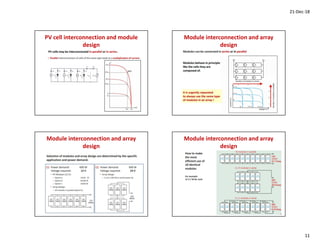
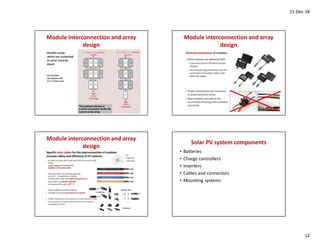
This document discusses solar photovoltaics (PV) and includes the following key points:
1. PV systems use electronic components to convert solar radiation into electricity, with greater intensity of sunlight producing greater electricity flow.
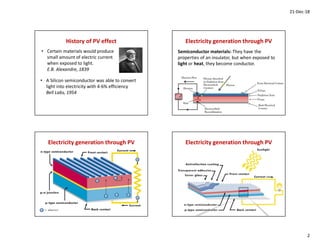
2. The photovoltaic effect was first observed in 1839, and silicon semiconductor cells that could convert light to electricity with 4-6% efficiency were developed by Bell Labs in 1954.
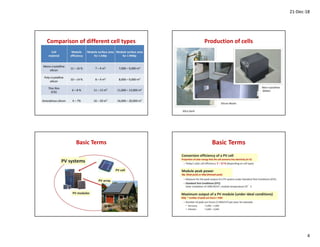
3. There are three main types of PV cell materials - mono-crystalline, polycrystalline, and amorphous thin-film - which have different efficiencies, costs, and appearances.