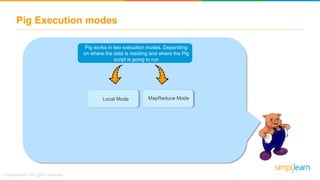
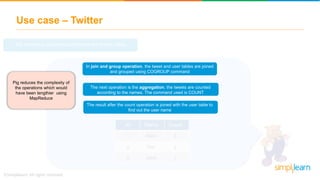
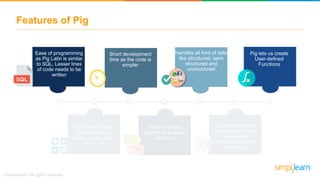
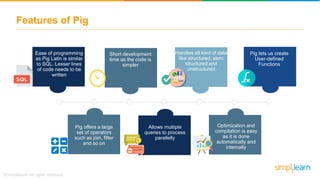
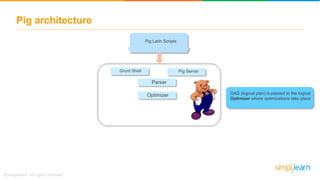
The document discusses key concepts related to the Pig analytics framework. It covers topics like why Pig was developed, what Pig is, comparisons of Pig to MapReduce and Hive, Pig architecture involving Pig Latin scripts, a runtime engine, and execution via a Grunt shell or Pig server, how Pig works by loading data and executing Pig Latin scripts, Pig's data model using atoms and tuples, and features of Pig like its ability to process structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data without requiring complex coding.


























































![Pig Latin data model
The data model of Pig Latin helps Pig to handle various
types of data
Examples
‘Rob’ or
50
Atom Tuple
(Rob,5)
Bag
{(Rob,5),(
Mike,10}
Map
[name#Mi
ke,
age#10]
Map is a set of key-value pairs. Key is of chararray type
and value can be of any type. It is represented by ‘[]’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pig-190607103738/85/Pig-Tutorial-Apache-Pig-Tutorial-What-Is-Pig-In-Hadoop-Apache-Pig-Architecture-Simplilearn-62-320.jpg)
![Pig Latin data model
The data model of Pig Latin helps Pig to handle various
types of data
Examples
‘Rob’ or
50
Atom Tuple
(Rob,5)
Bag
{(Rob,5),(
Mike,10}
Map
[name#Mi
ke,
age#10]
Map is a set of key-value pairs. Key is of chararray type
and value can be of any type. It is represented by ‘[]’
Pig Latin has a fully nestable data model
that means one data type can be nested
with another](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pig-190607103738/85/Pig-Tutorial-Apache-Pig-Tutorial-What-Is-Pig-In-Hadoop-Apache-Pig-Architecture-Simplilearn-63-320.jpg)