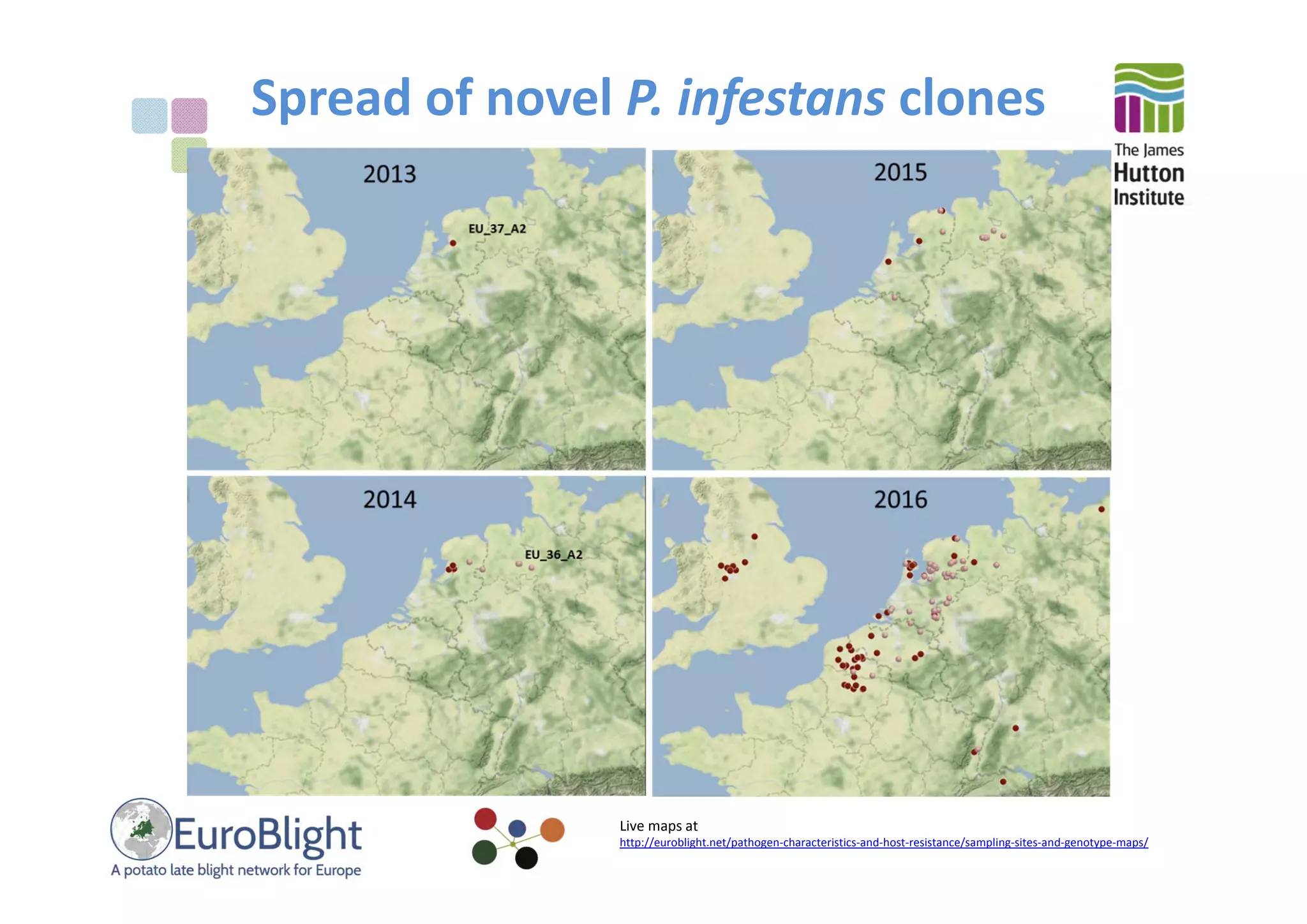
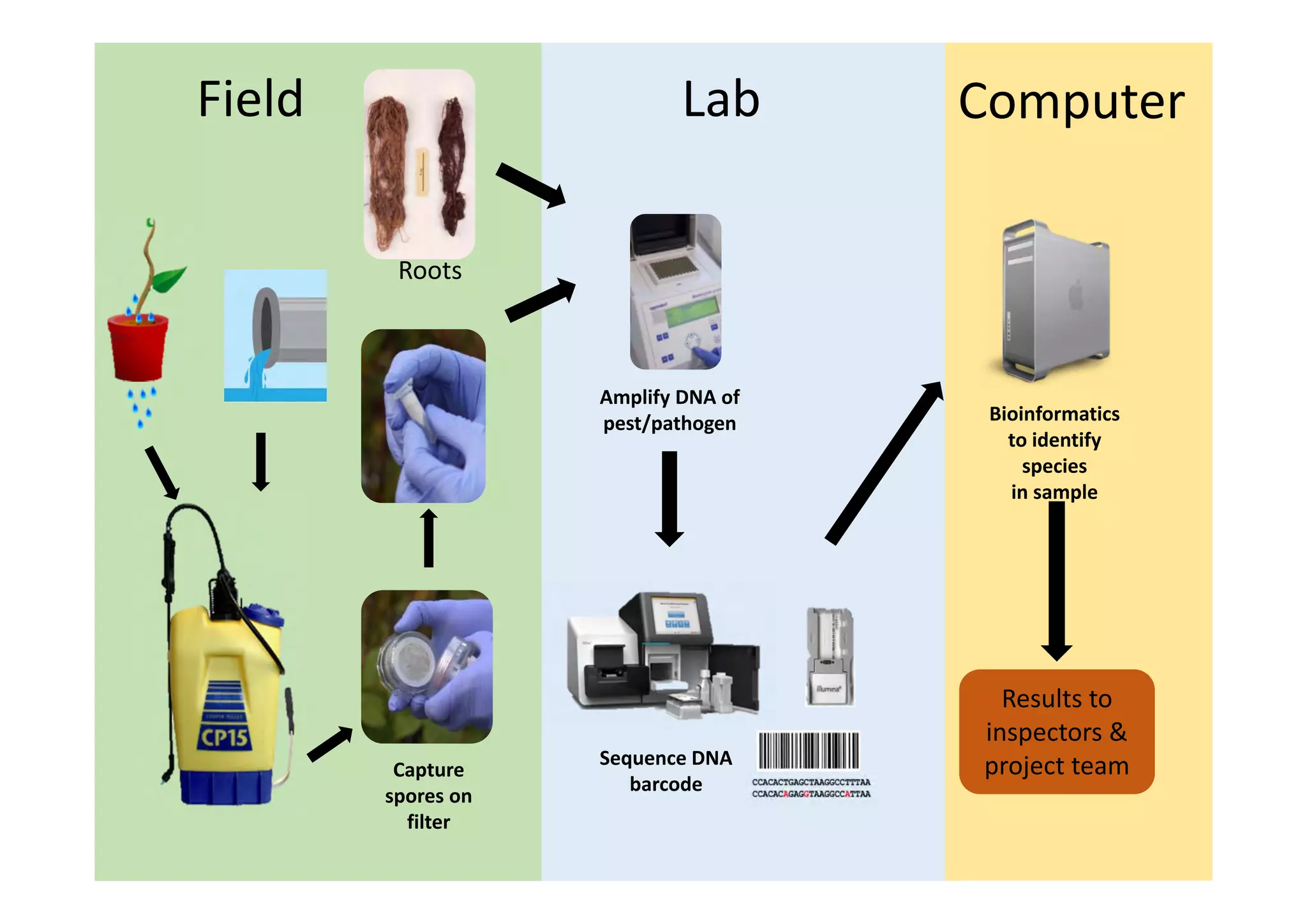
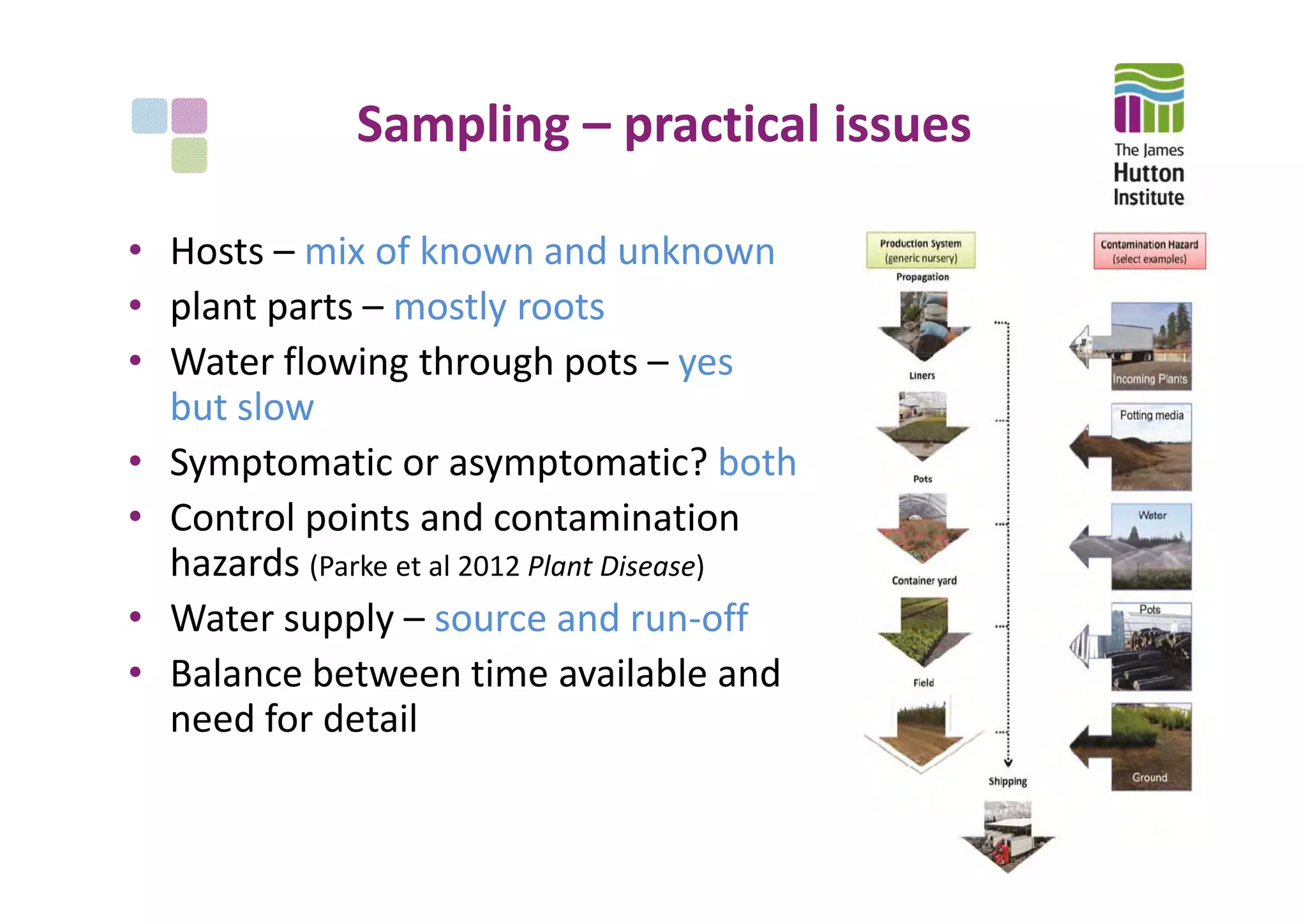
