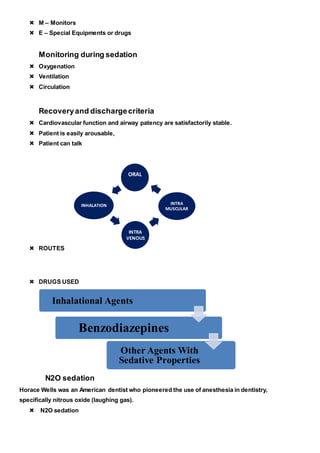
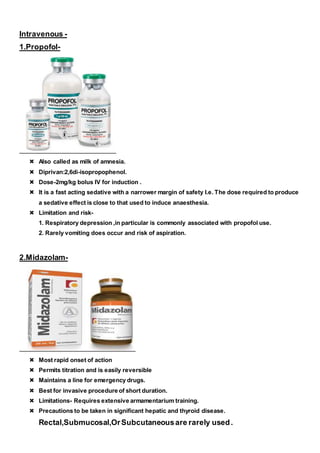
The document discusses pharmacological methods for behavior management in pediatric dentistry, including conscious sedation, general anesthesia, and various medications used for sedation. It outlines the objectives, indications, contraindications, and clinical guidelines for sedation procedures, emphasizing the importance of properly managing children's anxiety and behavior during dental treatments. Key sections include details on nitrous oxide sedation, premedication options, and considerations for safely administering anesthesia to young patients.