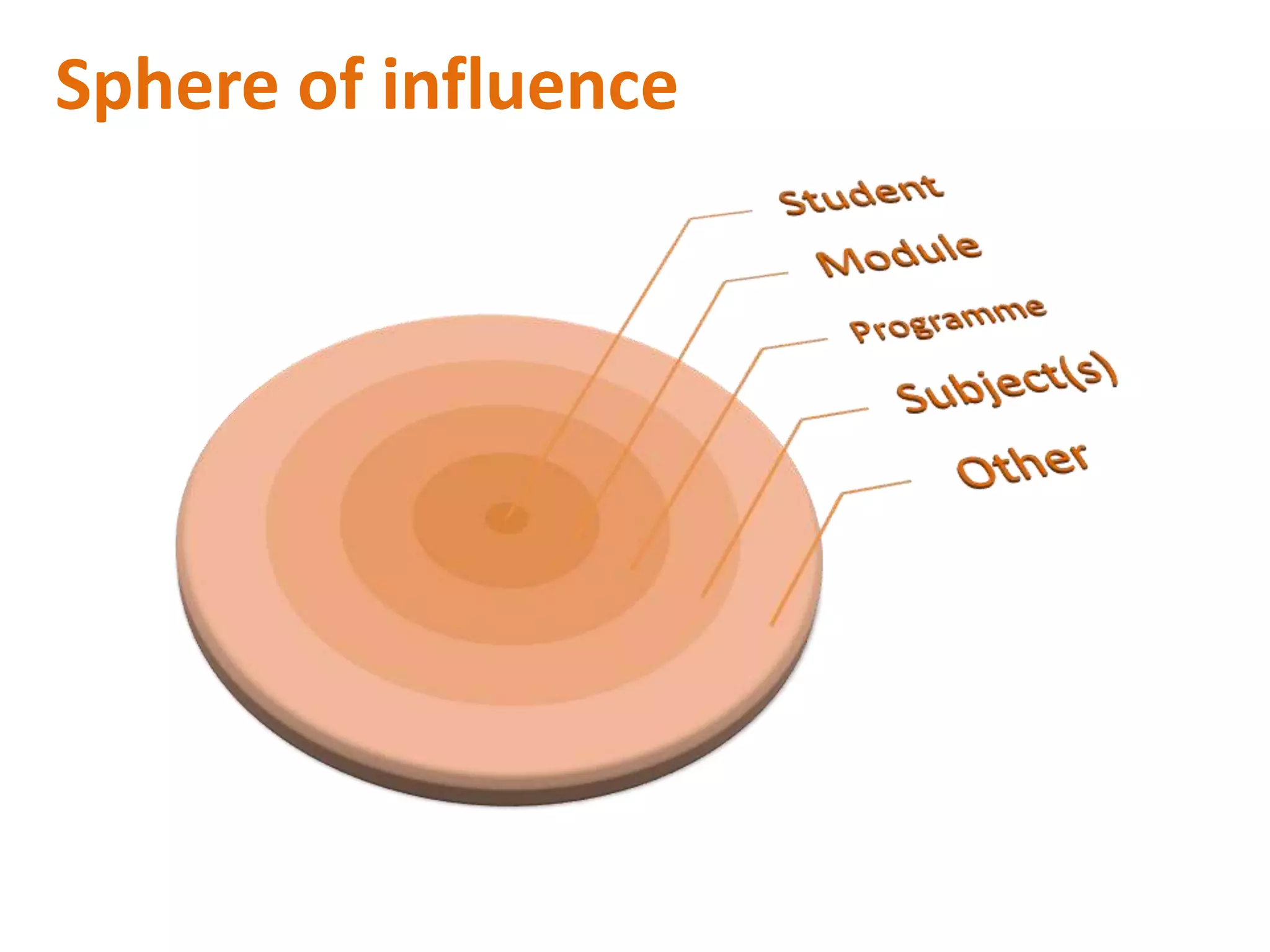
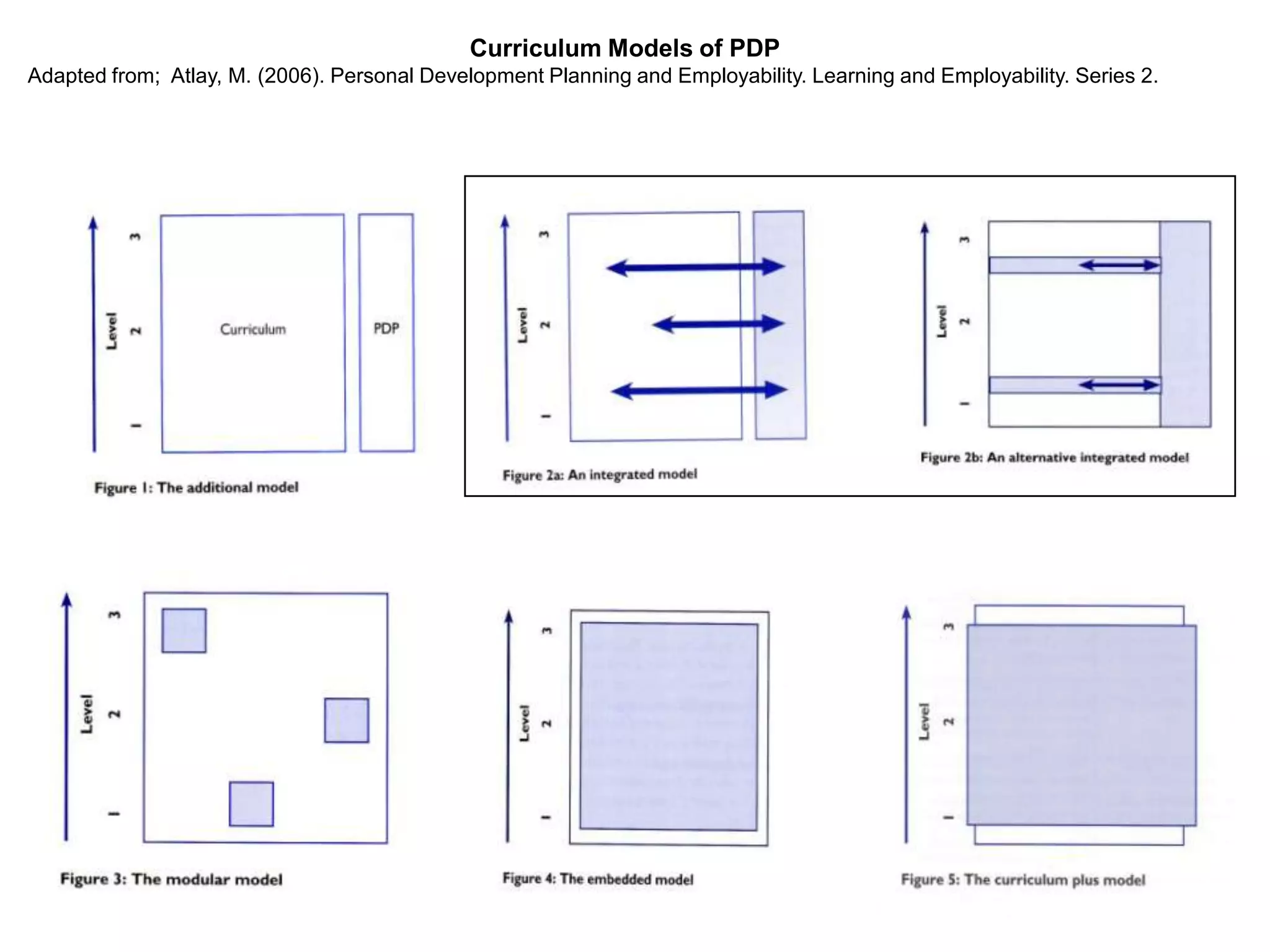
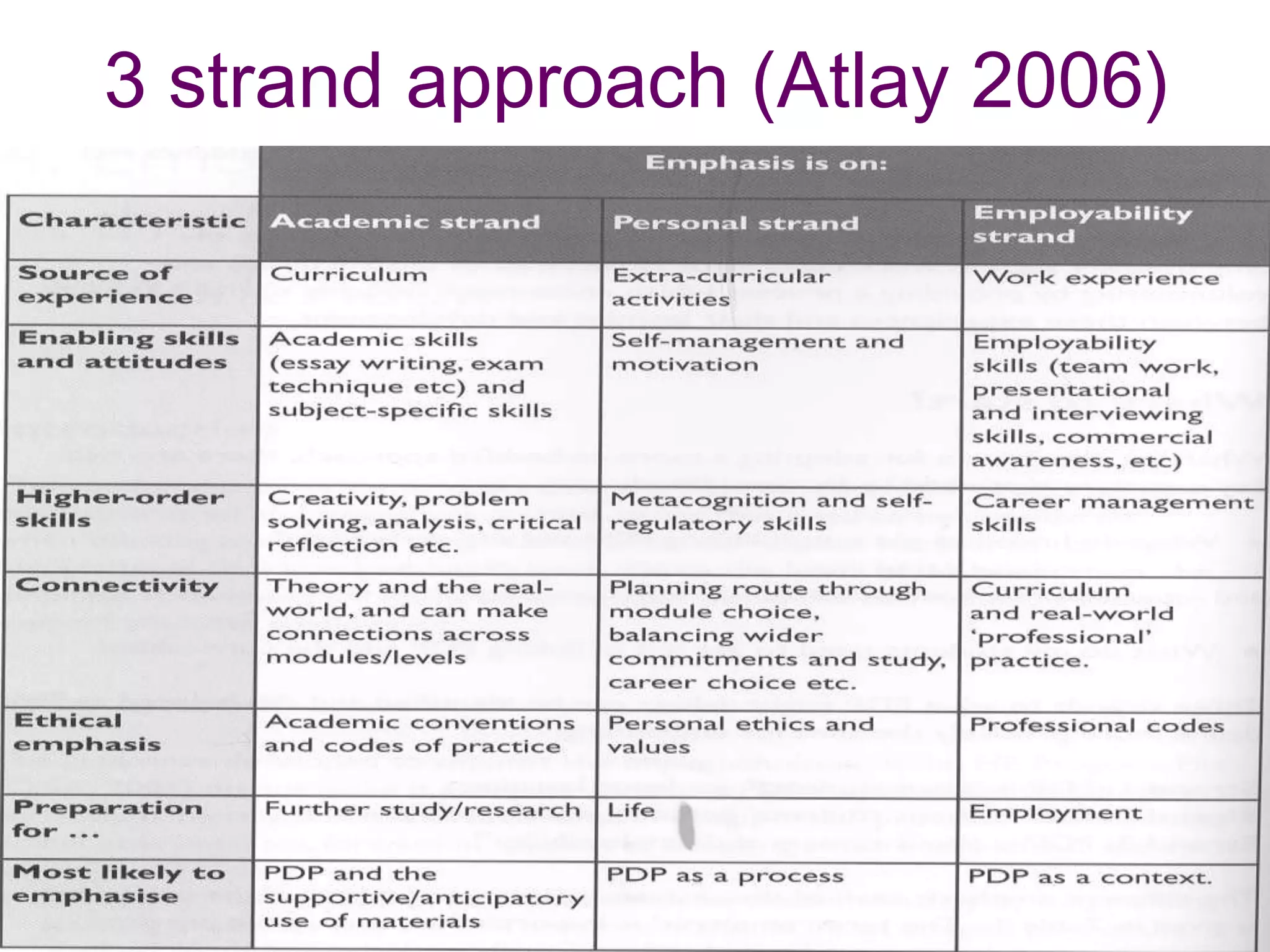
