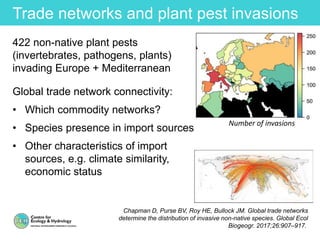
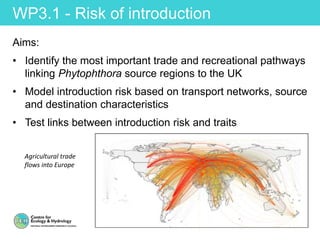
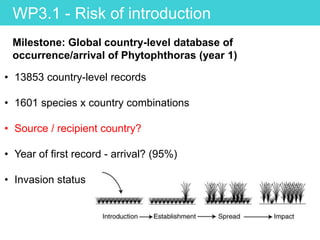
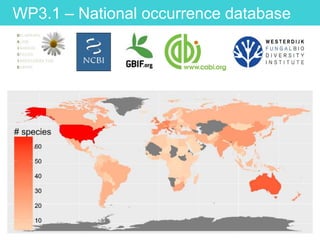
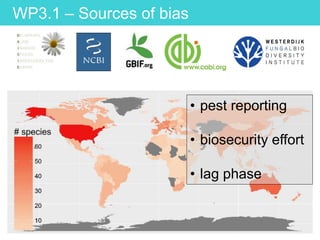
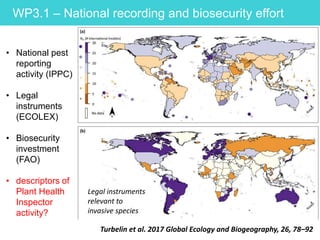
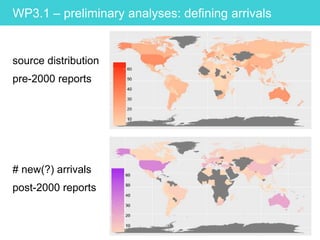
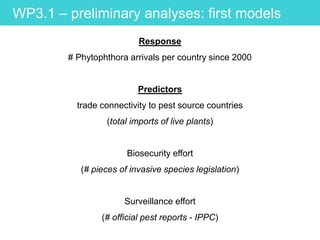
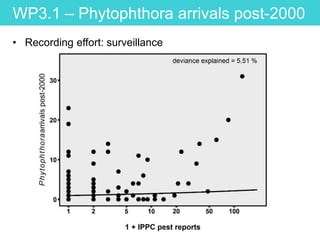
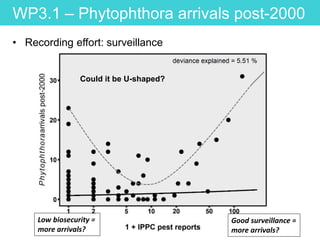
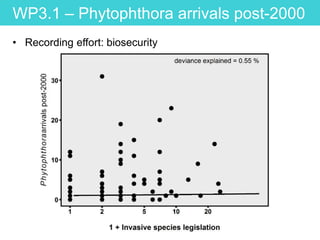
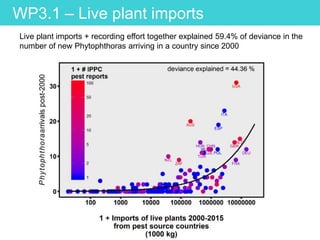
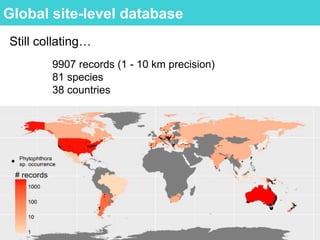
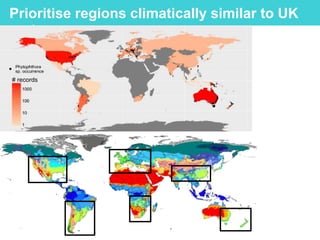
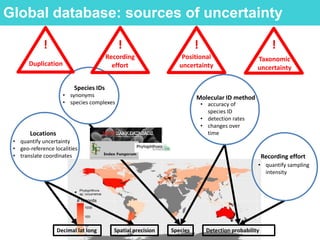
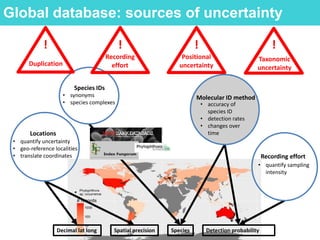
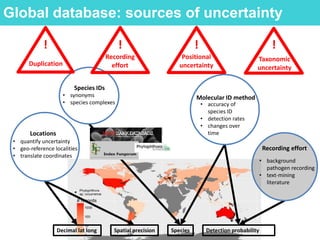
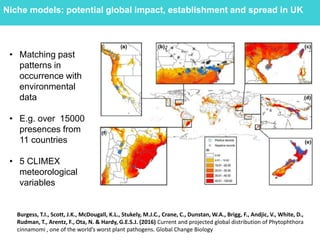
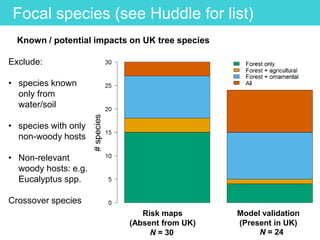
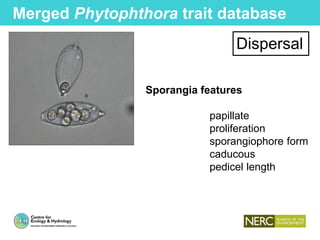
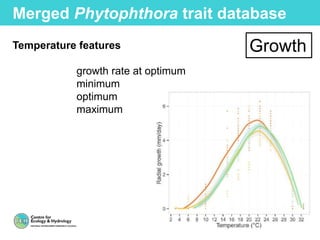
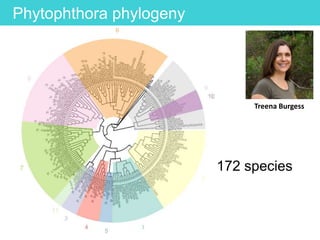
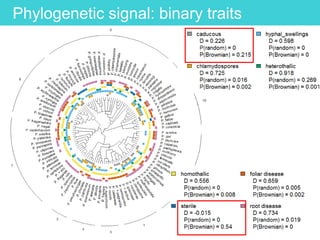
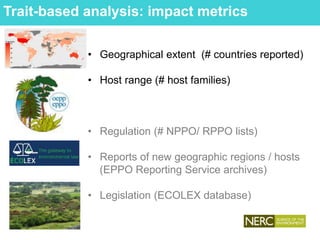
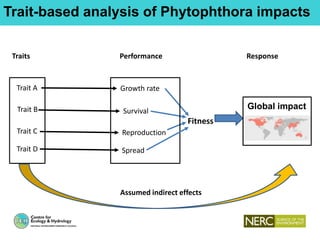
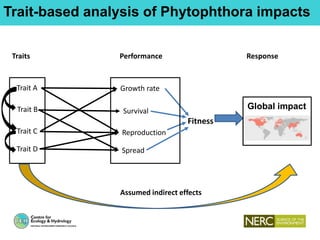
