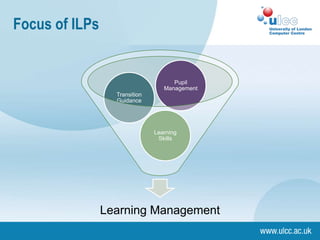
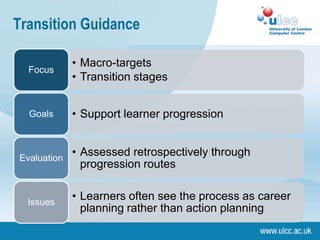
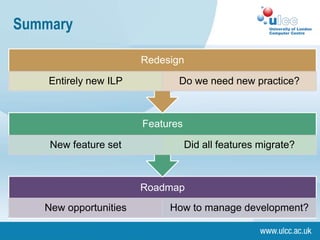
The document discusses the drivers behind individual learning plans (ILPs), focusing on the roles of learners, staff, and organizations in their implementation. It highlights the importance of learner engagement, assessment strategies, and the challenges faced in aligning educational goals with learner needs. Additionally, it emphasizes the potential for e-learning to enhance the personalization of learning experiences through adaptive customization and formative assessments.