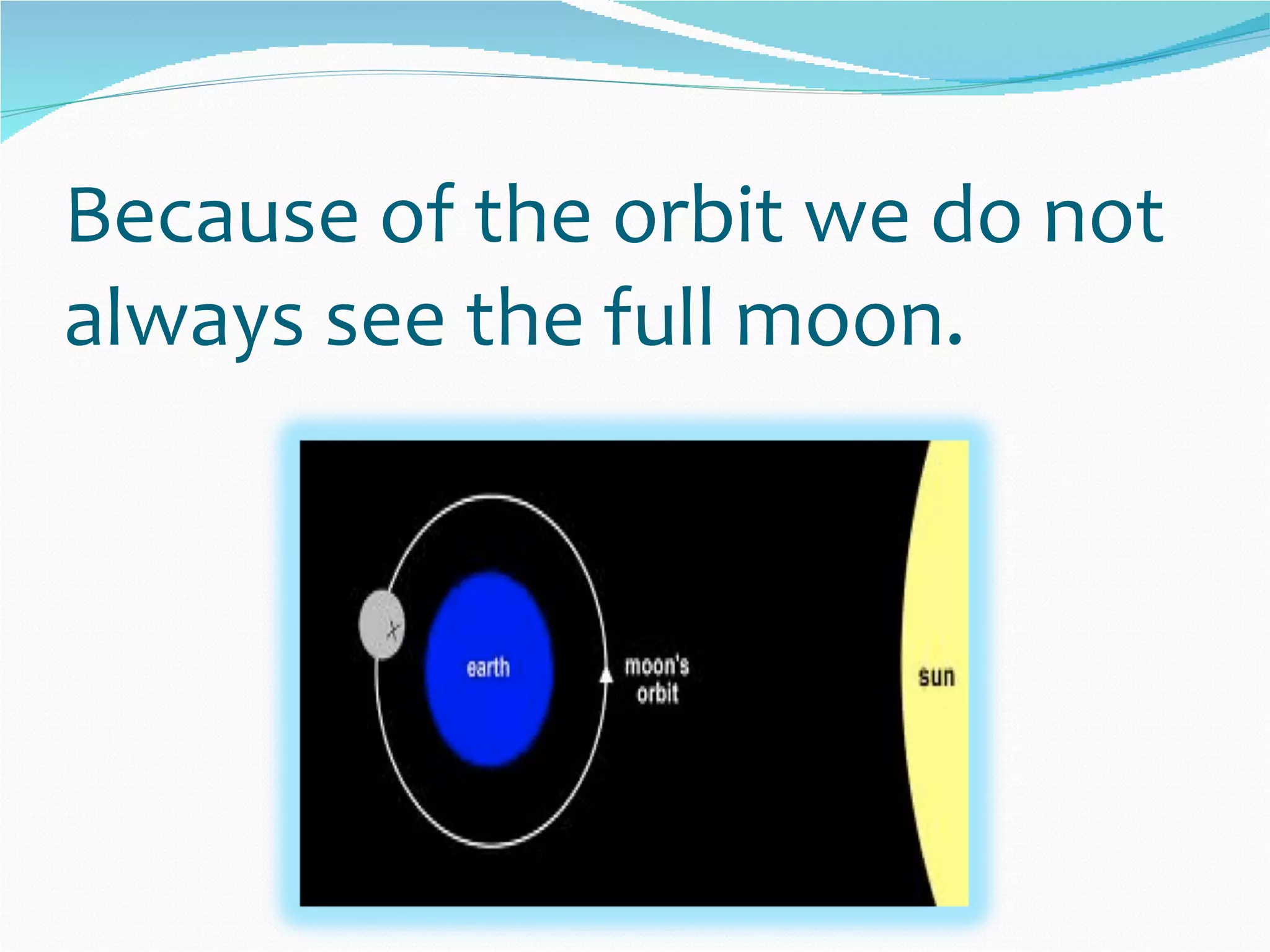
The document discusses the phases of the moon over a four week lunar cycle. It explains that the moon does not produce its own light, but rather reflects sunlight. The phase we see from Earth depends on the relative positions of the Earth, moon, and sun. As the moon orbits Earth, its illuminated portion waxes from a new moon to a full moon, then wanes back to a new moon again. The phases include the new moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, last quarter, and waning crescent.