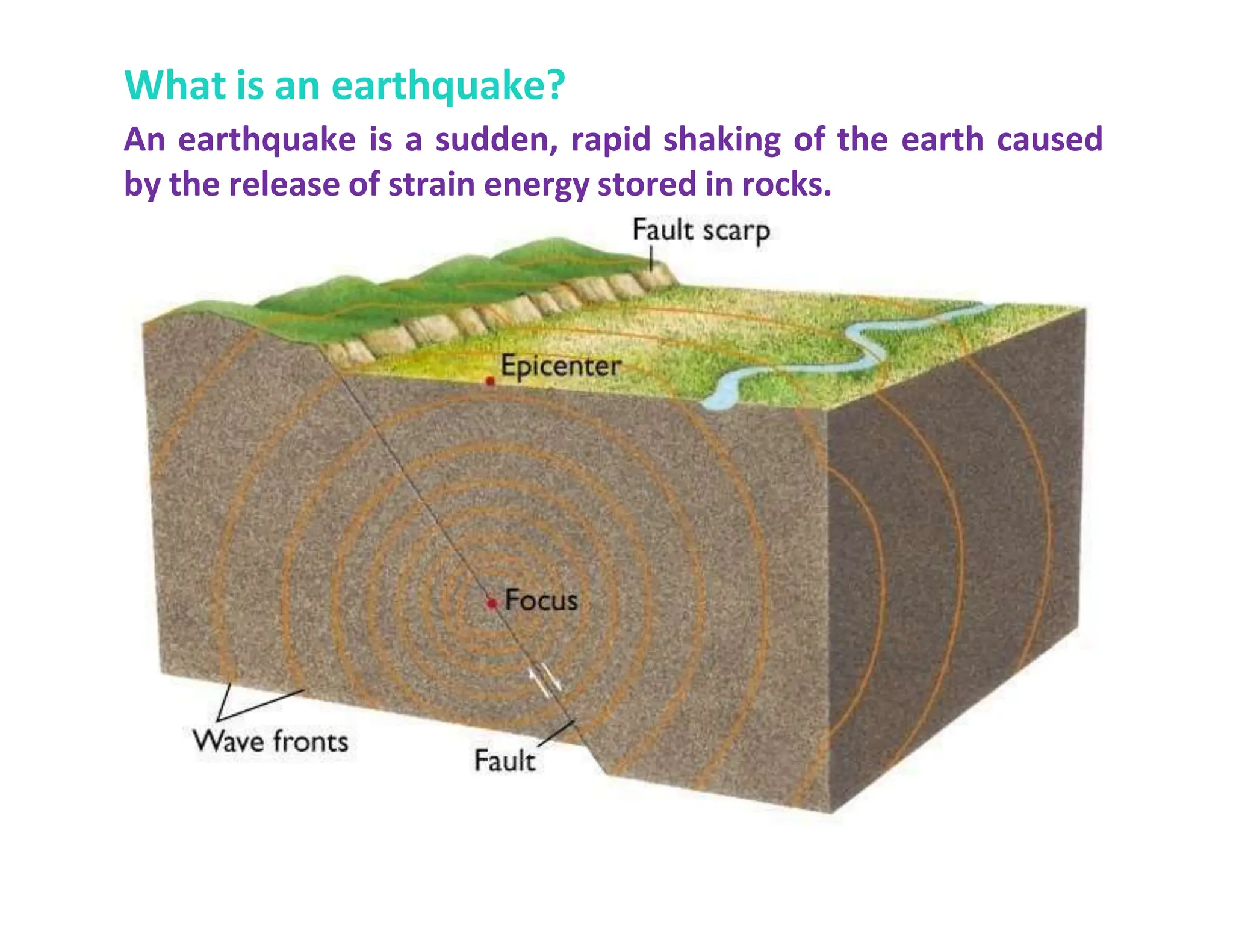
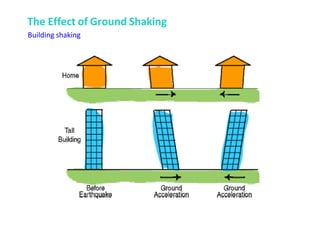
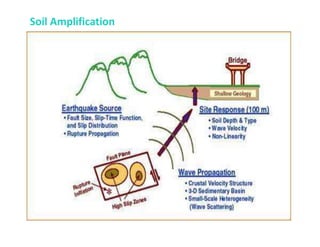
An earthquake is a sudden shaking of the earth caused by the release of stored strain energy in rocks, leading to various seismic hazards. These hazards include ground shaking, ground displacement, flooding, fire, landslides, liquefaction, and tsunamis, each having distinct impacts on the environment and structures. Additionally, secondary effects from earthquakes can exacerbate damage, such as ruptured dams causing flooding and damaged gas lines leading to fires.