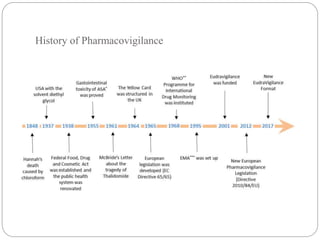
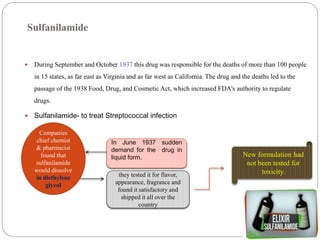
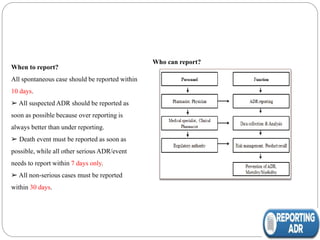
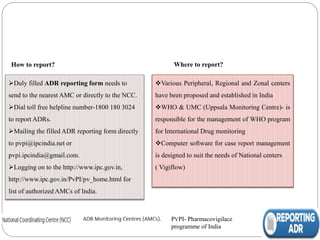
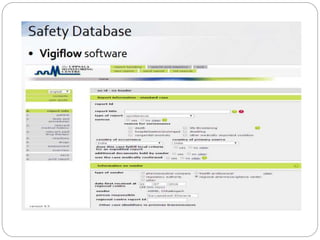
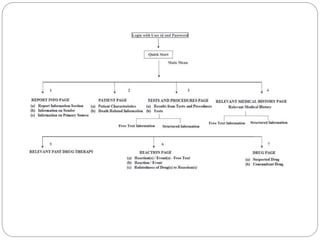
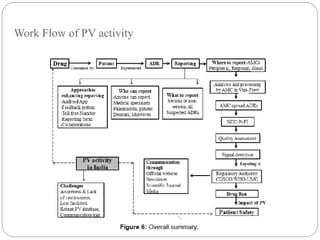
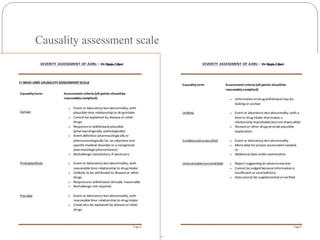
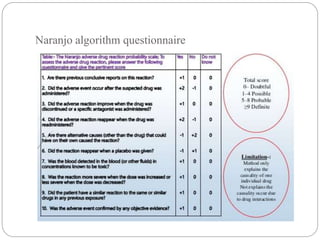
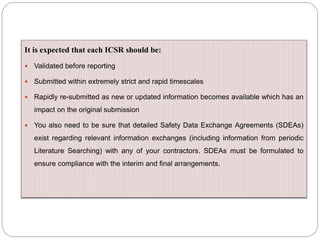
Pharmacovigilance is the science of monitoring the safety of pharmaceutical drugs. It aims to improve patient care, public health, and understanding of medication risks. The need for formal pharmacovigilance arose from tragedies like the deaths from chloroform in 1848 and the thalidomide disaster in the 1960s, which caused birth defects. This led to the establishment of organizations like the WHO Programme for International Drug Monitoring in 1968 to systematically collect and analyze reports of adverse drug reactions.