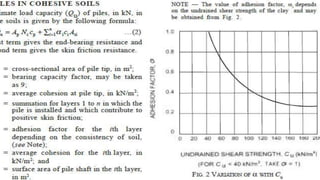
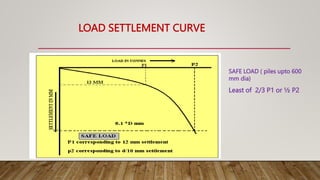
This document discusses pile foundations and provides classifications and details regarding pile types, requirements, construction, testing, and load determination. It defines a pile foundation as a deep foundation system that uses slender columns (piles) made of materials like concrete or steel to transfer structural loads into soil. Piles can be classified based on construction method (driven, bored), material (wood, steel, concrete), and load transfer mechanism (end bearing, friction, combined). Key factors requiring pile foundations and details regarding pile spacing, installation, concreting, and testing methods are also summarized.