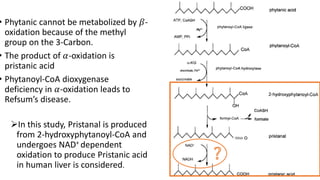
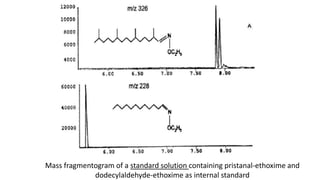
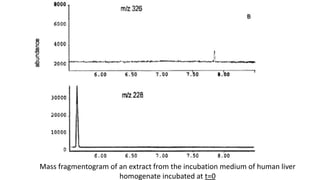
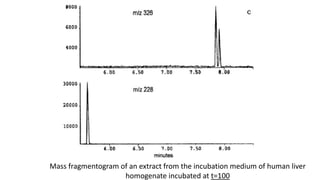
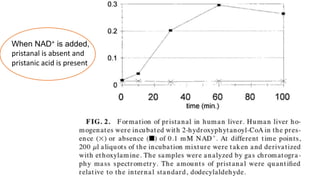
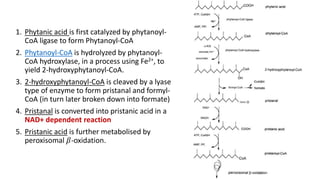
The document discusses the α-oxidation pathway of phytanic acid, identifying pristanal as a key product resulting from the decarboxylation of 2-hydroxyphytanoyl-CoA. The study outlines the metabolic process in human liver that converts phytanoyl-CoA into pristanic acid, highlighting deficiencies that lead to Refsum's disease. It also details the methods of analysis for pristanal and pristanic acid, emphasizing the enzymatic steps involved in their production and subsequent metabolism.