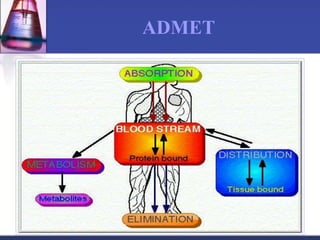
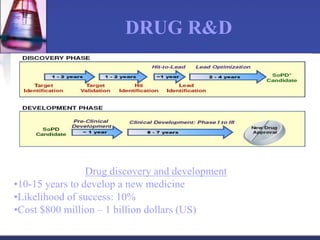
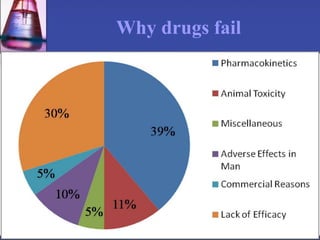
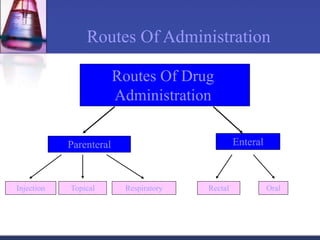
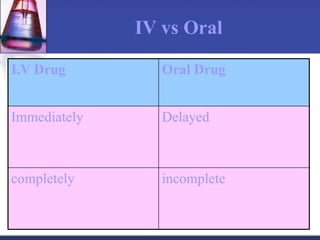
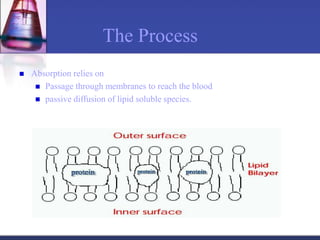
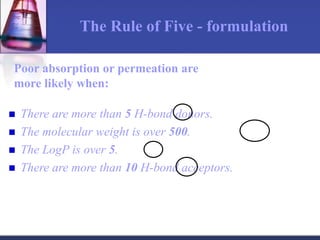
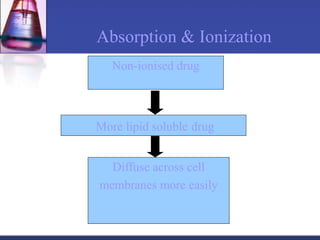
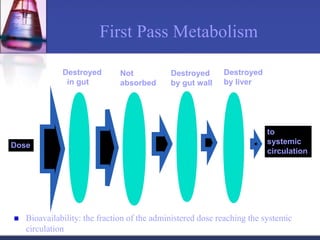
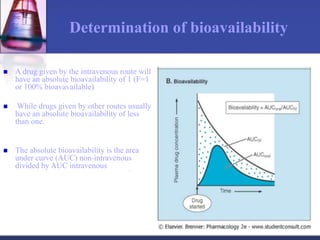
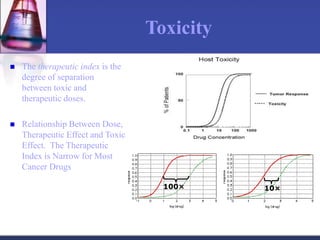
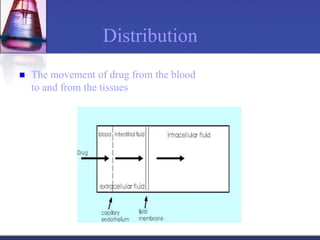
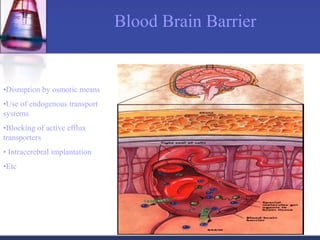
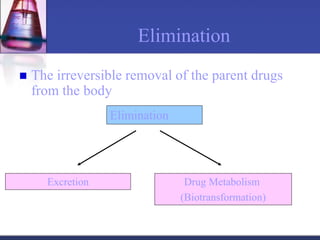
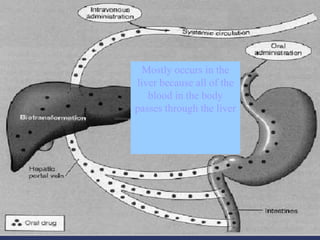
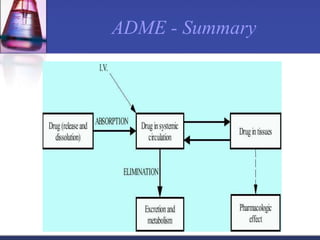
Pharmacokinetics is the study of what the body does to a drug, including absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Absorption involves a drug entering systemic circulation, which can be impacted by factors like solubility, ionization, and first-pass metabolism. Distribution of drugs is determined by properties like volume of distribution, plasma protein binding, and ability to cross membranes like the blood-brain barrier. Metabolism, usually by the liver, makes drugs more polar through Phase I and Phase II reactions to facilitate excretion. The major routes of excretion are renal and biliary, and metabolism is necessary to make many drugs water-soluble enough to be excreted from the body.