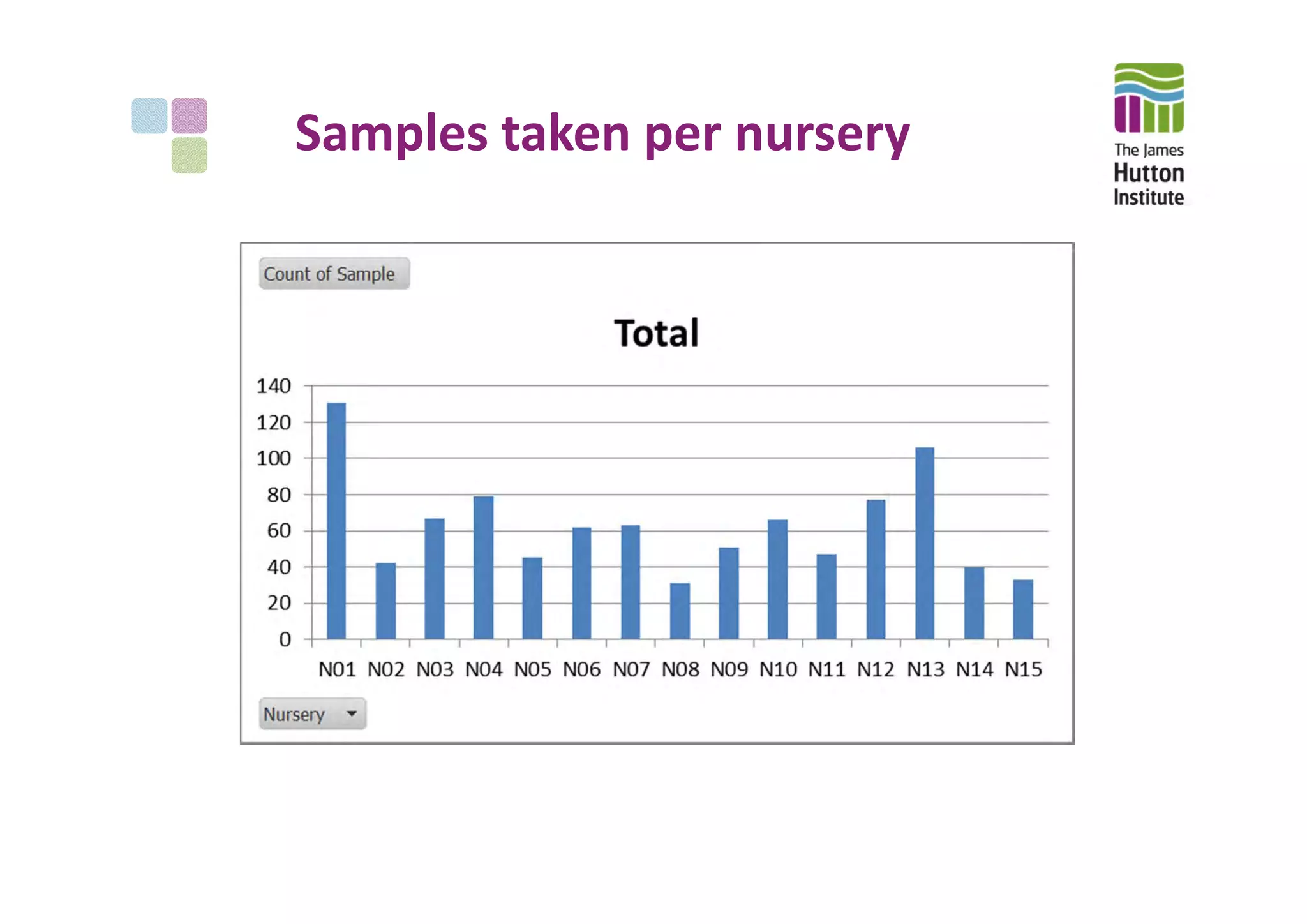
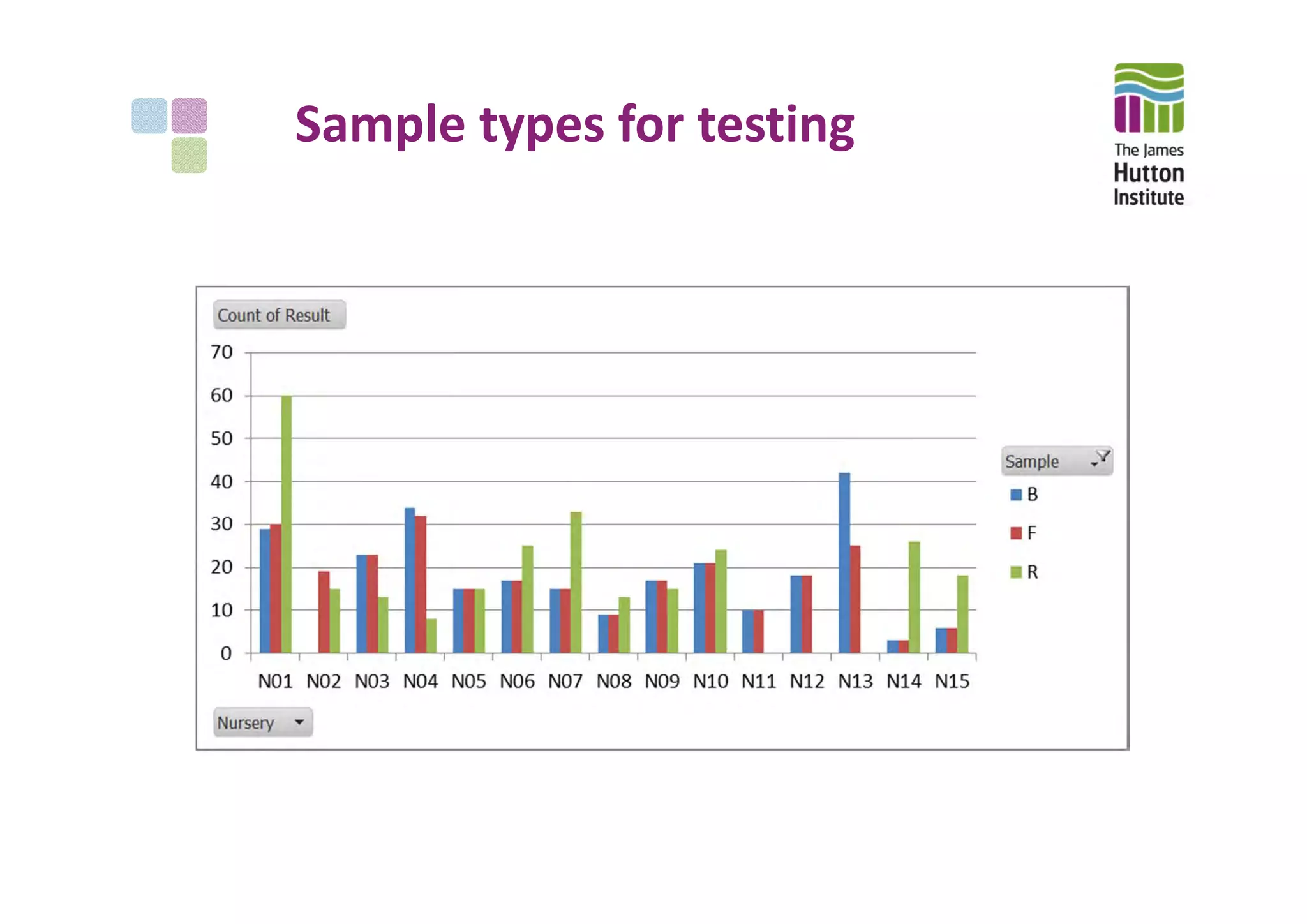
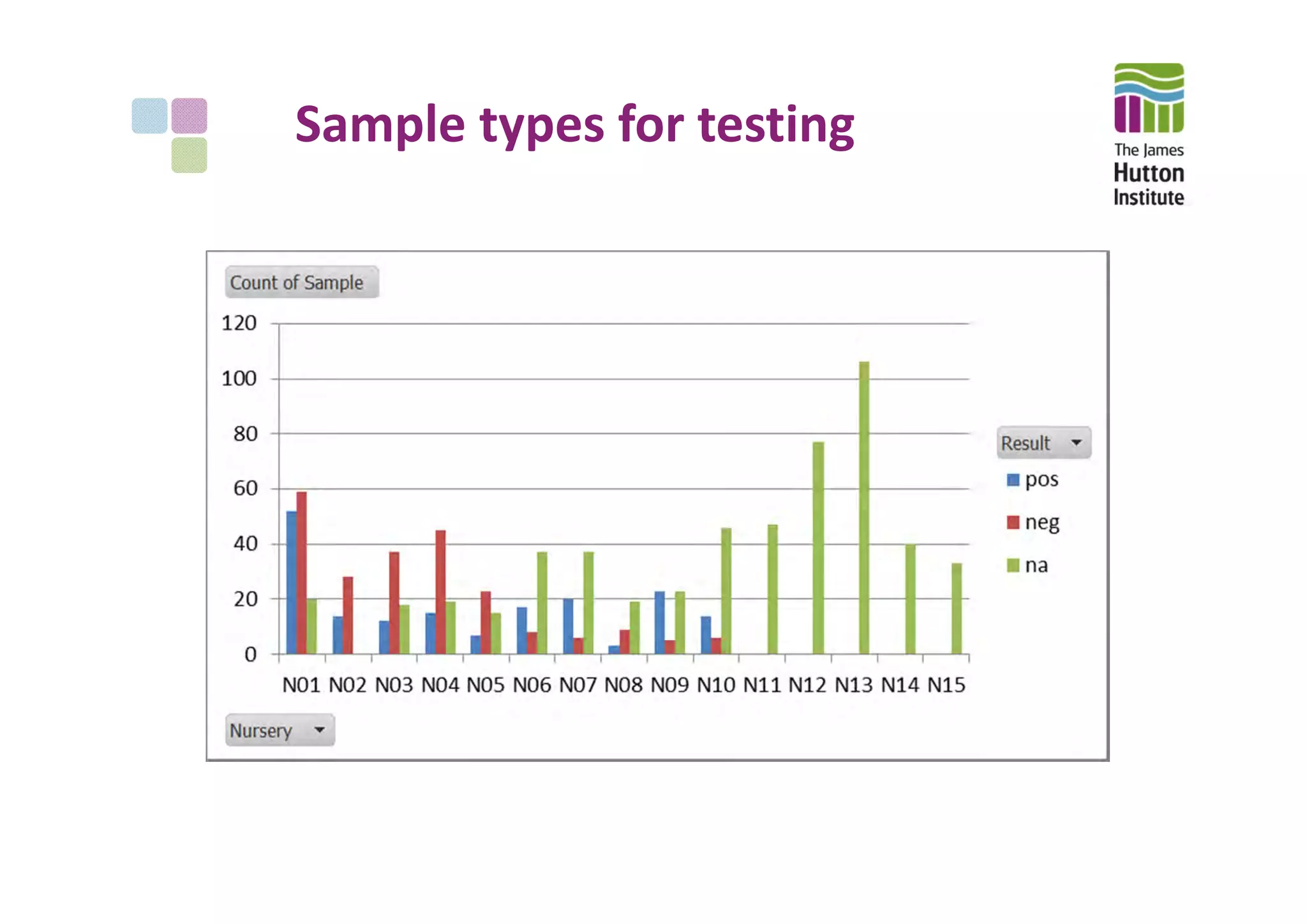
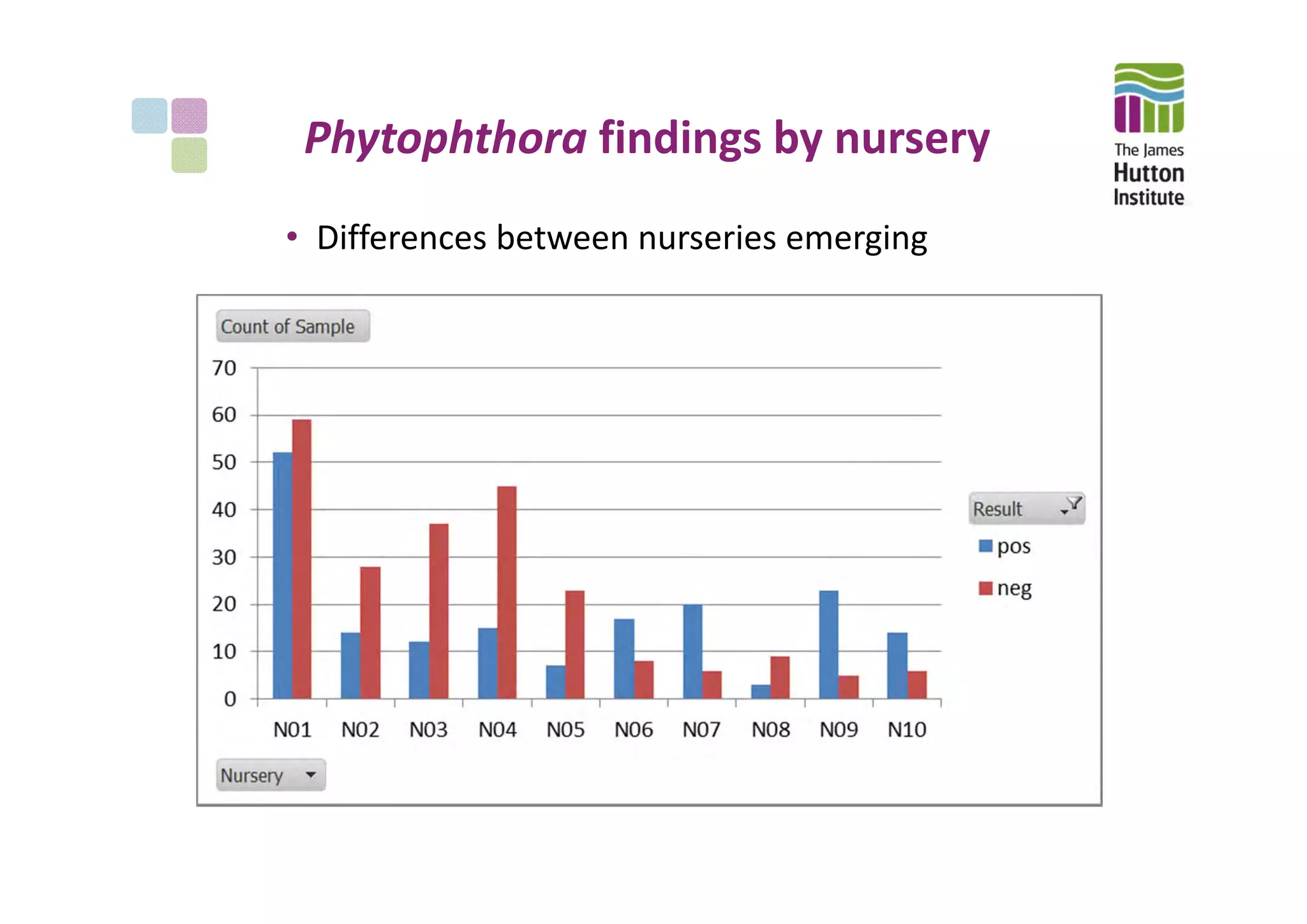
