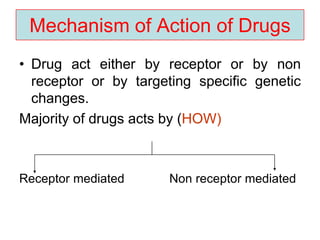
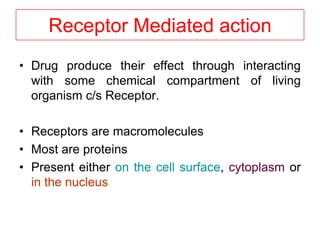
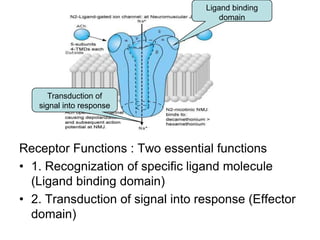
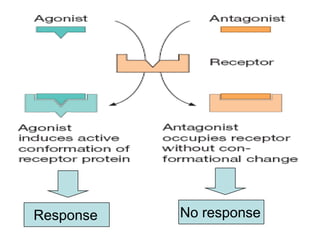
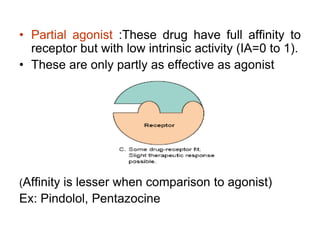
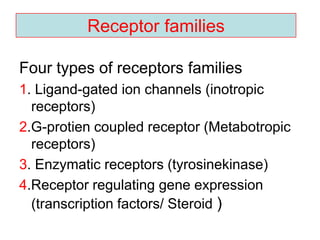
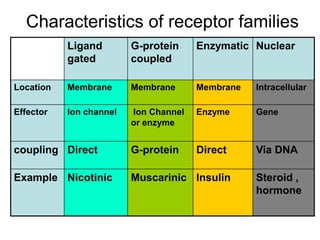
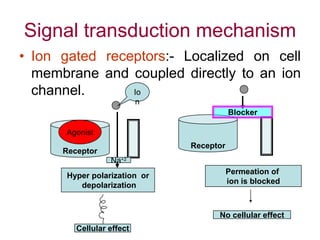
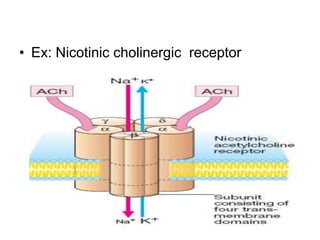
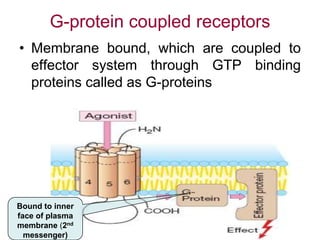
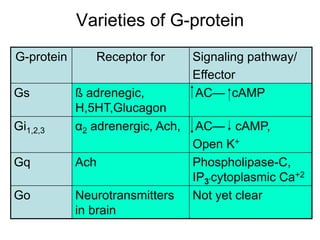
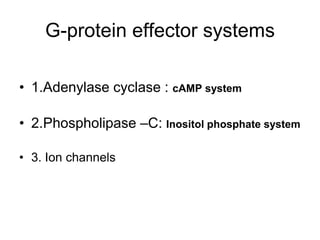
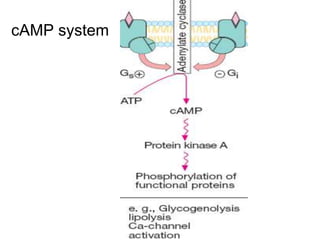
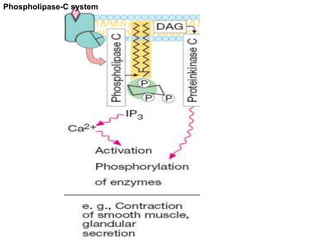
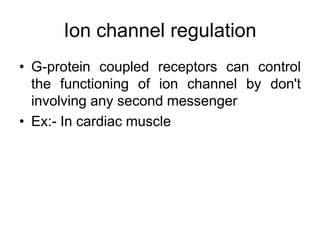
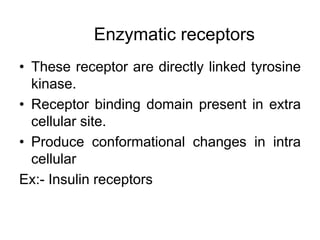
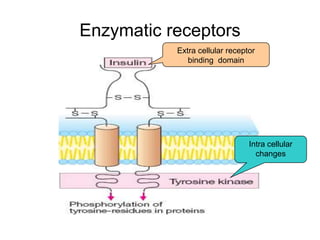
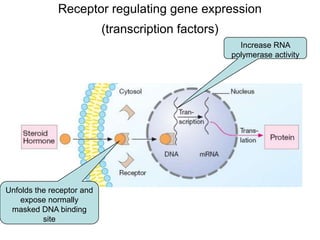
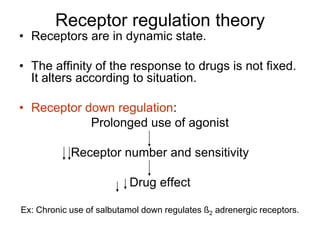
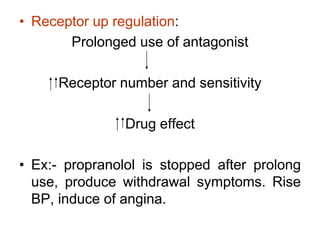
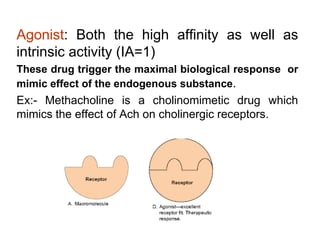
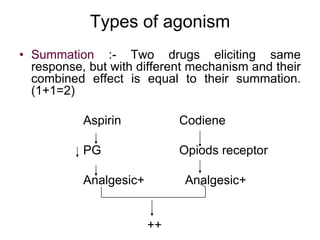
