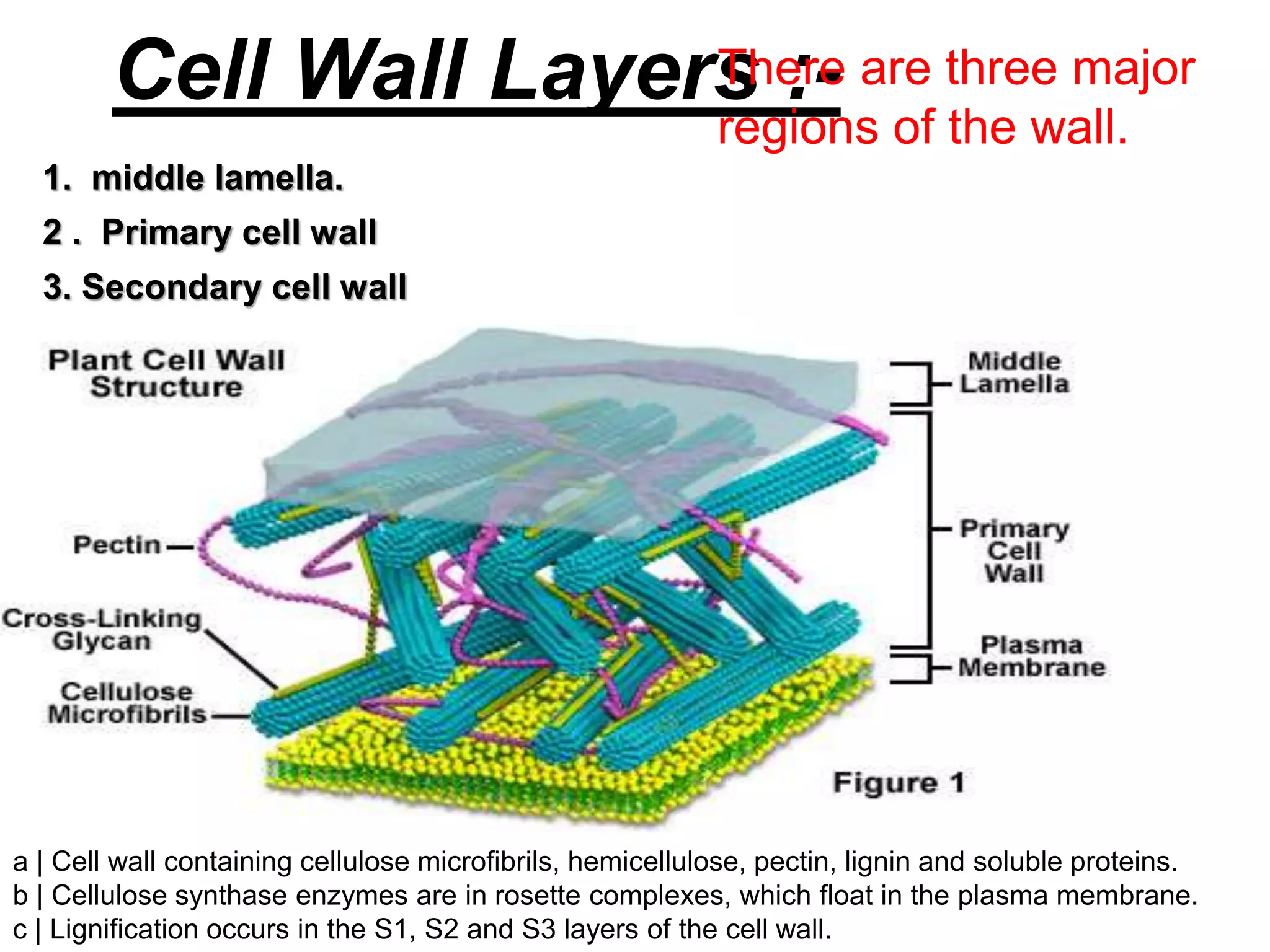
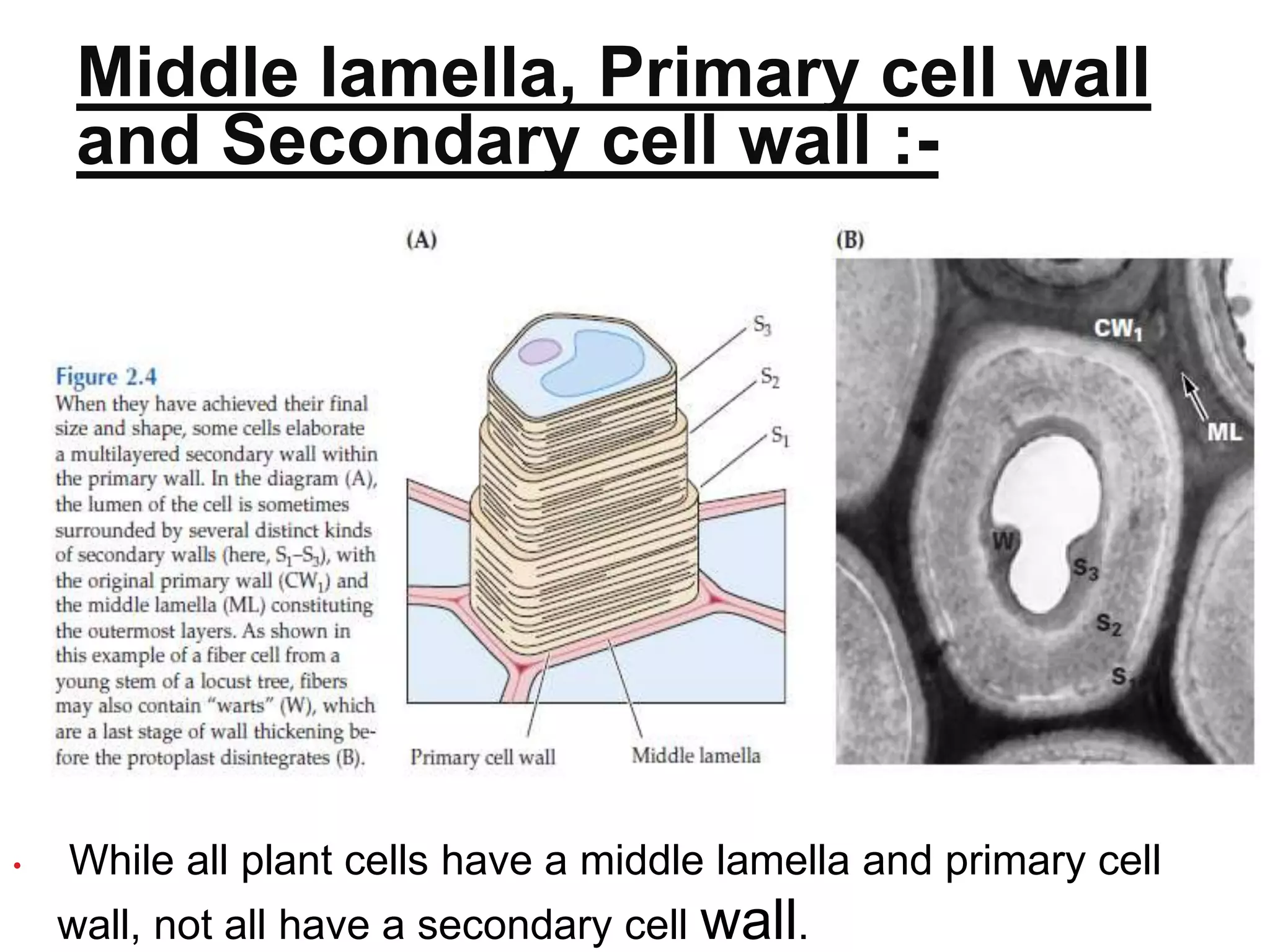
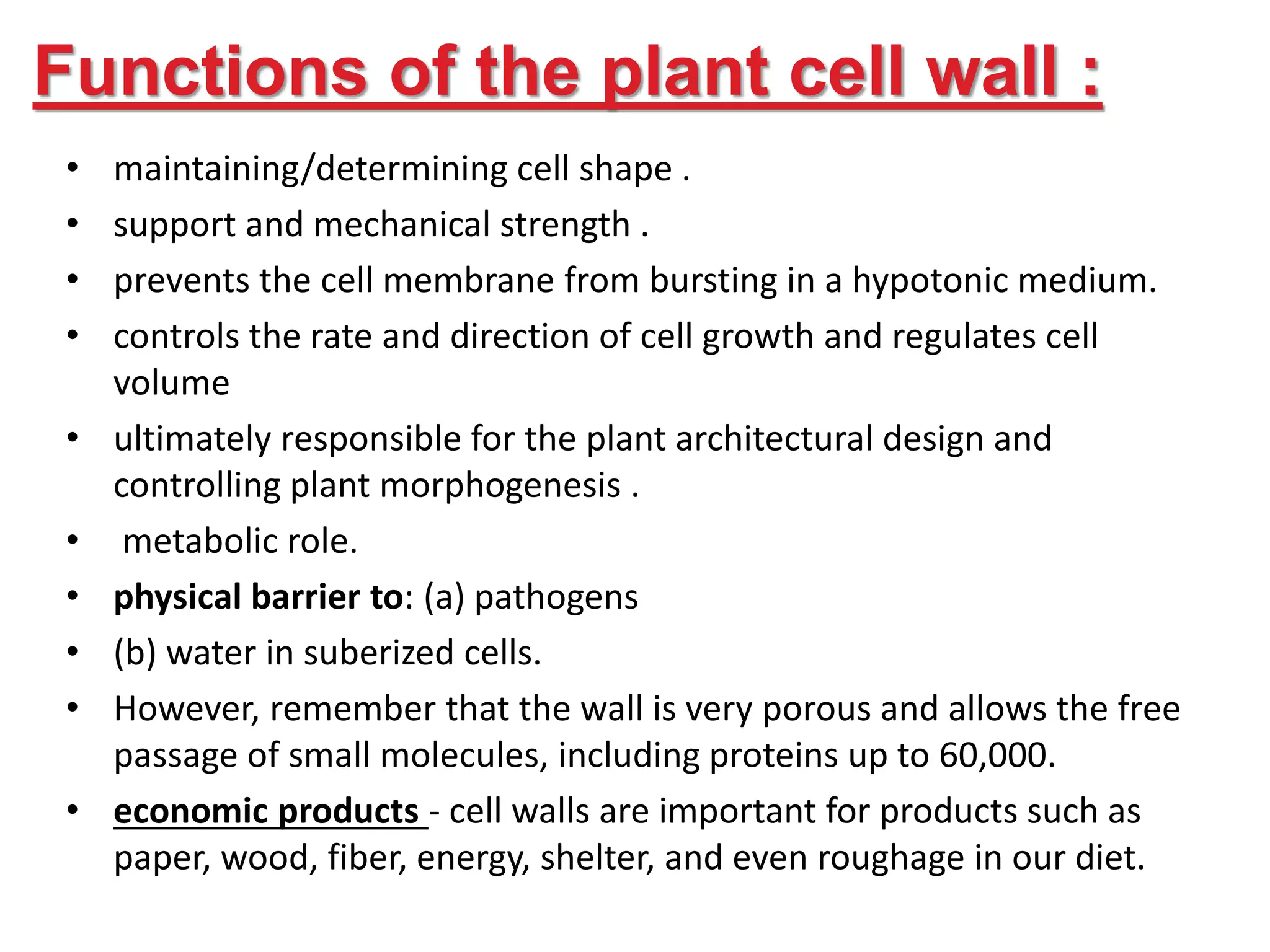
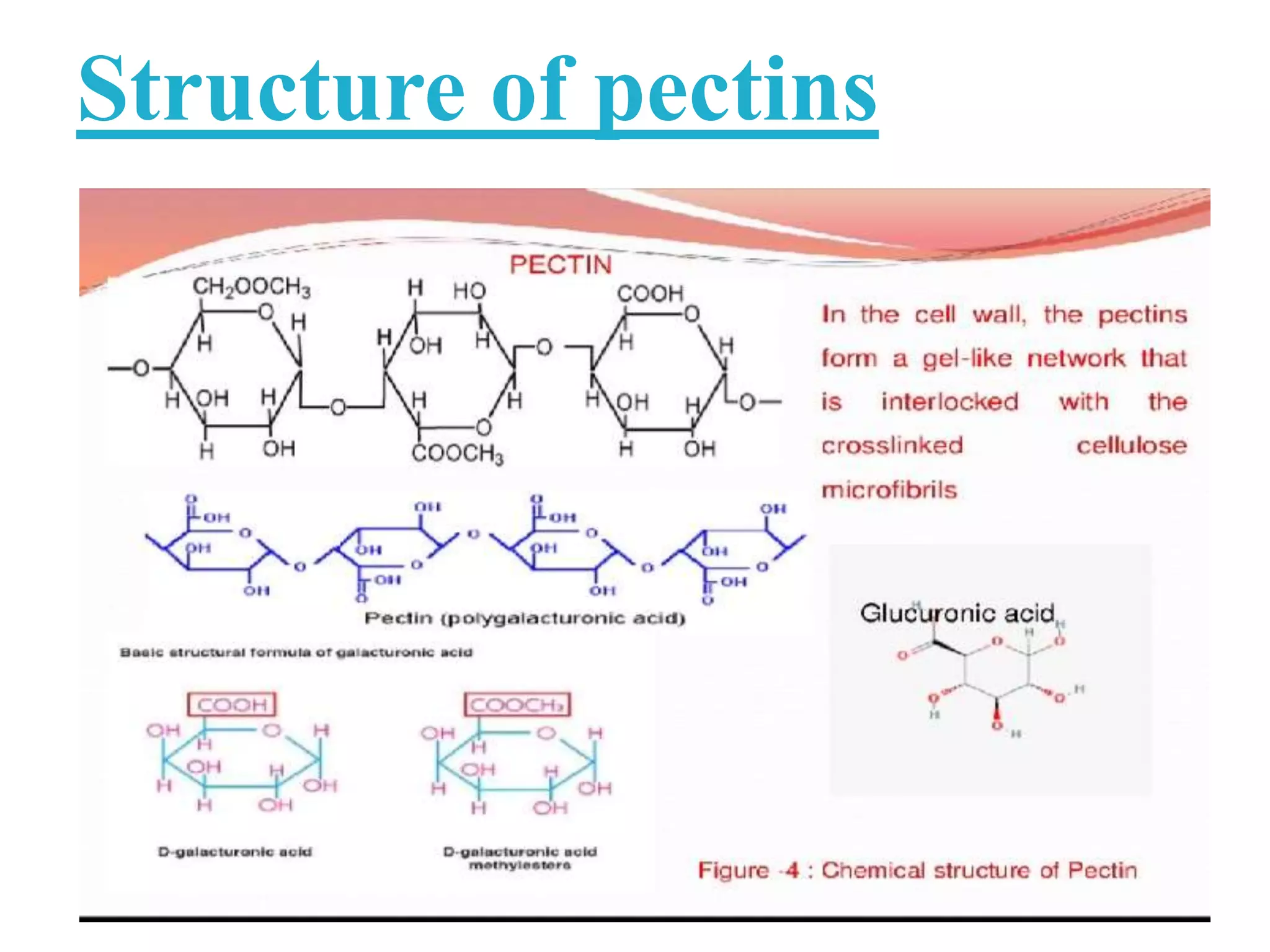
The document is a seminar paper from Jai Narain Vyas University focusing on the plant cell wall, covering its discovery, structure, functions, and components such as polysaccharides and proteins. It details the layers of the cell wall, including the middle lamella, primary, and secondary walls, and their roles in maintaining cell integrity and shape. Additionally, it discusses cell wall biosynthesis, economic importance, and various references related to cell biology.