is: " + count);
count++;
} while (count < 11);
}
}
class ForLoop
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samwdprograms-111126074750-phpapp01/85/Sam-wd-programs-6-320.jpg)

![public static void main(String[] args)
{
Cube cubeObj1, cubeObj2;
cubeObj1 = new Cube();
cubeObj2 = new Cube(10, 20, 30);
System.out.println("Volume of Cube is : " + cubeObj1.getVolume());
System.out.println("Volume of Cube is : " + cubeObj2.getVolume());
}
}
5. String Methods
import java.lang.*;
class StrStartWith
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("String start with example!");
String str = "Welcome to my Coding!!!";
String start = "Welcome";
System.out.println("Given String : " + str);
System.out.println("Start with : " + start);
if (str.startsWith(start))
{
System.out.println("The given string is start with Welcome");
}
else
{
System.out.println("The given string is not start with Welcome");
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samwdprograms-111126074750-phpapp01/85/Sam-wd-programs-8-320.jpg)
![import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class StringLength
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
System.out.println("String lenght example!");
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Please enter string:");
String str = bf.readLine();
int len = str.length();
System.out.println("String lenght : " + len);
}
}
import java.lang.*;
class StringTrim
{
public static void main(String[] args)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samwdprograms-111126074750-phpapp01/85/Sam-wd-programs-9-320.jpg)
![{
public static void main(String args[])
{
OverloadDemo ob = new OverloadDemo();
double result;
// call all versions of test()
ob.test();
ob.test(11);
ob.test(11, 2);
result = ob.test(11.2);
System.out.println("Result of ob.test(11.2): " + result);
}
}
7. Inheritance
class Base
{
int a = 11;
void show()
{
System.out.println(a);
}
}
class Super extends Base
{
int a = 22;
void show()
{
super.show();
System.out.println(a);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new Super().show();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samwdprograms-111126074750-phpapp01/85/Sam-wd-programs-11-320.jpg)
![}
}
8.executing speak() and eat() methods using animal interface
interface IAnimal
{
public void speak();
}
public class Cat implements IAnimal
{
public void speak()
{
System.out.println("Cat speaks meaown!!!");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Cat c = new Cat();
c.speak();
}
}
public class Dog implements IAnimal
{
public void speak()
{
System.out.println("Dog eats Cat!!!");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Dog d = new Dog();
d.speak();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samwdprograms-111126074750-phpapp01/85/Sam-wd-programs-12-320.jpg)
![9. Exception handling
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class MyException extends Exception
{
private String ssb="";
public String getMessage(String s)
{
ssb=s;
return ("you are not permitted to enter inside "+ ssb);
}
}
class ExcepDemo
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws MyException,IOException
{
String temp="";
try
{
String str="Soumya Subhadarshi Behera";
System.out.println("Enter your name");
BufferedReader br= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
temp=br.readLine();
if(!temp.equals(str))
throw new MyException();
else
System.out.println("Welcome to MDU");
}
catch(MyException e)
{
System.err.println(e.getMessage(temp));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samwdprograms-111126074750-phpapp01/85/Sam-wd-programs-13-320.jpg)
![catch(Exception e)
{
System.err.println(e);
}
}
}
10.Writing inside a file
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class FileWrite
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
FileWriter fstream = new FileWriter("KeyboardInput.txt");
BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(fstream);
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Please enter string:");
String str = bf.readLine();
out.write(str);
out.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.err.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samwdprograms-111126074750-phpapp01/85/Sam-wd-programs-14-320.jpg)