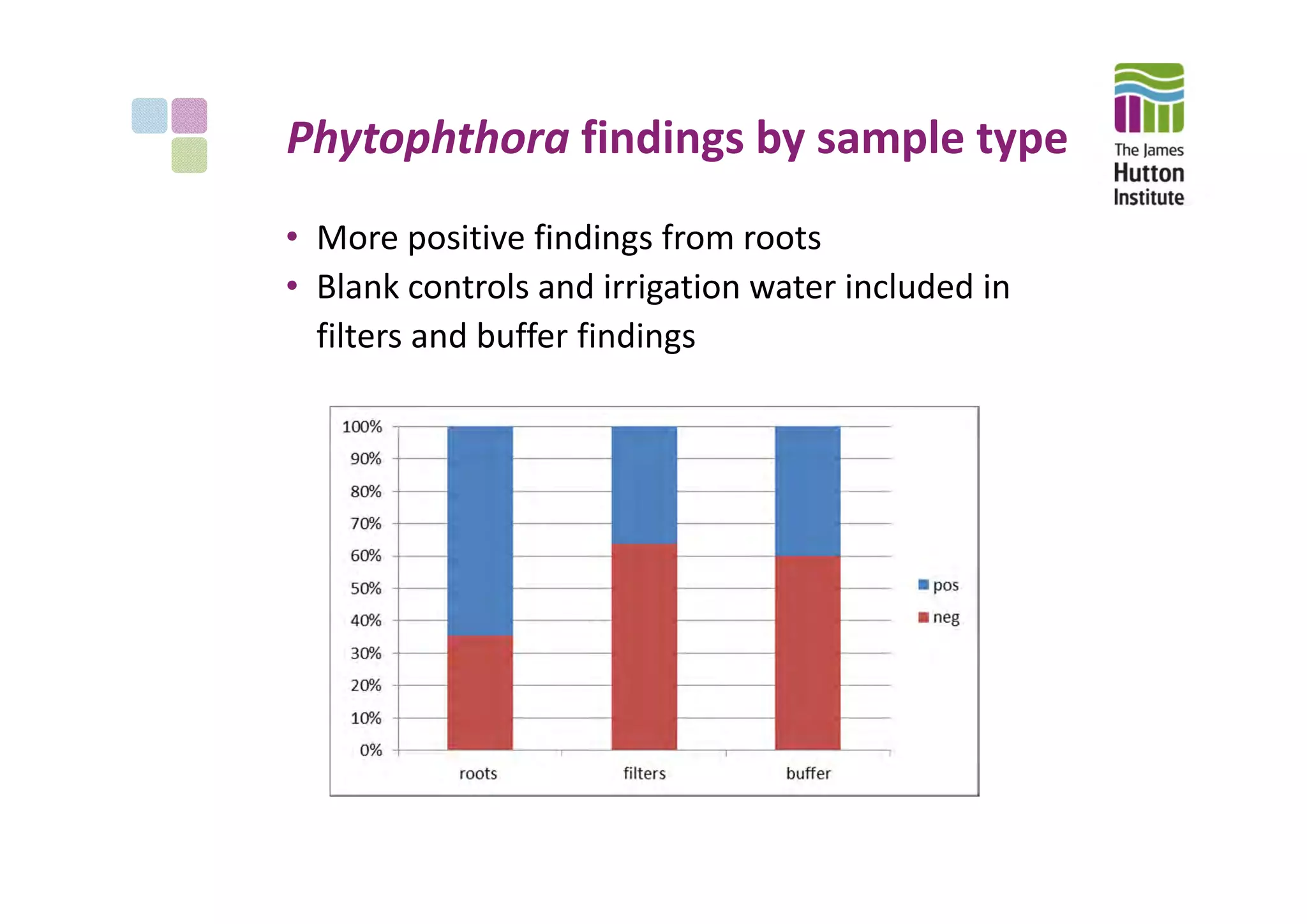
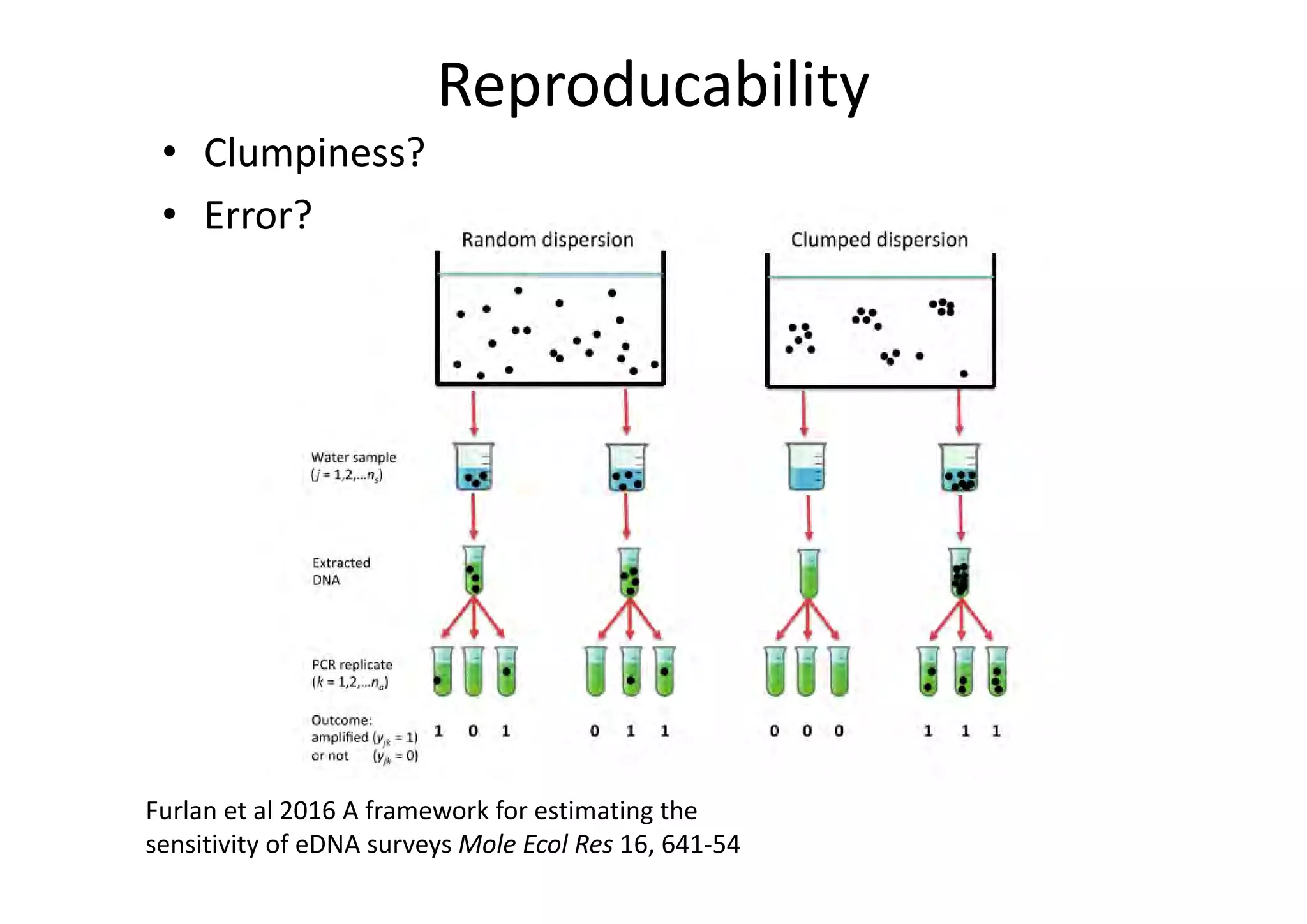
This document summarizes the objectives, methods, and progress of a project studying Phytophthora in UK plant nursery systems. The project aims to analyze Phytophthora communities in nurseries using metabarcoding, and model variation among nurseries based on trade, management, and ecology factors. Methods include surveying nurseries, sampling at fine and broad scales, detecting and identifying Phytophthora via sequencing, and providing feedback. To date, over 1000 samples from 15 nurseries have been collected and 395 tested, finding Phytophthora in roots and irrigation water. Next steps include broad-scale sampling, resampling partner nurseries, extracting and sequencing additional samples, and estimating sequencing error rates.