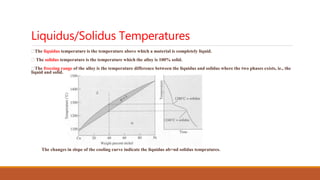
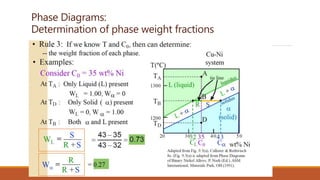
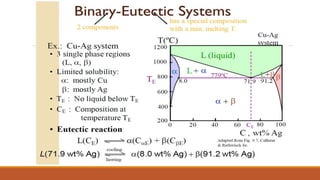
The document provides information about phase diagrams and equilibrium diagrams. It defines a phase as a state of matter that has uniform structure, composition, and properties throughout, with a clear interface between it and other phases. A phase diagram graphically represents the phases present in a material at different temperatures, pressures, and compositions, describing equilibrium conditions. It indicates melting/solidification temperatures and phase formation ranges. General types of solid solutions and Hume-Rothery's rules for substitutional solutions are discussed. Gibbs' phase rule relates the number of coexisting phases to components and degrees of freedom. Different types of phase diagrams including unary, binary, ternary and quaternary are classified.