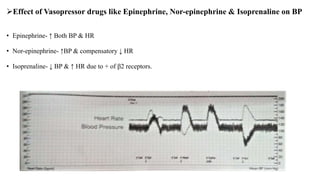
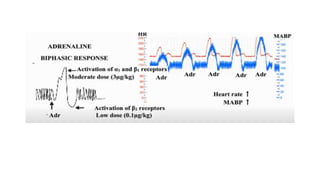
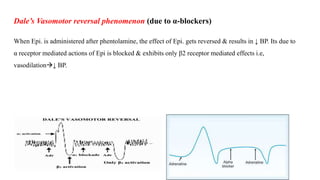
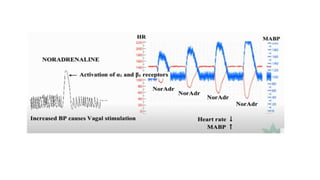
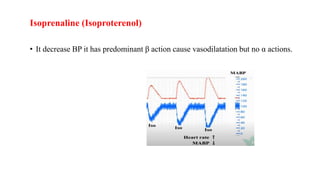
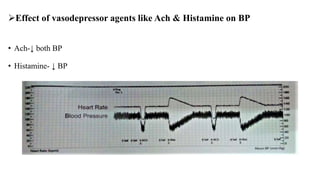
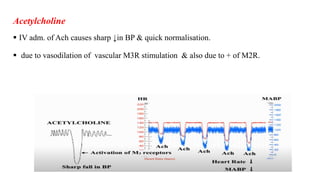
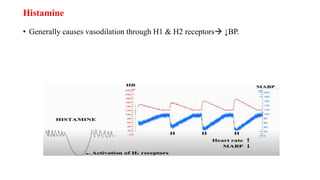
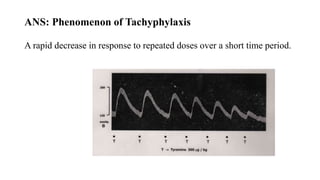
This document discusses demonstrating the effects of various drugs on blood pressure and heart rate using simulation software. It describes how vasopressors like epinephrine, norepinephrine, and isoproterenaline affect blood pressure and heart rate. Epinephrine causes an initial sharp increase in blood pressure followed by a decrease. Norepinephrine causes a sharp increase in blood pressure. Isoproterenaline decreases blood pressure. It also discusses vasodepressor drugs like acetylcholine and histamine, which decrease blood pressure.