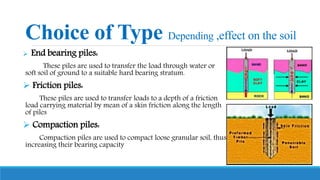
The document provides a comprehensive overview of pile foundations, detailing preliminary investigations, soil tests, and various types and techniques of piles used in construction. It highlights the advantages and disadvantages of using piles compared to raft foundations, including cost-effectiveness and structural strength, as well as challenges related to planning and installation. A soil investigation report is essential for determining the appropriate type of pile based on ground conditions.