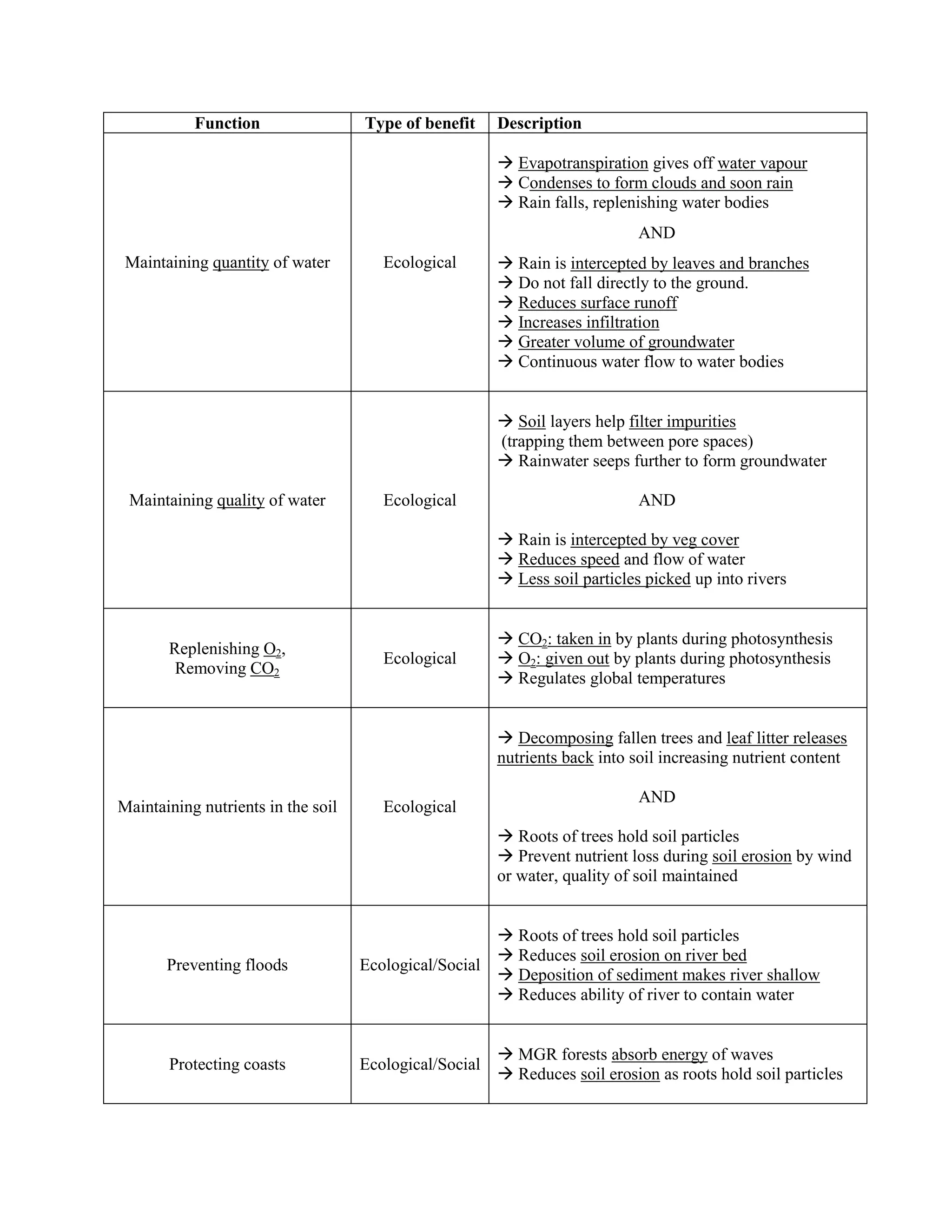
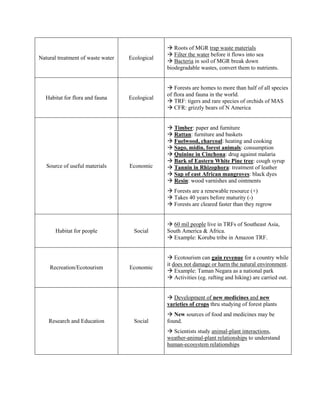
The document describes various functions and benefits that forests provide, including ecological, economic, and social benefits. Ecologically, forests help maintain water quantity and quality by intercepting rain and reducing runoff, replenish oxygen levels through photosynthesis, maintain soil nutrients, and provide habitat. Economically, forests are a source of useful materials for industry, fuel, food and medicine. They also enable recreation and ecotourism. Socially, forests provide habitat for indigenous people and allow for research and education.