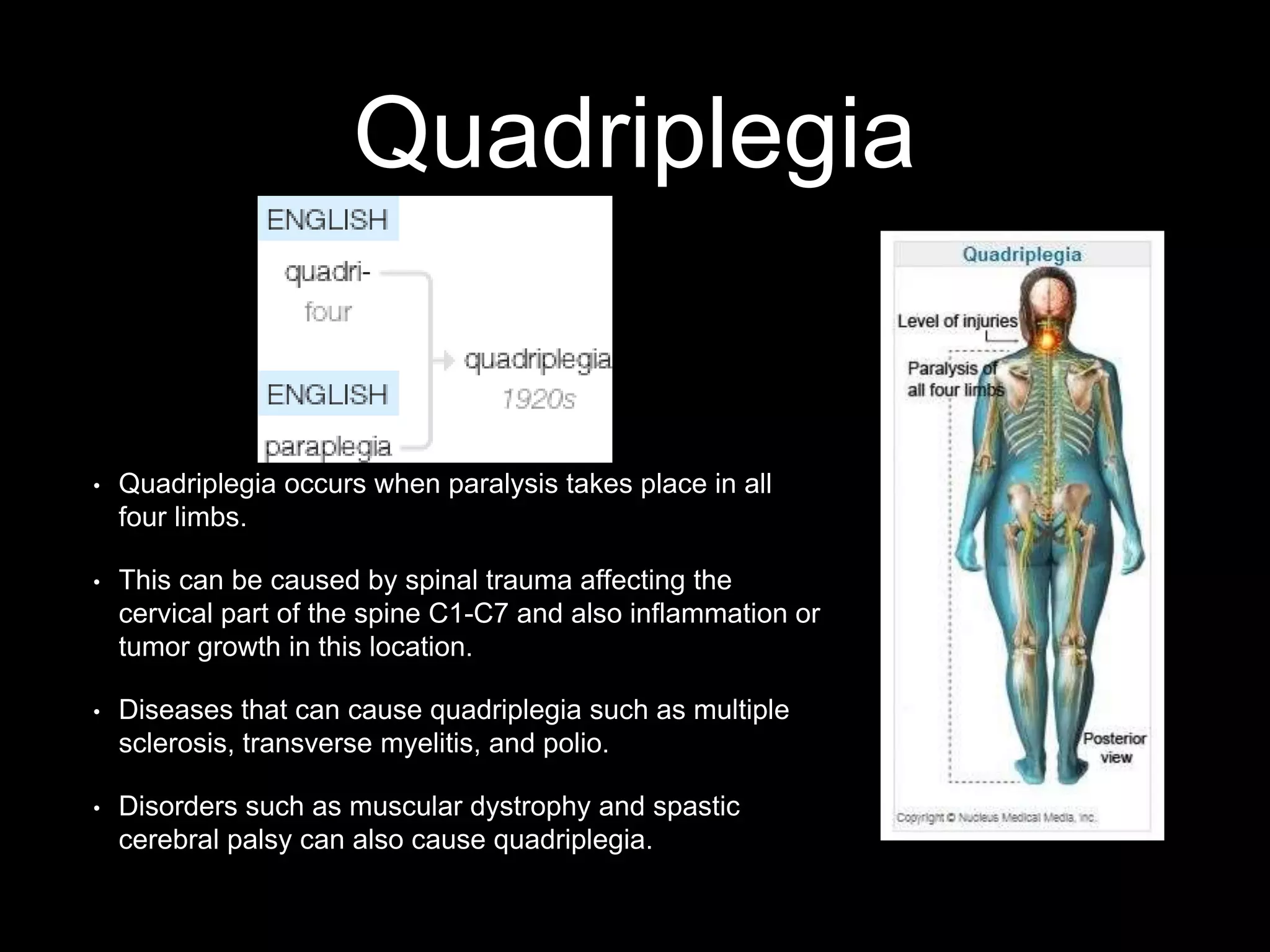
This document discusses medical terminology related to suffixes, specifically -phasia and -plegia. It defines suffixes as parts of words that add meaning related to conditions, diseases or procedures. -Plegia indicates paralysis and is seen in quadriplegia (paralysis of all four limbs caused by spinal cord injury) and paraplegia (paralysis of the legs, also from spinal issues). -Phasia relates to speech and is seen in aphasia (inability to communicate verbally or in writing due to brain damage) and dysphasia (difficulty communicating or writing, often due to stroke). The document provides details on the symptoms, causes and characteristics of these medical conditions involving paralysis or speech issues.