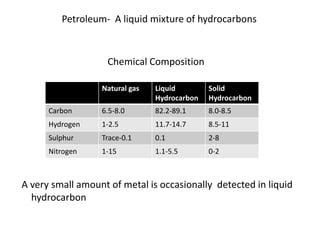
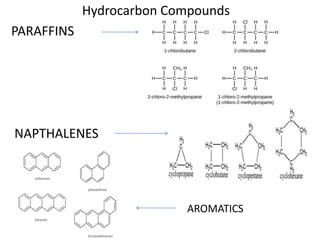
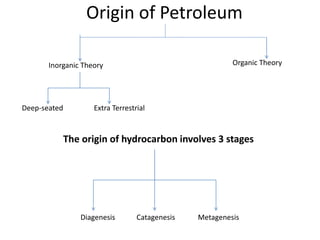
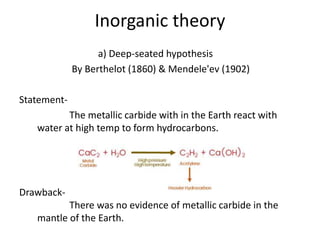
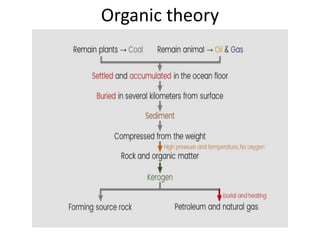
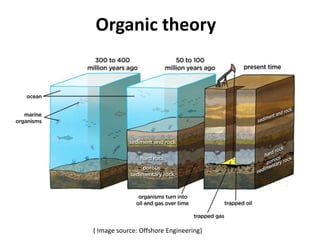
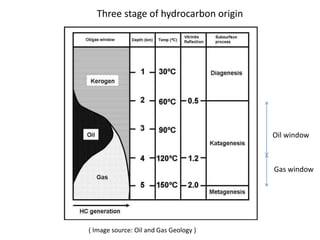
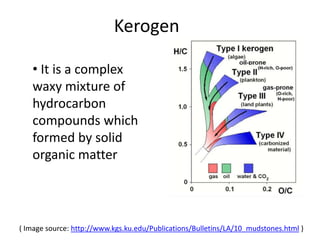
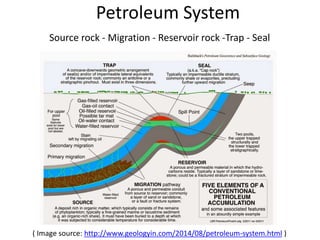
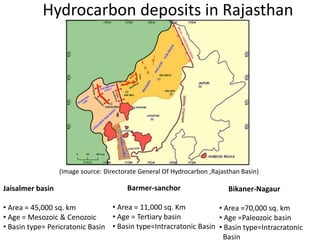
This document summarizes petroleum occurrences in Rajasthan, India. It discusses the chemical composition of petroleum including hydrocarbons like carbon, hydrogen, and sulfur. It describes the origin of petroleum involving stages of diagenesis, metagenesis, and catagenesis. Petroleum is formed from organic material deposited in sedimentary basins over millions of years. In Rajasthan, major hydrocarbon deposits are found in the Jaisalmer, Barmer-Sanchor, and Bikaner-Nagaur basins. The Barmer-Sanchor basin contains 38 oil and gas fields including the large Mangala oil field, and it began commercial production in 2009. Recent discoveries have also occurred in other