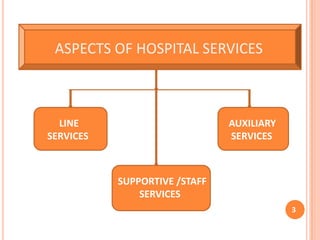
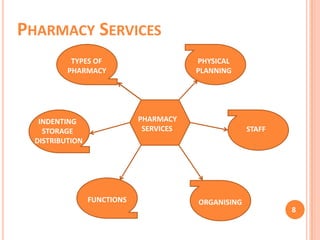
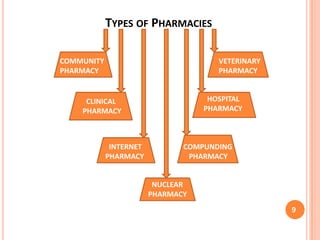
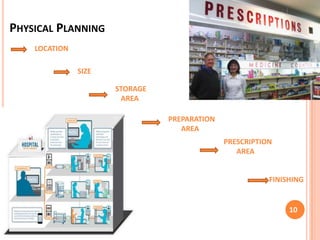
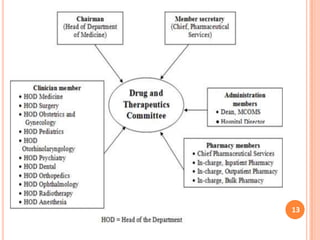
The document discusses aspects of pharmacy services in hospitals. It outlines the different types of services including line services like emergency care, inpatient and outpatient services. Supportive services include the pharmacy, laboratory, and radiology. The pharmacy purchases and dispenses all medications used in the hospital. A well-staffed pharmacy department headed by a qualified pharmacist is crucial for ensuring the right medications are available when needed. The pharmacist works closely with medical staff and a drug committee to establish treatment protocols and formularies. Effective pharmacy services are essential for patient treatment and care in hospitals.