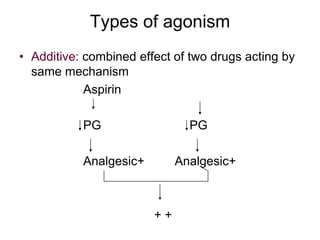
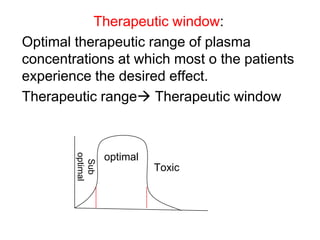
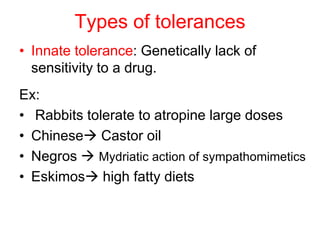
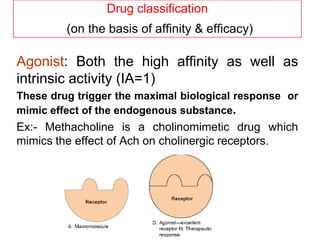
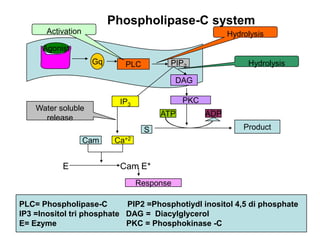
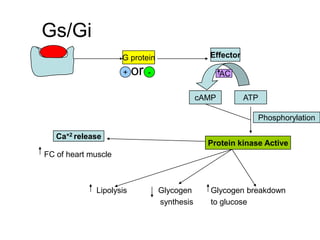
Pharmacodynamics covers how drugs act on the body. Drugs can act through receptor-mediated or non-receptor mediated mechanisms. Receptor-mediated actions involve drug binding to receptors, which then trigger signal transduction pathways. The main receptor families are ligand-gated ion channels, G-protein coupled receptors, enzymatic receptors, and nuclear receptors. Drugs can have different effects depending on their affinity and efficacy at receptors. Tolerance can develop with repeated drug use through pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic changes. Therapeutic dosing aims to achieve drug concentrations within the therapeutic window for maximum benefit.