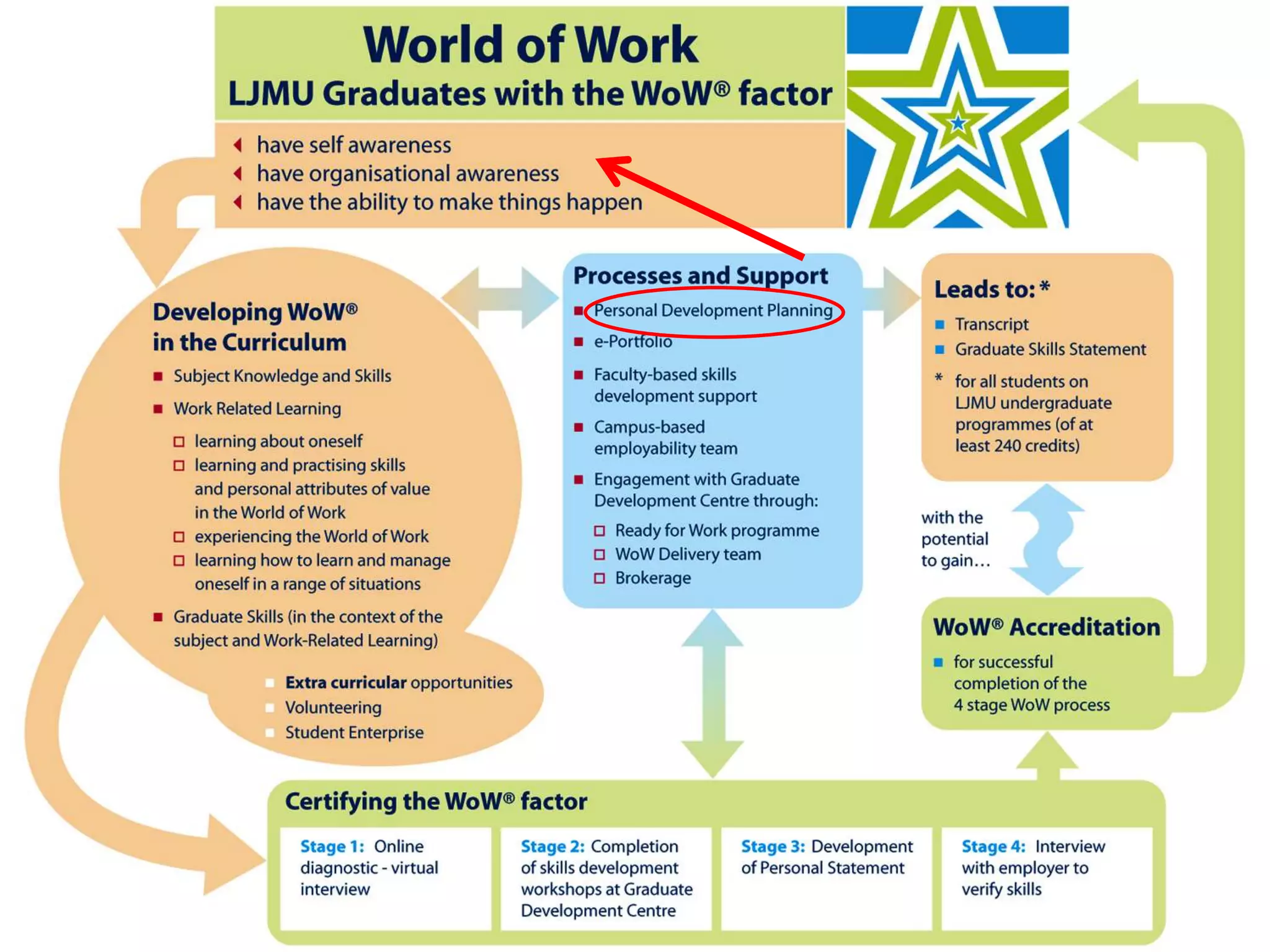
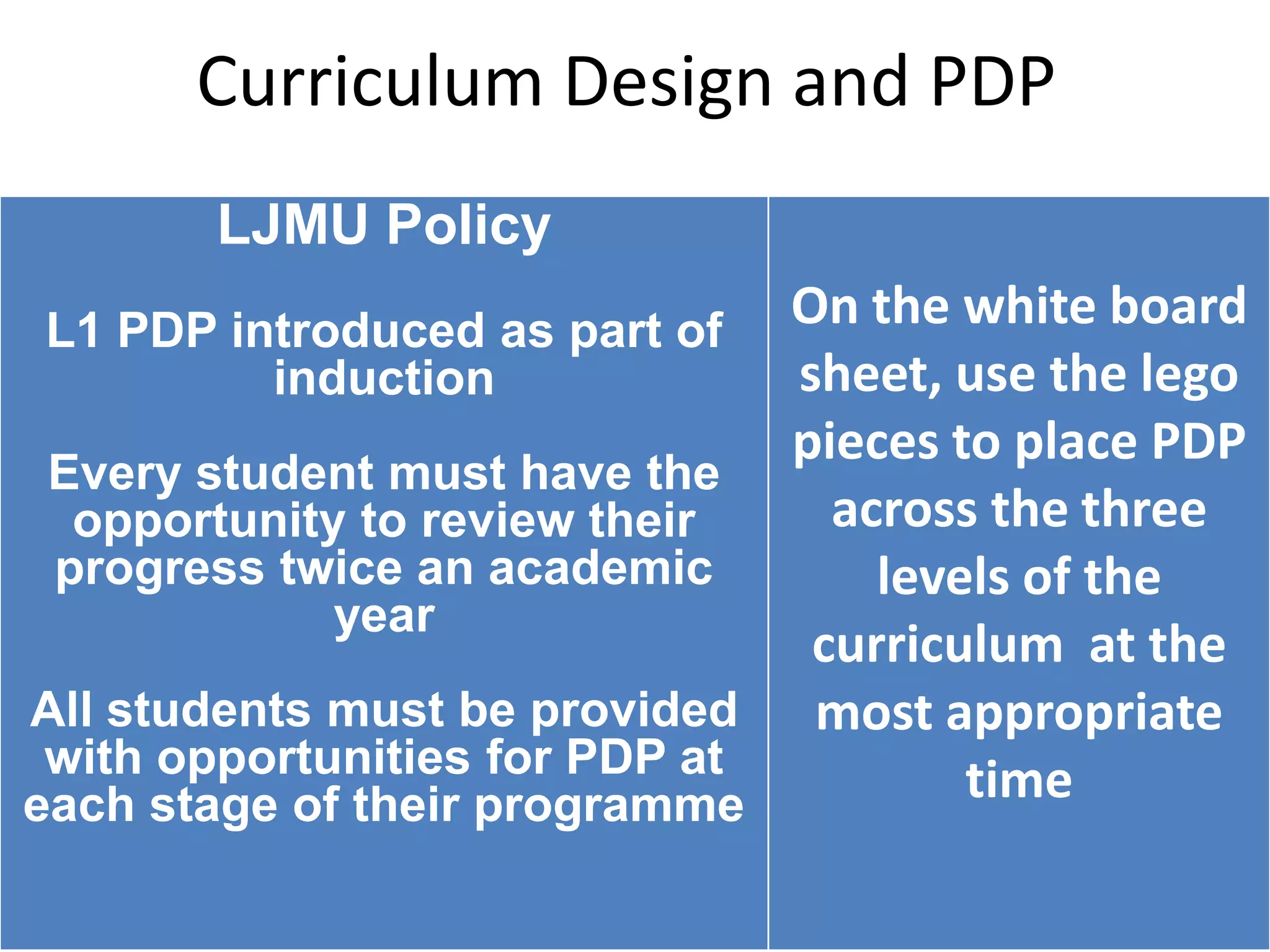
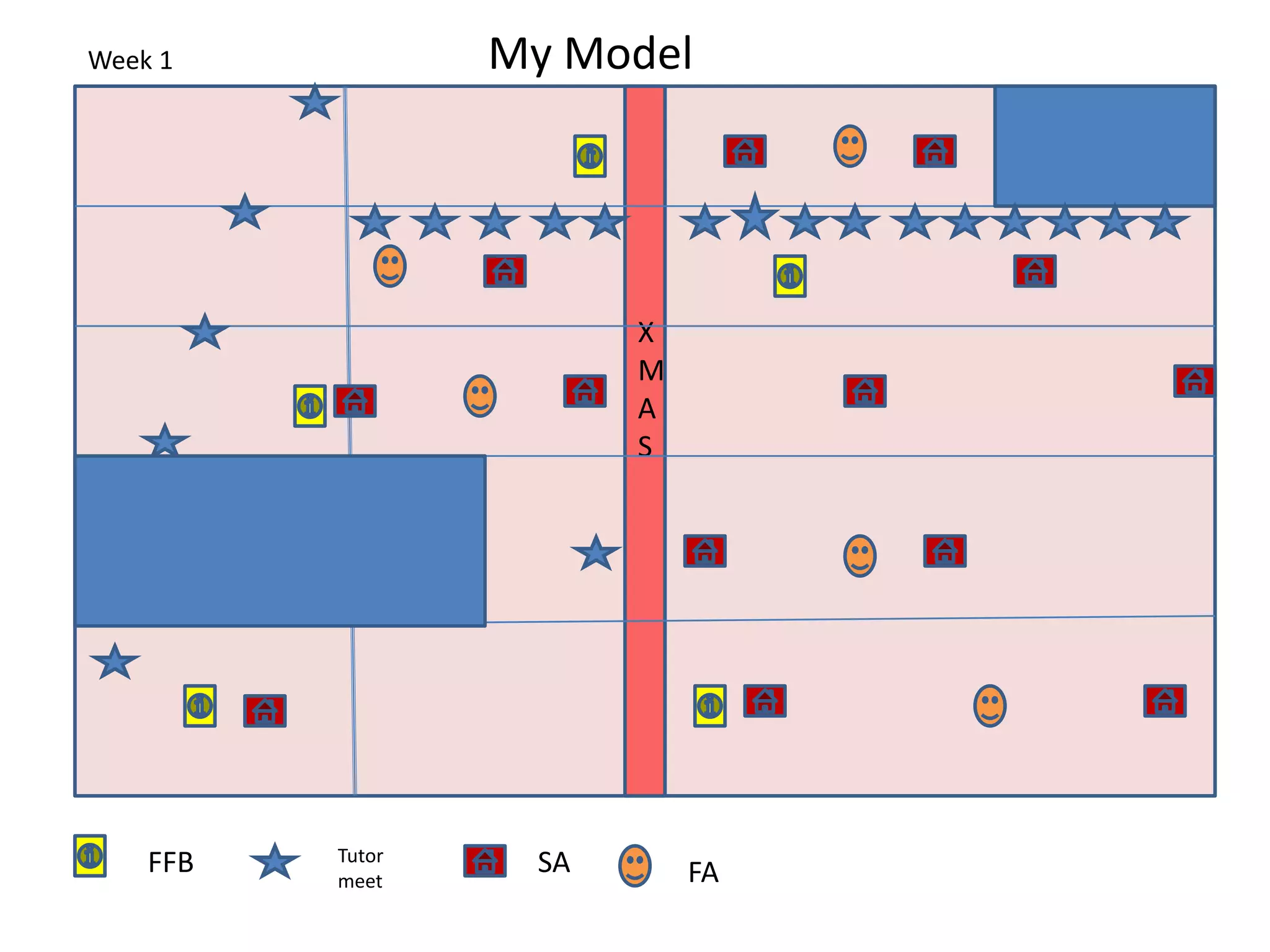