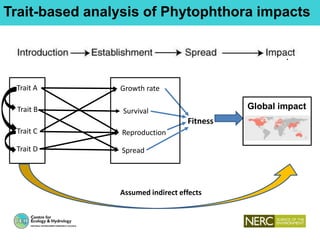
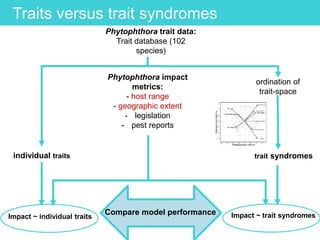
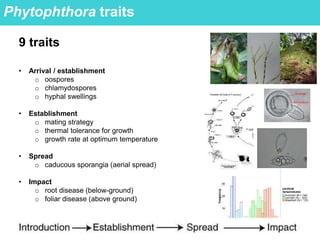
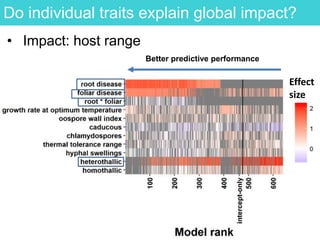
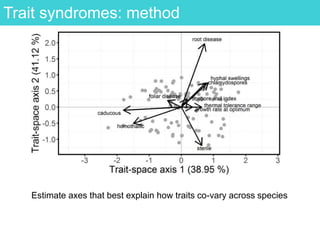
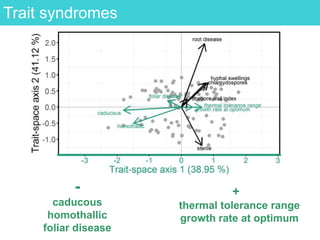
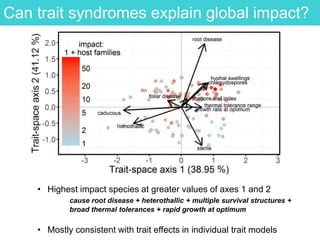
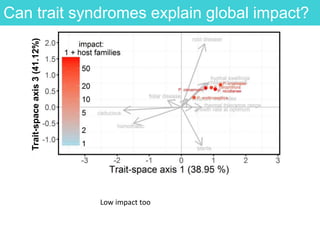
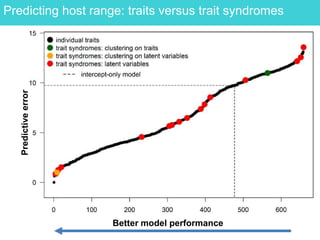
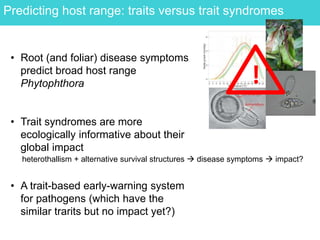
This document provides an overview of Work Package 3 (WP3) which aims to identify and rank global Phytophthora threats to the UK. WP3 has three main objectives: 1) assess the risk of introduction via pathways like trade and tourism; 2) evaluate the risk of establishment and spread based on traits, environments, and social factors; 3) conduct horizon scanning to identify knowledge gaps on emerging pathogens. The WP3 team and their roles are listed. Several milestones are outlined, including compiling occurrence and trait databases to inform risk models, which will result in a policy brief to improve Phytophthora risk ranking. Preliminary analyses on introduction risk are presented.