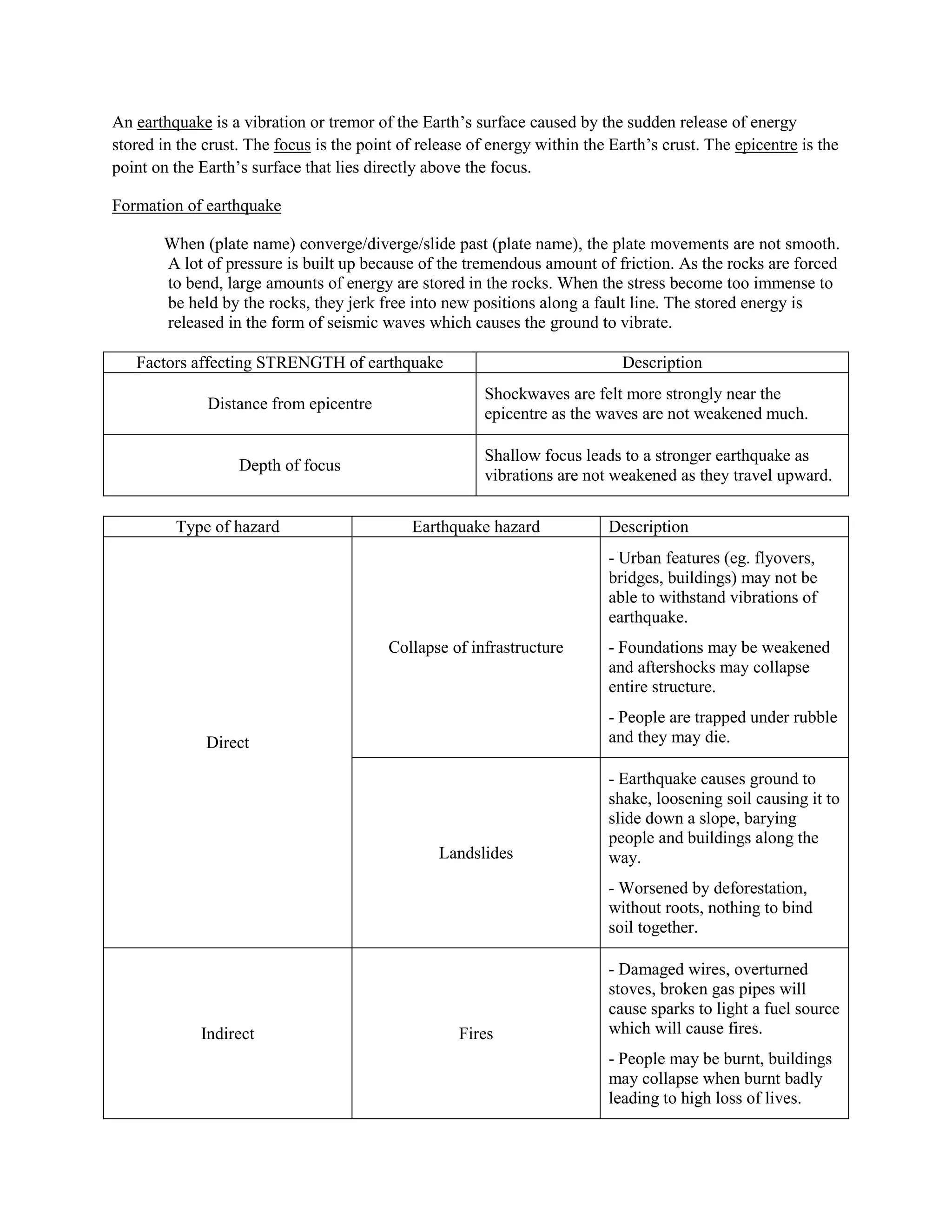
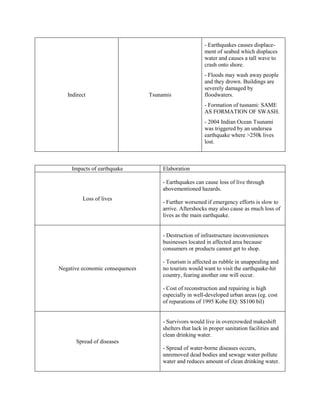
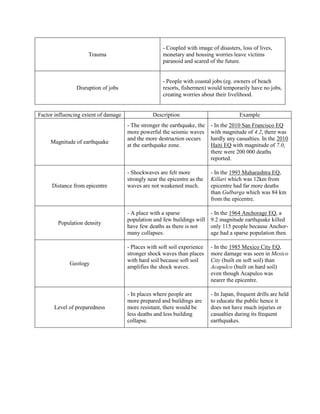
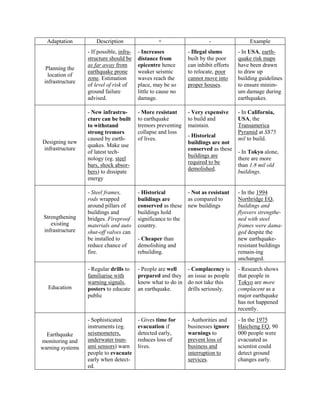
An earthquake is caused by a sudden release of energy stored in the Earth's crust along a fault line. The focus is the point of energy release within the crust, while the epicenter is the point directly above the focus on the surface. When plate movements cause built-up stress to exceed rocks' limits, the stored energy is released as seismic waves, causing the ground to vibrate and potentially damage infrastructure through collapse or landslides. Earthquakes can also indirectly cause fires, tsunamis, and other hazards.