1. Magnetic flux is the measure of magnetic field passing through a surface area and is calculated as the dot product of the magnetic field and area vectors. Magnetic flux density is the amount of magnetic flux passing through a unit area perpendicular to the flux.
2. Ampere's law can be used to determine magnetic flux density inside a solenoid. By applying the law to a rectangular loop enclosing the solenoid, the magnetic field strength inside is calculated to be proportional to the current through the solenoid.
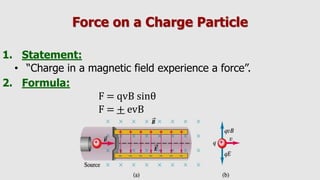
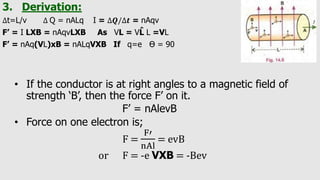
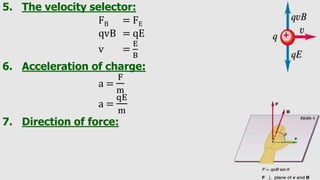
3. A moving charge experiences a magnetic Lorentz force perpendicular to both its velocity and the magnetic field. The direction of the force is given by the right hand grip rule.