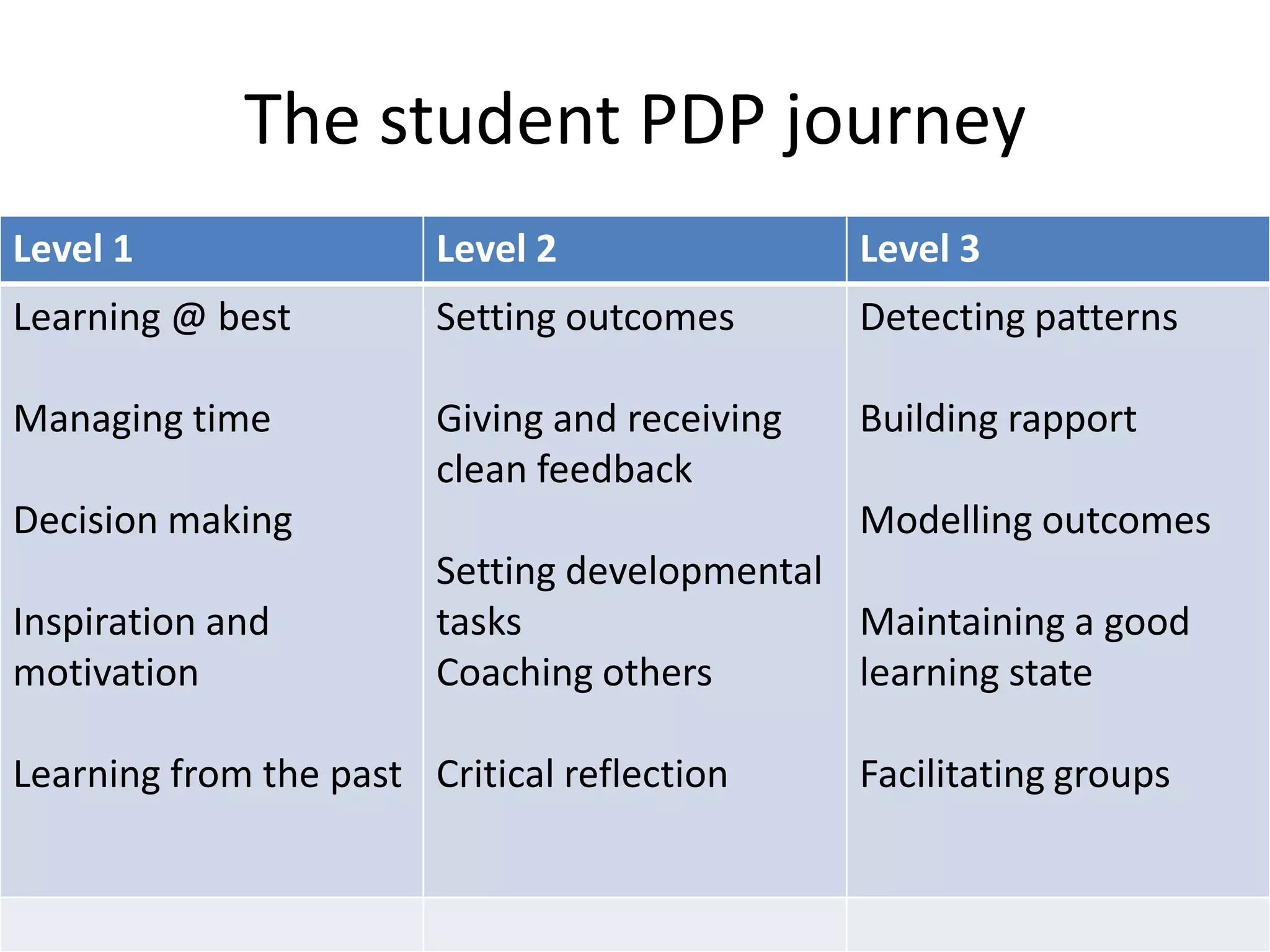
This document discusses personal development planning (PDP) including its definitions, philosophies, and processes. PDP is defined differently but generally involves reflection on learning and performance to plan personal, educational, and career development. The literature emphasizes PDP being integrated into the curriculum, supported by staff, and owned by both the institution and learner. Effective PDP is linked to learning objectives and occurs regularly with support, reflection, and evaluation of experiences and results. The document then provides examples of PDP models within a university curriculum.